tekmar 261 Boiler Control User Manual
Page 5
Copyright © D 261 - 0
3/09
5 of 20
Section B: Boiler Reset
Section B1
General
Section B2
Installer
Section B3
Advanced
Section B1: General
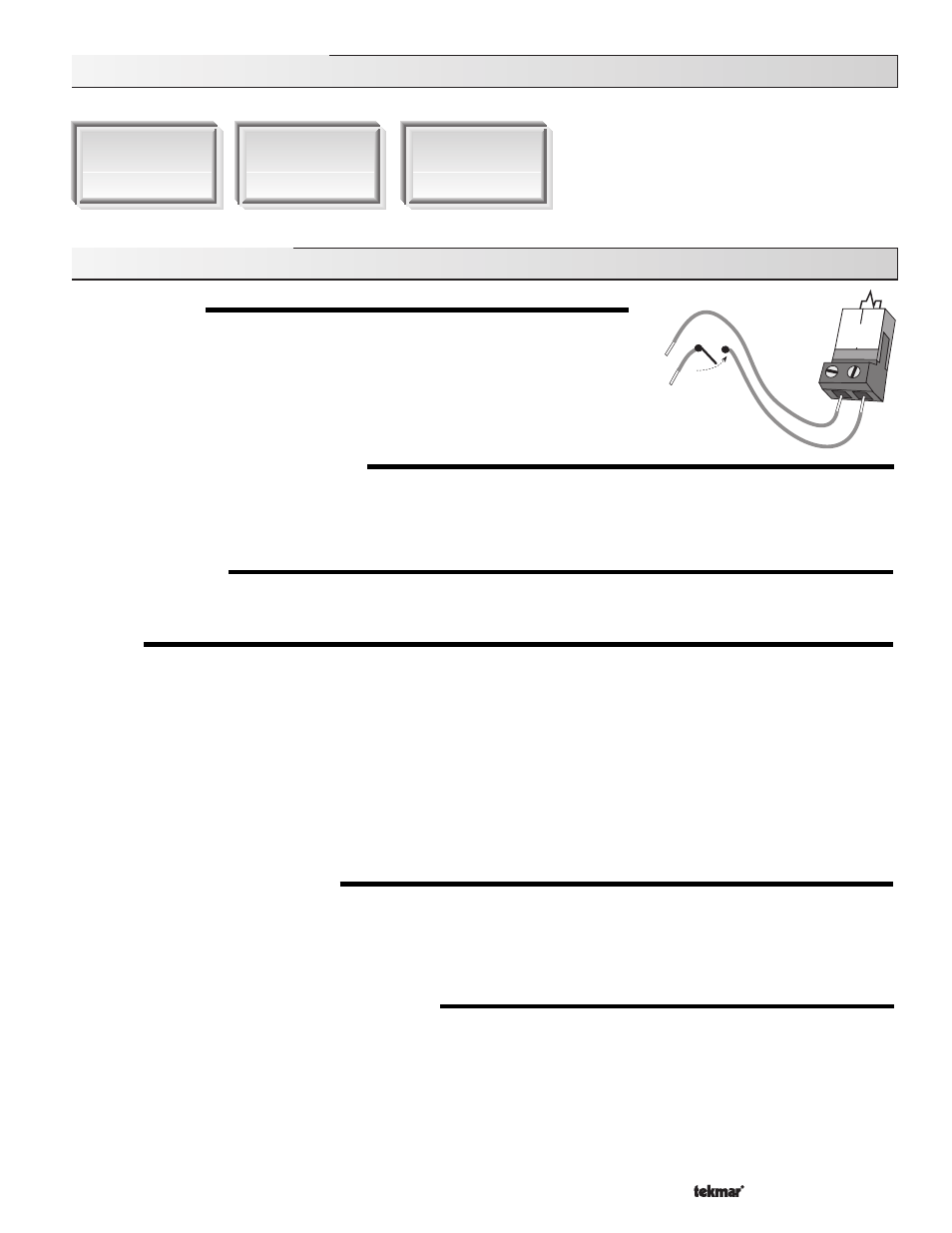
BOILER DEMAND
A boiler demand is required in order for the 261 to provide heat to the heating system. A
boiler demand is generated by applying a voltage between 24 and 240 V (ac) across the
Boiler Demand terminals (1 and 2). Once voltage is applied, the Boiler Demand pointer is
displayed in the LCD. If the 261 is not in WWSD, the 261 closes the
Boil Pmp contact. The
261 calculates a boiler target (BOIL TARGET) supply temperature based on the outdoor
air temperature and settings. The 261 then fires the boiler(s), if required, to maintain the
target supply temperature.
BOILER PUMP OPERATION (BOIL PMP)
The boiler pump contact (
Boil Pmp, terminal 7) closes whenever there is a boiler demand and the 261 is not in WWSD. The boiler
pump segment is displayed in the LCD. After the boiler demand has been satisfied, the 261 continues to operate the boiler pump for
20 seconds. This allows any excess heat to be purged out to the heating system. During WWSD, the boiler pump is operated based
on the exercise function. For boiler pump contact operation during setpoint operation, refer to section C.
BOILER OPERATION
When the 261 determines that boiler operation is required, the boiler
Stage contact(s) (9 and 10 and / or 11 and 12) close. While the
boiler contact(s) is closed, the burner and stage segment in the LCD is displayed.
STAGING
The 261 controls up to two stages in order to supply the required target temperature. After the first stage is turned on in the firing
sequence, the control waits a minimum amount of time before turning on the next stage. After the minimum time delay between stages
has expired, the 261 examines the control error to determine when the next stage is to fire. The control error is determined using
Proportional, Integral and Derivative (PID) logic.
Proportional - compares the actual supply temperature (BOIL) to the boiler target (BOIL TARGET) temperature. The colder the supply
water temperature, the sooner the next stage is turned on.
Integral - compares the actual supply temperature (BOIL) to the boiler target (BOIL TARGET) temperature over a period of time.
Derivative - determines how fast or slow the supply water temperature is changing. If the supply temperature is increasing slowly, the
next stage is turned on sooner. If the supply temperature is increasing quickly, the next stage is turned on later, if at all.
Each stage has a minimum on time, and a minimum off time.
CHARACTERIZED HEATING CURVE
The 261 varies the supply water temperature based on the outdoor air temperature. The control takes into account the type of terminal
unit that the system is using. Since different types of terminal units transfer heat to a space using different proportions of radiation,
convection and conduction, the supply water temperature must be controlled differently. Once the control is told what type of terminal
unit is used, the control varies the supply water temperature according to the type of terminal unit. This improves the control of the air
temperature in the building.
BOILER TARGET TEMPERATURE (BOIL TARGET)
The BOIL TARGET temperature is determined from the
Characterized Heating Curve settings and the outdoor air temperature. The
control displays the temperature that it is currently trying to maintain as the boiler supply temperature. If the control does not presently
have a requirement for heat, it does not show a boiler target temperature. Instead, “- - -” is displayed in the LCD.
1
2
Boiler
Demand
24 to 240 V (ac)
