Rockwell Automation T8xxx Trusted Communications Interface User Manual
Page 30
Trusted
TM
Communication Interface T8151B
Issue 21 Apr 10
PD-T8151B
30
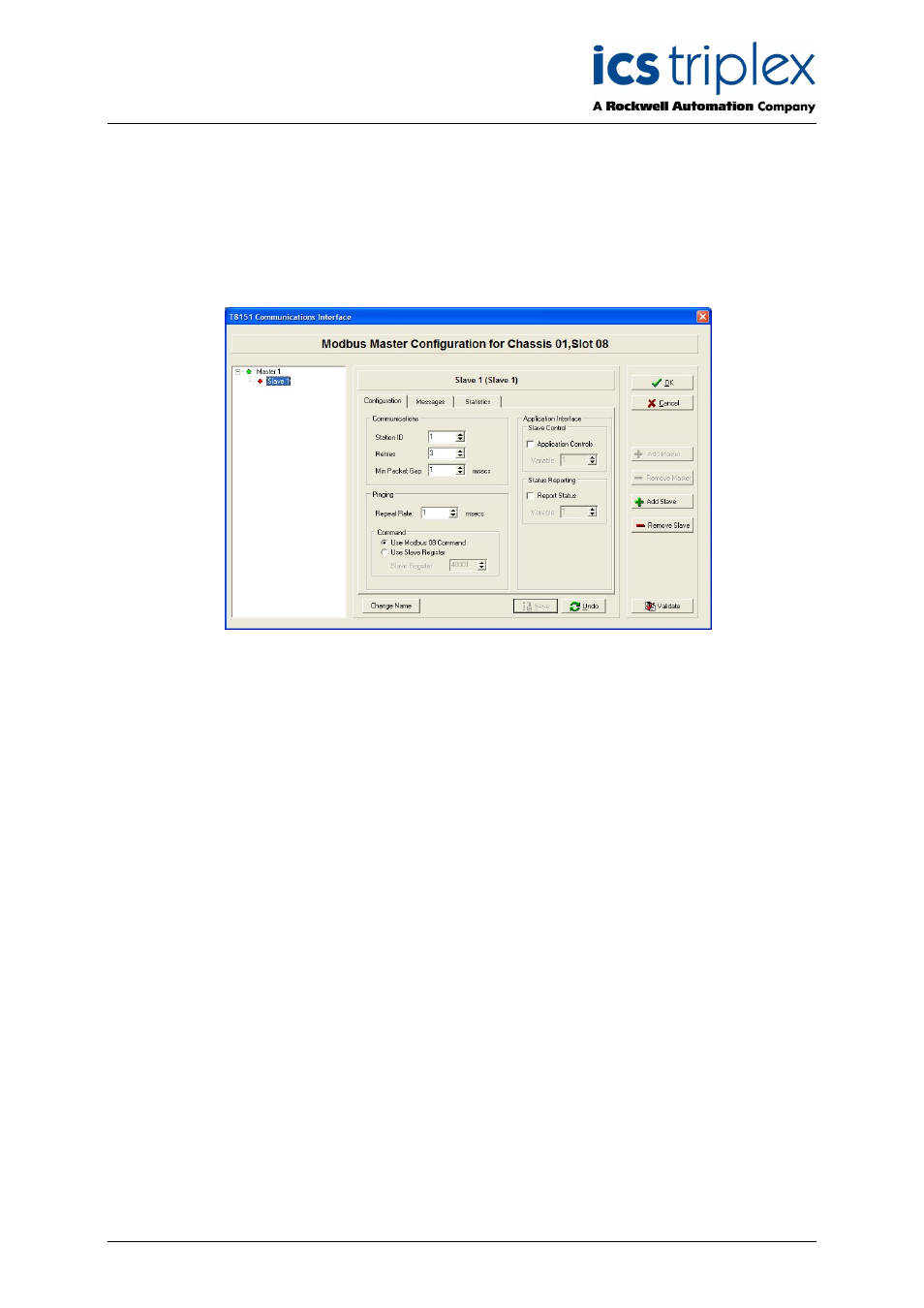
3.5.5. Modbus Slave Configuration
To add a slave to a Modbus Master, click on the appropriate Master on the left hand tree window.
Create a new Modbus Slave by clicking ‘+ Add Slave’. This enables the controls to remove the slave.
The three configuration tabs (Configuration, Messages and Statistics) are now available for the new
slave. The slave name can be changed by double clicking on the name or clicking on ‘Change Name’.
‘Save’ stores changes made so far, and ‘Undo’ loads the last saved state. ‘Validate’ will check the
settings for any obvious errors and omissions (but will not guarantee it will work).
Figure 11 Modbus Slave Configuration
3.5.6. Configuration Tab
The Configuration tab for a Modbus Slave includes the communications settings and controls for the
Slave.
Station ID: The station ID is the Modbus communications identity for the slave device. This value must
be unique for all slaves connected to a single master device. For Ethernet-based slaves, only single
point-to-point communications is possible. In this case an ID of 1 is usually used.
Retries: The number or attempts that the master will make to communicate with a slave before
declaring a communications failure.
Min Packet Gap: The minimum packet gap is used for slave devices that must not be accessed by the
master device at the full communications speed. The value in milliseconds is the time the Master will
wait between messages sent to the slave device.
Pinging: The pinging section defines how the Master will attempt to test the communication to an
individual slave device. The repeat rate defines how long the master device will wait between each
attempt to communicate with the slave device. The command sub section defines whether the Master
uses the Modbus ‘Query Data’ command 08, subcommand 0 (which compatible slaves will echo
exactly, similar to an Ethernet ‘ping’) or reads data from a slave register to test communications to the
slave device (if it does not support command 08). When a register is used for communications testing,
the data read from the register is discarded.
Communications Control: The communications control section defines the Modbus address of an
application variable that will be used to control the slave device. If the slave device is not controlled by
the application then the check box should be left unchecked.
Status Reporting: The Status reporting section defines the Modbus address of an application variable
which will be used to report the status of the communications link to the application. If status reporting
is not required then the check box should be left unchecked.
