Modbus slave – Rockwell Automation T8xxx Trusted Communications Interface User Manual
Page 20
Trusted
TM
Communication Interface T8151B
Issue 21 Apr 10
PD-T8151B
20
3.4. Modbus Slave
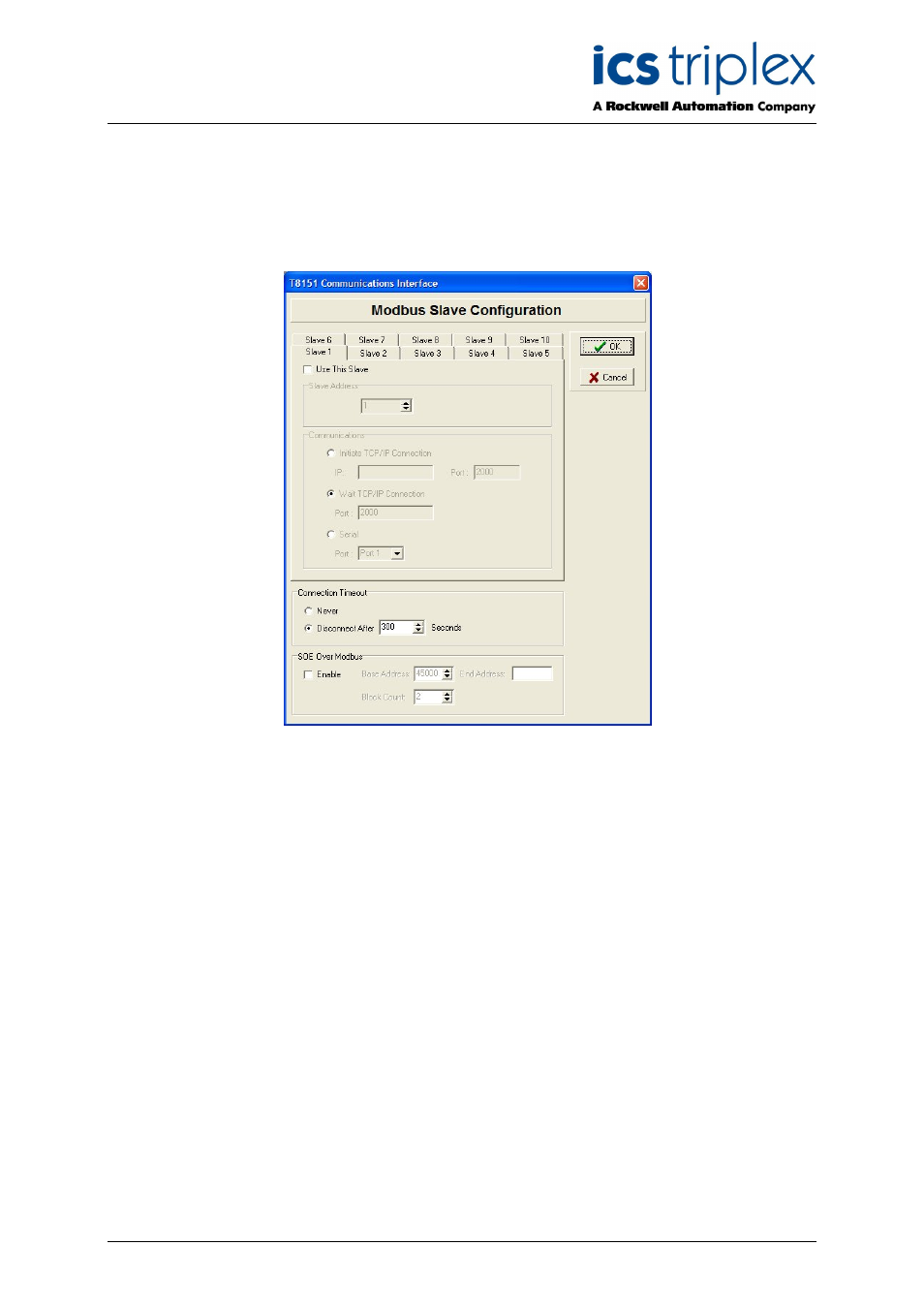
Clicking ’Configure Modbus Slave’ opens the Slave configuration window.
Figure 4 Modbus Slave Configuration Window
It is possible to configure up to 10 Modbus slaves operating in the Communications Interface (not to be
confused with the setup of remote Modbus slaves which the communication interface Modbus masters
communicate with). These may be allocated to serial or Ethernet ports.
If a slave is required, check the box ‘Use This Slave’. Set the slave address that the communication
interface will respond to, usually 1 on a point to point link but in the range 1 to 127.
If the slave will appear on a serial port, check ‘Serial’. Choose the port to be used. A serial port can
only be used for Modbus slave or master but not both.
If the slave will appear on an Ethernet port, it is packaged in Internet Protocol (IP). The IP layer must
be established before Modbus data can be delivered. The communication interface can either set up a
TCP/IP connection itself or await a call from the remote end. This connection will probably be to a
terminal server, and it may require trial and error and a close look at the terminal server configuration
to find whether it is expecting to set up or wait for connection. The default port used for Modbus on the
communication interface is 2000; although this may be changed it is rarely necessary (only if port 2000
is used elsewhere). If the communication interface is to initiate the connection, enter the IP address of
the remote end.
Port 502 is reserved for the Modicon Open TCP Modbus protocol. The slave port should be set to 502
if this protocol is to be used. This protocol is only available as a Modbus slave.
The settings above relate to each individual slave. The following settings are common to the operation
of Modbus slaves.
