HMC Electronics 41550 Loctite 415 SuperBonder, Instant Adhesive, Gap Filling Metal Bonder User Manual
Loctite
Technical Data Sheet
LOCTITE
®
415™
January
-
2010
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
LOCTITE
®
415™
provides
the
following
product
characteristics:
Technology
Cyanoacrylate
Chemical Type
Methyl cyanoacrylate
Appearance (uncured)
Clear colorless slightly hazy to light
yellow liquid
LMS
Components
One part - requires no mixing
Viscosity
High
Cure
Humidity
Application
Bonding
Key Substrates
Metals, Rubbers and Plastics
LOCTITE
®
415™ is a general purpose adhesive and is
particularly suited to bonding of metal substrates.
Mil-A-46050C
LOCTITE
®
415™ is tested to the lot requirements of Military
Specification Mil-A-46050C. Note: This is a regional approval.
Please contact your local Technical Service Center for more
information and clarification.
Commercial Item Description A-A-3097:
LOCTITE
®
415™ has been qualified to Commercial Item
Description A-A-3097. Note: This is a regional approval.
Please contact your local Technical Service Center for more
information and clarification.
TYPICAL PROPERTIES OF UNCURED MATERIAL
Specific Gravity @ 25 °C
1.1
Viscosity, Cone & Plate, 25 °C, mPa·s (cP):
PHYSICA MK22 @ 100 s-1
900 to 1,500
LMS
Viscosity, Brookfield - LVF, 25 °C, mPa·s (cP):
Spindle 2, speed 12 rpm
1,100 to 1,600
Vapour Pressure, hPa
<1
Flash Point - See MSDS
TYPICAL CURING PERFORMANCE
Under normal conditions, the atmospheric moisture initiates the
curing process. Although full functional strength is developed
in a relatively short time, curing continues for at least 24 hours
before full chemical/solvent resistance is developed.
Cure Speed vs. Substrate
The rate of cure will depend on the substrate used. The table
below shows the fixture time achieved on different materials
at 22 °C / 50 % relative humidity. This is defined as the time to
develop a shear strength of 0.1 N/mm².
Fixture Time, seconds:
Steel (degreased)
30 to 60
Aluminum
40 to 80
Zinc dichromate
30 to 90
Neoprene
<10
Rubber, nitrile
<10
ABS
20 to 50
PVC
30 to 90
Polycarbonate
30 to 90
Phenolic
10 to 40
Cure Speed vs. Bond Gap
The rate of cure will depend on the bondline gap. Thin bond
lines result in high cure speeds, increasing the bond gap will
decrease the rate of cure.
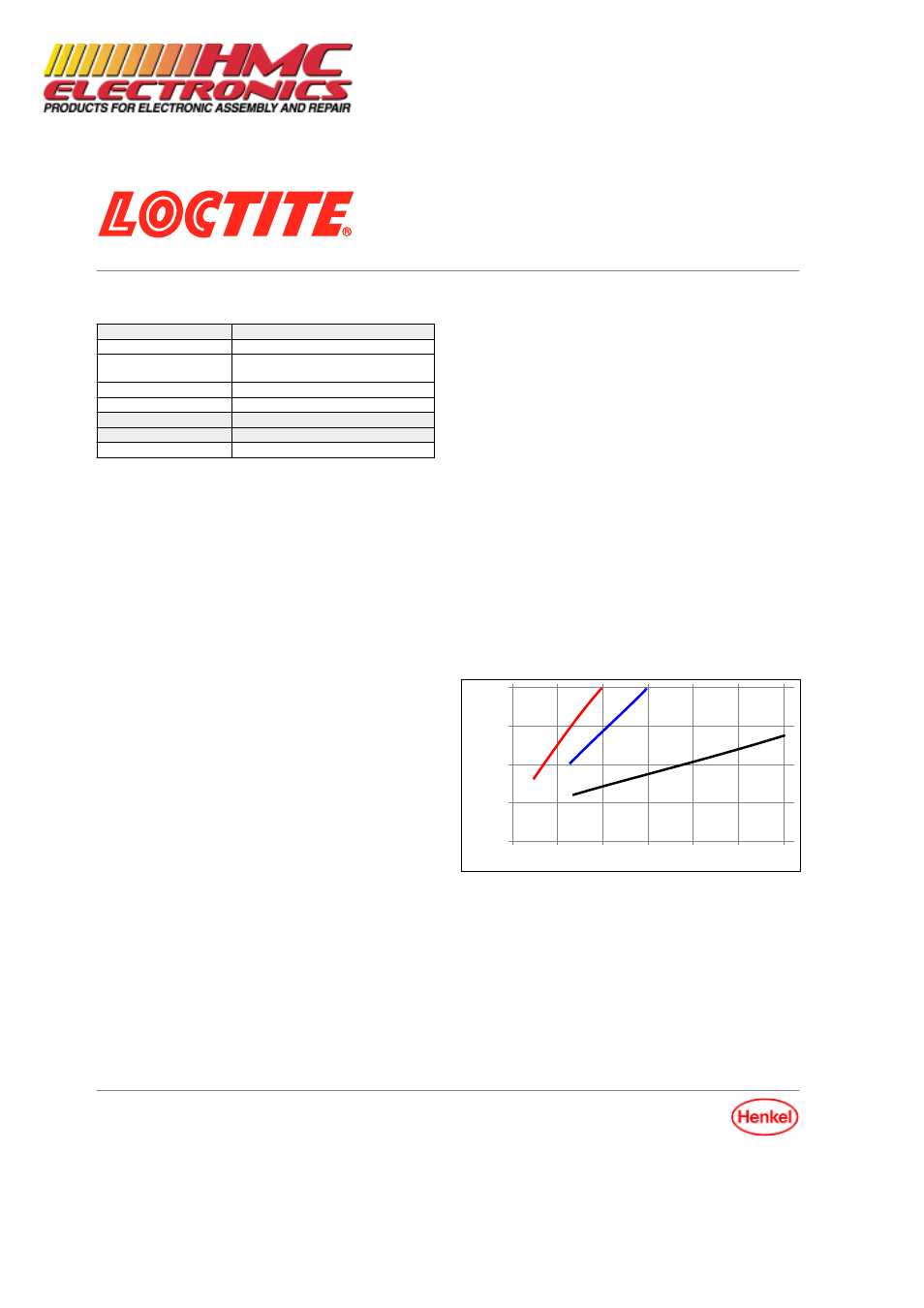
Cure Speed vs. Humidity
The rate of cure will depend on the ambient relative humidity.
The following graph shows the tensile strength developed with
time on Buna N rubber at different levels of humidity.
% Full Cured Strength @ 22 °C
Cure Time, seconds
100
75
50
25
0
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
60% RH
40% RH
20% RH
Cure Speed vs. Activator
Where cure speed is unacceptably long due to large gaps,
applying activator to the surface will improve cure speed.
However, this can reduce ultimate strength of the bond and
therefore testing is recommended to confirm effect.
Documentation Provided By HMC Electronics
33 Springdale Ave. Canton, MA 02021
(800) 482-4440
