NOVUS Line N320 User Manual
Line n320
Line N320
Communication Protocol
Manual 5001292 V2.0
1.
COMMUNICATION SERIAL
The optional serial interface RS485 allows to address up to 247 controllers in a network
communicating remotely with a host computer or master controller.
RS485 Interface
•
Compatible line signals with RS485 standard
•
2 wire connection from master to up to 31 slaves indicators in a multidrop bus. It is
possible address 247 nodes with multiple outputs converters.
•
Maximum communication distance: 1000 meters
•
The RS485 signals are:
D1: Bidirectional data line.
D0: Bidirectional inverted data line.
C: Optional connection which left communication better.
General Characteristics
•
Serial interface not isolated from input circuitry.
•
Serial interface isolated from input circuitry, except in 24 V powered model.
•
Baud rate: 9600
•
Data Bits: 8
•
Parity: None
•
Stop Bits: 1
Communication Protocol
The MOSBUS RTU slave is implemented, available in most SCADA softwares in the
market.
All configurable parameters can be accessed (for reading or writing) through the
Registers Table. Broadcast commands are supported as well (address 0).
The available Modbus commands are:
03 - Read Holding Register
06 - Preset Single Register
The registers are arranged in a table in such a way that several registers can be read in
the same request.
1.1
CONFIGURATION OF SERIAL COMMUNICATION PARAMETERS
Two parameters must be configured in the device for serial communication:
addr
addr
addr
addr
Device communication address. Each device must have an exclusive address.
1.2
REGISTERS TABLE
The Modbus registers hold the internal controller parameters. Each parameter is a 16-
bit word, with negative values represented as 2’s complement.
Holding
Registers
Parameter
Description
0000
SP1
Read: OUTPUT1 Setpoint (control output).
Write: OUTPUT1 Setpoint (control output).
Range: from
spl
spl
spl
spl to the value specified in spk
spk
spk
spk.
Note: In the N320, this address also corresponds to the
Process Variable “PV” parameter.
0001
PV
Read: input temperature as measured by the sensor.
Write: not allowed.
Span: according to the sensor type used.
0002
IHM Status1
Read: IHM Status.
Write: not allowed.
Value format:
Bit 0 – OUT1 LED
Bit 1 – OUT2 LED
Bit 10 – decimal Point
Bit 12 – negative signal
0003
Control Status1
Read: measurement and OUTPUT1 status.
Write: not allowed.
Value format:
Bit 0 – Input Underflow
Bit 1 –Input Overflow
Bit 8 – OUTPUT1 status
Bit13 – defrost
0004
Value of the
parameter being
displayed
Read: Value of the parameter being presented on the display
Write: not allowed.
Max. Span: -199 to 999. The actual span depends on the
parameter being displayed.
0005
Firmware version
Parameter
sequence number
Read: controller firmware version & the sequential number that
identifies the parameter currently being displayed.
Write: not allowed.
Value format: XXYYh, where:
XX
→
Firmware version;
YY
→
parameter number.
0006
Serial number
(High)
Read: first 3 digits of the serial number.
Write: not allowed.
Value format: XXXXh.
0007
Serial number
(Low)
Read: last 3 digits of the controller serial number.
Write: not allowed.
Value format: XXXXh.
0008
Hysteresis 1
Read: OUTPUT1 hysteresis.
Write: OUTPUT1 hysteresis.
Range: 0.1 a 50.0
0009
Control Status2
Read: OUTPUT2 Status.
Write: not allowed.
Value format:
Bit 0 – status de OUTPUT2
0010
SP2
Read: OUTPUT2 Setpoint.
Write: OUTPUT2 Setpoint.
Range: from
spl
spl
spl
spl to the value specified in spk
spk
spk
spk.
0011
Hysteresis 2
Read: OUTPUT2 hysteresis.
Write: OUTPUT2 hysteresis.
Range: 0.1 a 50.0.
0012
Offset
Read: Offset value
Write: Offset value
Range: -10.0 a 10.0
0013
Control Status3
Read: OUTPUT3 Status.
Write: not allowed.
Value format:
Bit 0 – status de OUTPUT3
0014
SP3
Read: OUTPUT3 Setpoint.
Write: OUTPUT3 Setpoint.
Range: from
spl
spl
spl
spl to the value specified in spk
spk
spk
spk.
0015
Hysteresis 3
Read: OUTPUT3 hysteresis.
Write: OUTPUT3 hysteresis.
Range: 0.1 a 50.0
Table 1 - Modbus registers table
Notes:
1-
For the N320 model, the available registers are 0000 to 0007. In this model, both
registers 0000 and 0001 are assigned to the Process Variable value.
2-
For the N321 model, the available registers are 0000 to 0008.
3-
For the N322 model, the available registers are 0000 to 0012.
4-
The N323 makes use of all registers (0000 to 0015).
5-
The SP, PV and Hysteresis values are always multiplied by 10 to account for the
decimal point.
1.3
EXCEPTION RESPONSES – ERROR CONDITIONS
The MODBUS RTU protocol checks the CRC in the data blocks received.
Reception errors are detected by the CRC, causing the controller to discard the packet,
not sending any reply to the master.
After receiving an error-free packet, the controller processes the packet and verifies
whether the request is valid or not, sending back an exception error code in case of an
invalid request. Response frames containing error codes have the most significant bit of
the Modbus command set.
If a WRITE command sends an out-of-range value to a parameter, the controller will
clamp the value to the parameter range limits, replying with a value that reflects these
limits (maximum or minimum value allowed for the parameter).
The controller ignores broadcast READ commands; the controller processes only
broadcast WRITE commands.
Error Code
Error Description
01
Invalid Command
02
Invalid Register Number or out of range
03
Invalid Register Quantity or out of range
Table 2 – Error code
1.4
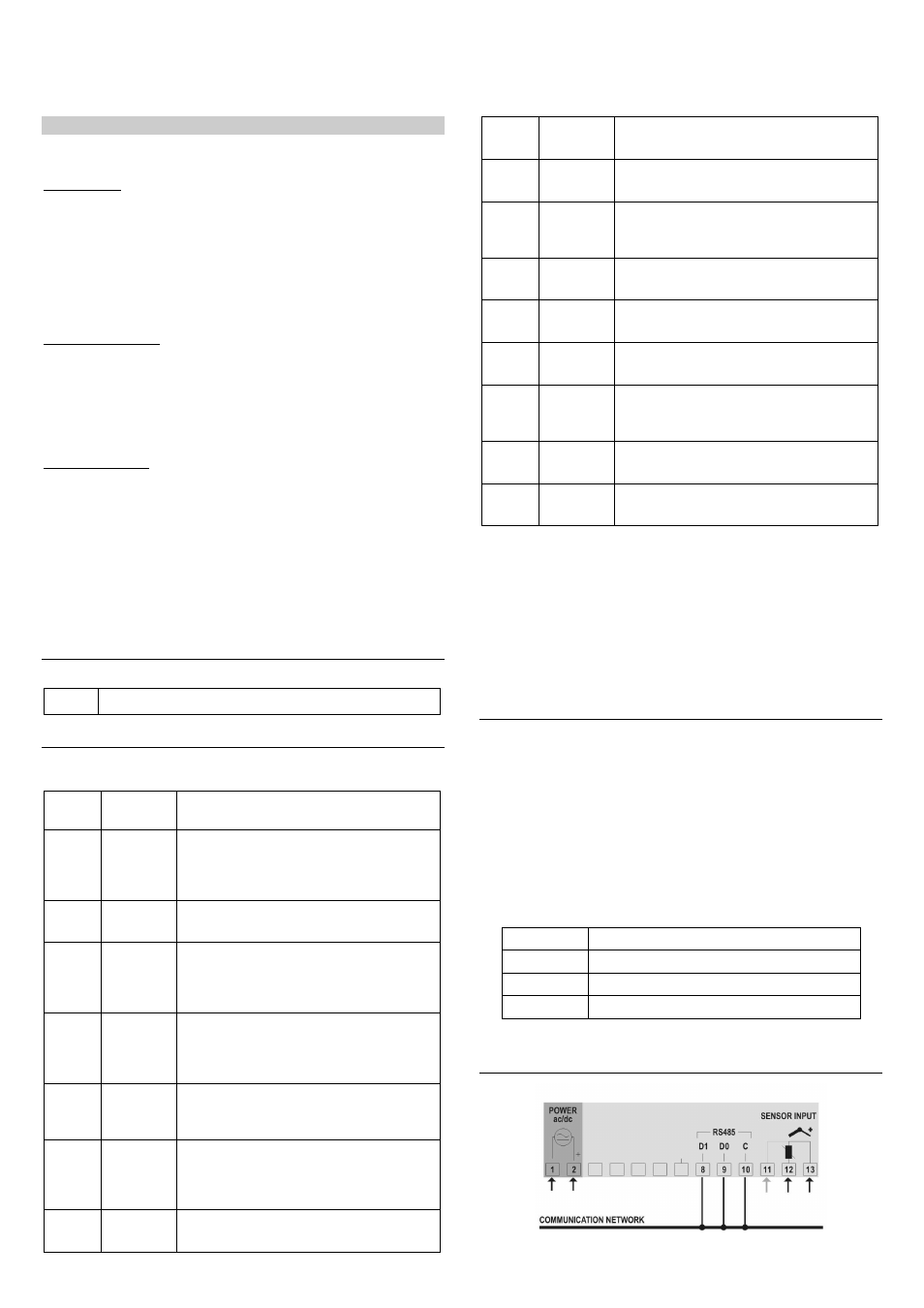
ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
Figure 1 – Connections
