3 pyranometers – Campbell Scientific NR01 Net Radiometer User Manual
Page 9
NR01 Four-Component Net Radiation Sensor
2.3 Pyranometers
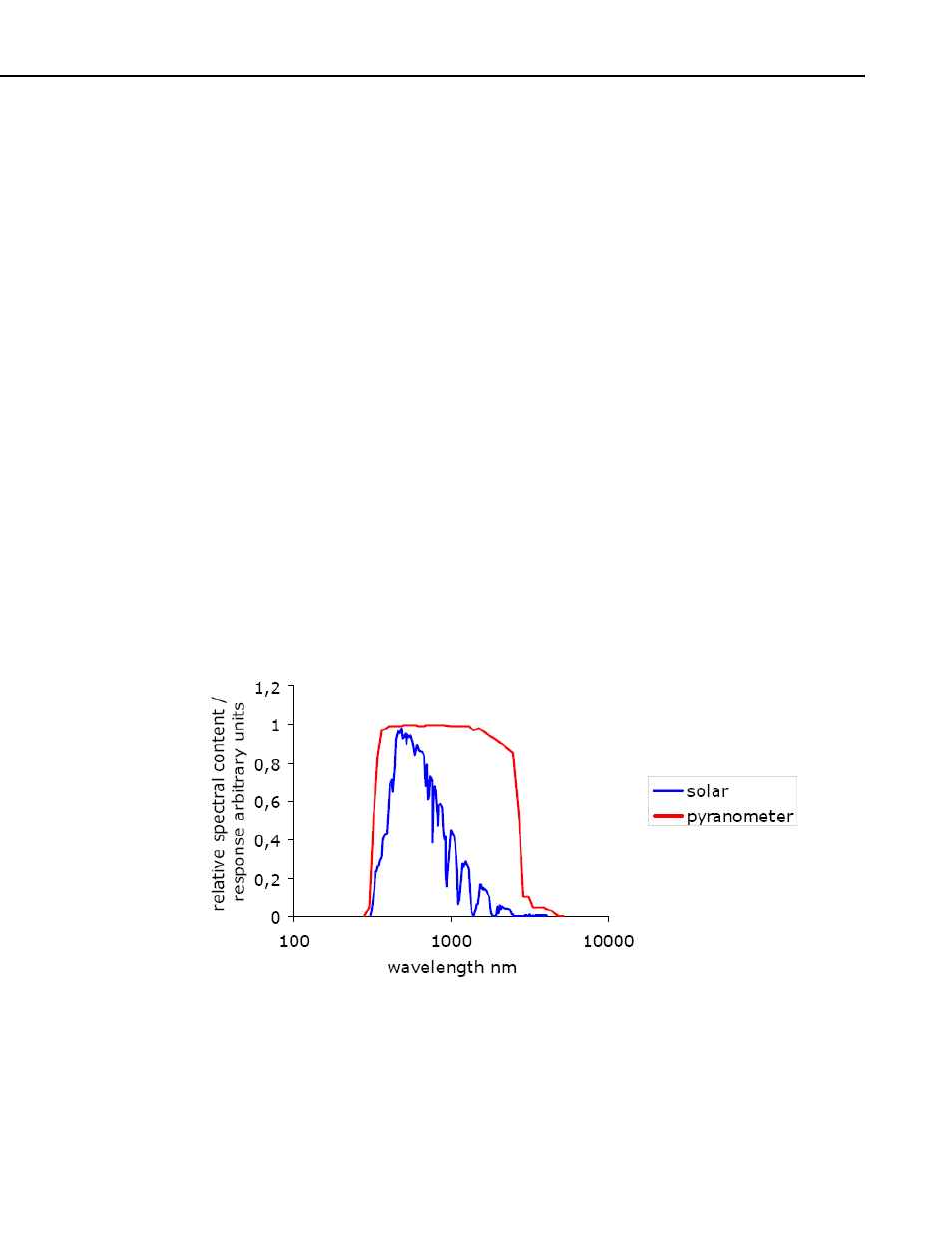
A pyranometer should measure the solar or SW radiation flux from a field of
view of 180 degrees. The atmospheric SW radiation spectrum extends roughly
from 300 to 2800 nm. It follows that a pyranometer should cover that
spectrum with a spectral sensitivity that is as “flat” as possible.
For a flux measurement, it is required by definition that the response to “beam”
radiation varies with the cosine of the angle of incidence. For example, full
response occurs when the solar radiation hits the sensor perpendicularly
(normal to the surface, sun at zenith, 0 degrees angle of incidence); zero
response occurs when the sun is at the horizon (90 degrees angle of incidence,
90 degrees zenith angle), and half a response occurs at 60 degrees angle of
incidence. It follows from the definition that a pyranometer should have a so-
called “directional response” or “cosine response” that is close to the ideal
cosine characteristic.
In order to attain the proper directional and spectral characteristics, a
pyranometer’s main components are:
1. Thermopile sensor with a black coating—absorbs all solar radiation,
provides a flat spectrum covering the 300 to 50000-nanometer range, and
has a near-perfect cosine response.
2. Glass dome—limits the spectral response from 300 to 2800 nanometers
(cutting off the part above 2800 nm) while preserving the 180 degrees
field of view. Another function of the dome is that it shields the
thermopile sensor from convection.
FIGURE 2.3-1. Spectral Response of the Pyranometer Compared to the Solar Spectrum
The pyranometer only cuts off a negligible part of the total solar spectrum.
5
