Campbell Scientific CR5000 Measurement and Control Module User Manual
Page 143
Section 7. Measurement Instructions
7-17
Unless the AllRanges option is selected, the calibrate instruction only measures
the range and integration combinations that occur in the measurements in the
program. For the 250
µs and zero integration calibrations multiple
measurements are averaged for the calibration values. The 250
µs integration
calibration averages five measurements and the zero integration calibration
averages ten measurements.
The Calibration instruction can occur in a fast scan or in a slow sequence scan.
In a fast scan the entire calibration is completed at once. In a slow sequence
scan the calibration measurements are separated into sections that can be
spliced on to the end of fast sequence scans.
If it is necessary to update the calibration more rapidly than is done by the
background calibration, try running the Calibrate instruction in the fast scan
with the measurements. If there isn’t time for it to run there it can be placed in
a slow sequence scan, but remember, unless the slow scan is faster than about
40 seconds the calibration isn’t being updated any faster than with the
background calibration.
Running Calibrate in a slow sequence scan is not an option when there is not
time for the automatic background calibration. The instruction requires more
time because of the multiple measurements for the 250
µs and zero
integrations.
When the results of the calibration are placed in an array, the array must have
at least 60 elements, more if the program contains instructions which use
excitations. The calibration values will be in the following order, followed by
the calibrations of the excitations if any. If a range is not calibrated, 0 will be
returned for the gain and offset.
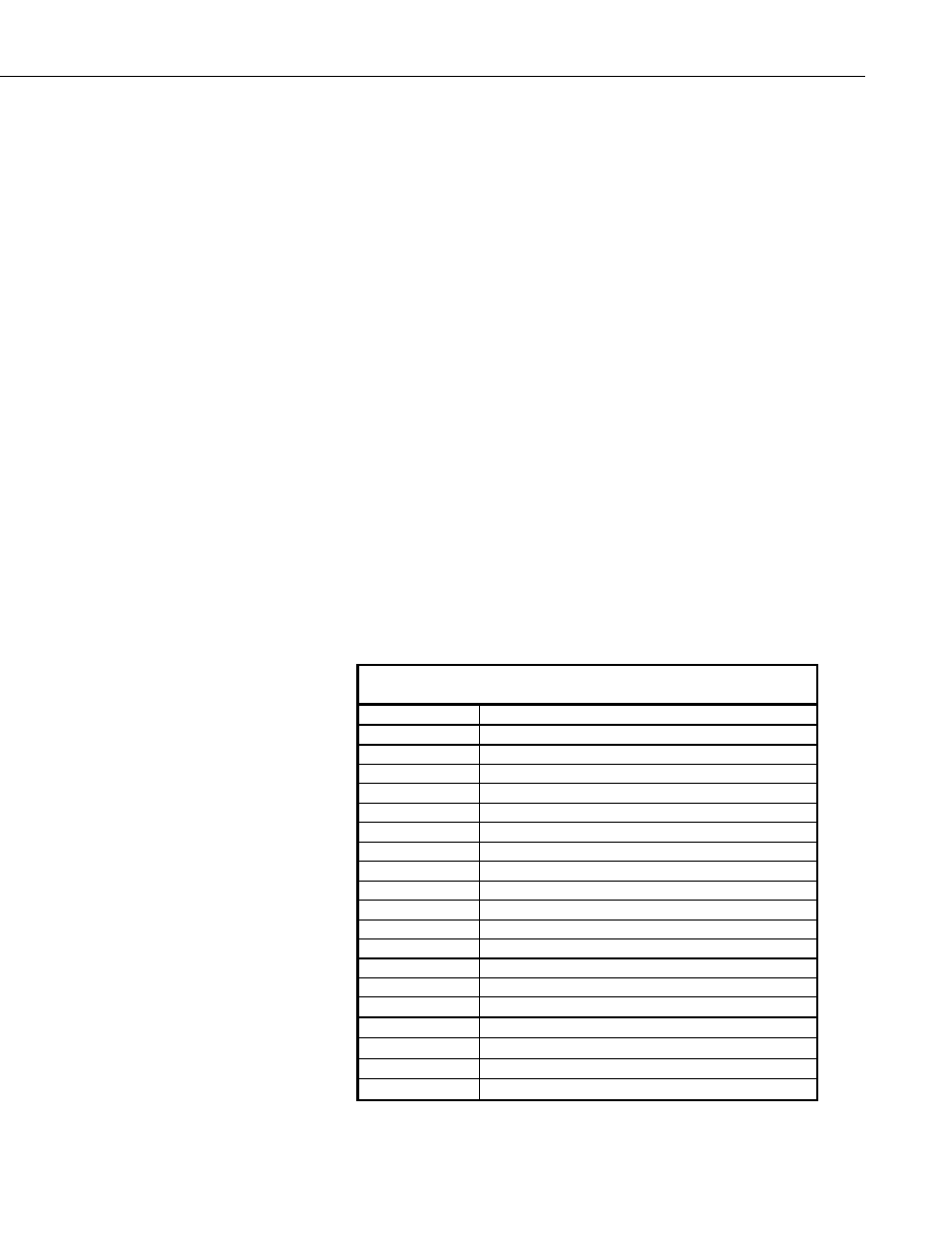
Table 7.7-1. Calibrate Return Value Decode
Array Element
Description
1
zero integrate 5000 mV single ended offset
2
zero integrate 5000 mV differential offset
3
zero integrate 5000 mV gain
4
zero integrate 1000 mV single ended offset
5
zero integrate 1000 mV differential offset
6
zero integrate 1000 mV gain
7
zero integrate 200 mV single ended offset
8
zero integrate 200 mV differential offset
9
zero integrate 200 mV gain
10
zero integrate 50 mV single ended offset
11
zero integrate 50 mV differential offset
12
zero integrate 50 mV gain
13
zero integrate 20 mV single ended offset
14
zero integrate 20 mV differential offset
15
zero integrate 20 mV gain
16
250
µSec integrate 5000 mV single ended offset
17
250
µSec integrate 5000 mV differential offset
18
250
µSec integrate 5000 mV gain
19
250
µSec integrate 1000 mV single ended offset
