1 using mpich with slurm allocation, 2 using mpich with lsf allocation, Mpich wrapper script – HP XC System 3.x Software User Manual
Page 124: Figure 11-1
respectively. These subsections are not full solutions for integrating MPICH with the HP XC
System Software.
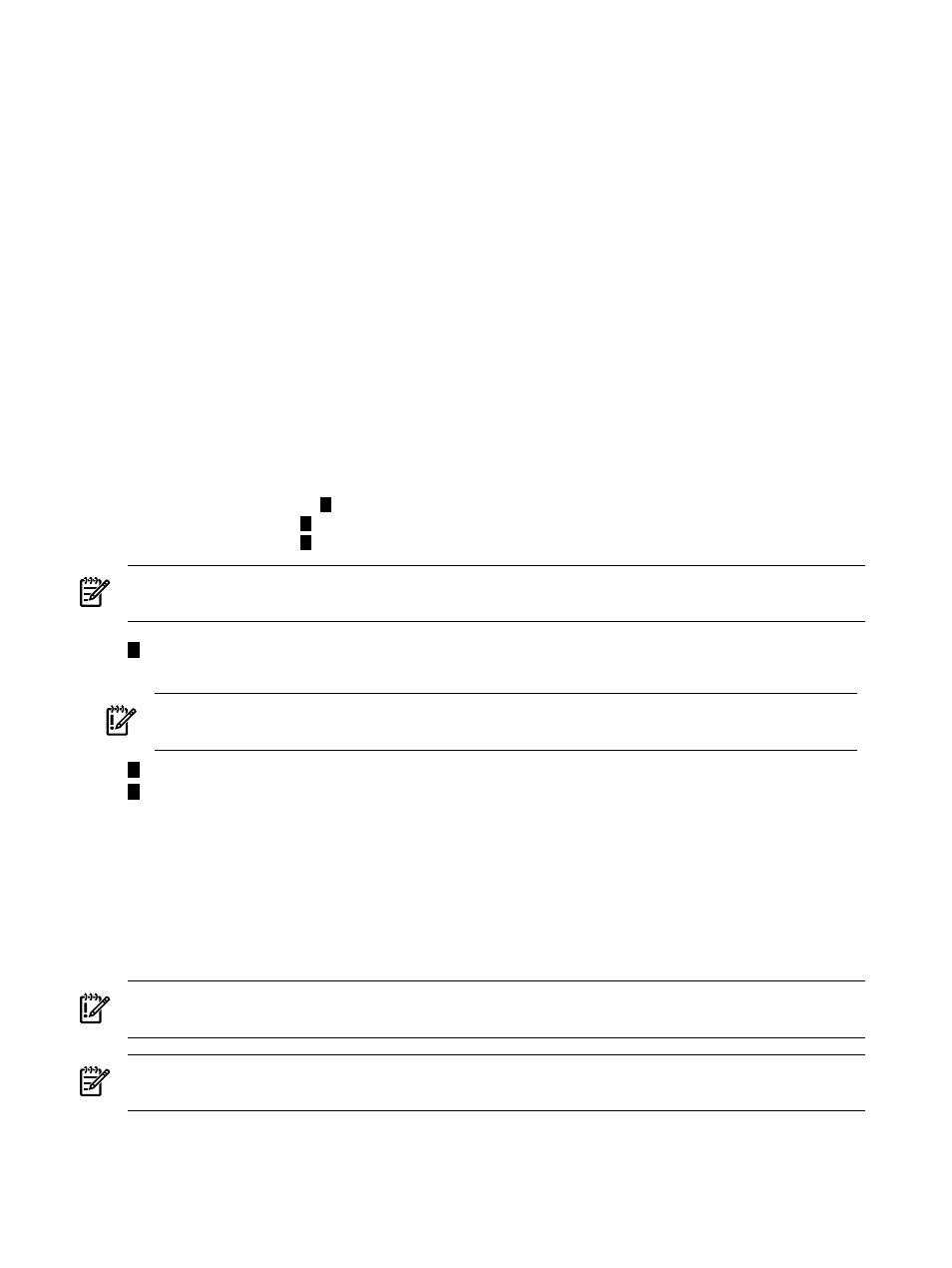
Figure 11-1 MPICH Wrapper Script
#!/bin/csh
srun csh -c 'echo `hostname`:2' | sort | uniq > machinelist
set hostname = `head -1 machinelist | awk -F: '{print $1}'`
ssh $hostname /opt/mpich/bin/mpirun options... -machinefile machinelist a.out
The wrapper script is based on the following assumptions:
•
Each node in the HP XC system contains two CPUs.
•
The current working directory is available on all nodes on which an MPICH job might run.
•
You provide the mpirun options that are appropriate to your requirements.
•
The executable file is named a.out.
•
The wrapper script has the appropriate permissions.
You need to modify the wrapper script accordingly if these assumptions are not true.
11.7.1 Using MPICH with SLURM Allocation
The SLURM-based allocation method uses the srun command to spawn a shell; the remote job
is run from within the shell, as shown here:
% srun -A options
1
% ./wrapper
2
% exit
3
NOTE:
This method assumes that the communication among nodes is performed using ssh
and that passwords are not required.
1
The srun -A command allocates the resources and spawns a new shell without starting a
remote job. For more information on the -A option, see srun(1) .
IMPORTANT:
Be sure that the number of nodes and processors in the srun command
correspond to the numbers specified in the wrapper script.
2
This command line executes the wrapper script to start the job on the allocated nodes.
3
After the MPICH job specified by the wrapper completes, the exit command terminates
the shell and releases the allocated nodes.
11.7.2 Using MPICH with LSF Allocation
The LSF-based allocation method uses a single bsub command to create an allocation, as shown
here:
% bsub -I options... wrapper
The bsub command launches the wrapper script.
IMPORTANT:
Be sure that the number of nodes and processors in the bsub command
corresponds to the number specified by the appropriate options in the wrapper script.
NOTE:
This method assumes that the communication among nodes is performed using ssh
and that passwords are not required.
124
Advanced Topics
