How lsf-hpc and slurm launch and manage a job, User – HP XC System 3.x Software User Manual
Page 73
•
Use the bjobs command to monitor job status in LSF-HPC.
•
Use the bqueues command to list the configured job queues in LSF-HPC.
How LSF-HPC and SLURM Launch and Manage a Job
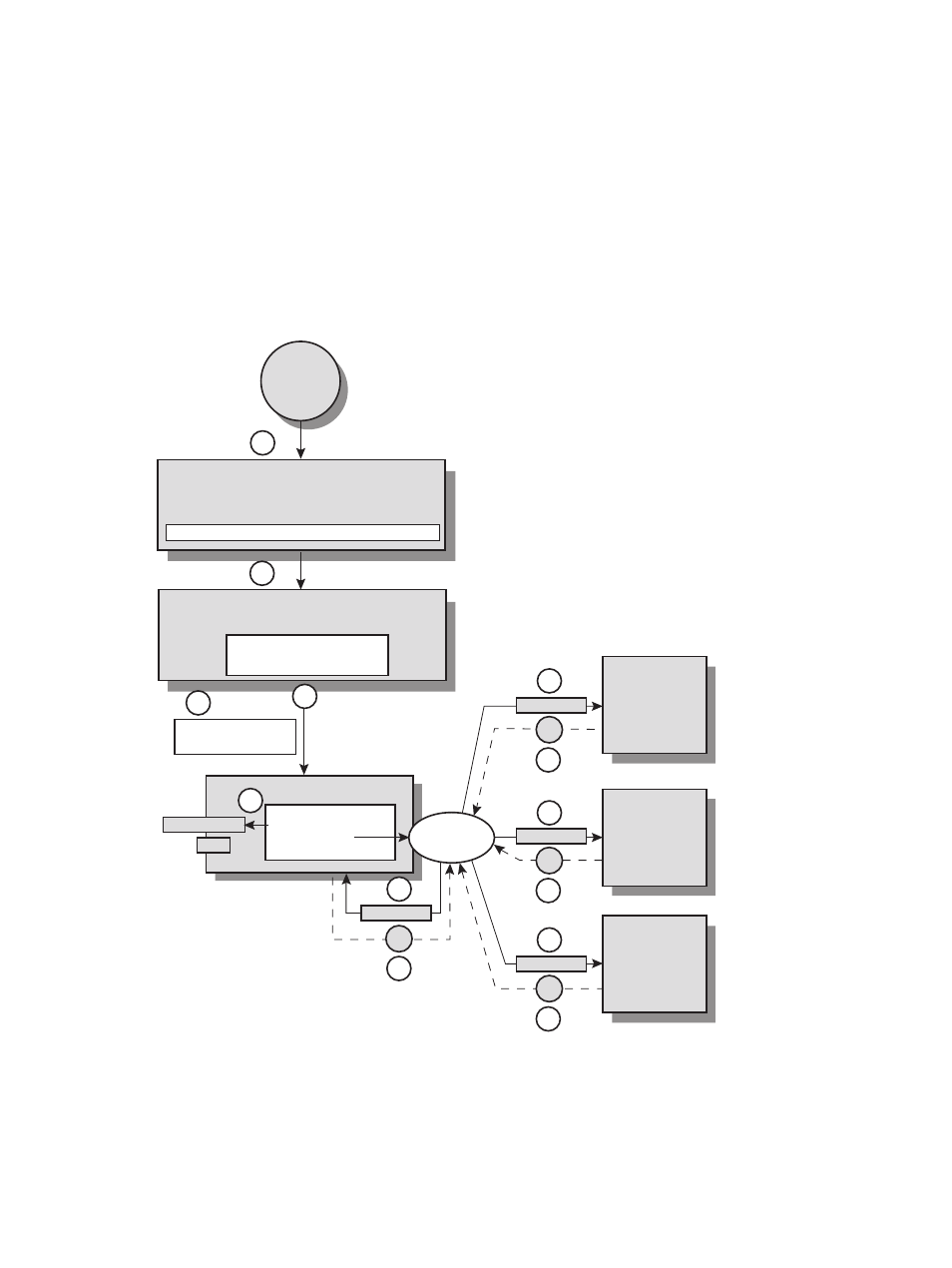
This section describes what happens in the HP XC system when a job is submitted to LSF-HPC.
illustrates this process. Use the numbered steps in the text and depicted in the illustration as an aid to
understanding the process.
Consider the HP XC system configuration shown in
, in which lsfhost.localdomain is the
virtual IP name assigned to the LSF execution host, node n16 is the login node, and nodes n[1-10] are
compute nodes in the lsf partition. All nodes contain two cores, providing 20 cores for use by LSF-HPC
jobs.
Figure 9-1 How LSF-HPC and SLURM Launch and Manage a Job
N 1 6
N16
User
1
2
4
6
6
6
6
7
7
7
7
5
job_starter.sh
$ srun -nl
myscript
Login node
$ bsub-n4 -ext ”SLURM[nodes-4]” -o output.out./myscript
LSF Execution Host
lsfhost.localdomain
SLURM_JOBID=53
SLURM_NPROCS=4
$ hostname
hostname
$ hostname
n1
n1
hostname
hostname
hostname
Compute Node
N2
Compute Node
N3
Compute Node
N4
n2
n3
n4
N16
Compute Node
srun
N1
myscript
$ srun hostname
$ mpirun -srun ./hellompi
3
1.
A user logs in to login node n16.
2.
The user executes the following LSF bsub command on login node n16:
$ bsub -n4 -ext "SLURM[nodes=4]" -o output.out ./myscript
Using LSF-HPC
73
