Data retention term function, Expiration lock function – HP XP20000XP24000 Disk Array User Manual
Page 10
To assign access attributes to volumes, you use Remote Web Console to start Data Retention Utility, and
then edit the access attributes in the Data Retention window.
Data Retention Utility does not allow you to assign any access attribute to:
•
mainframe volumes
•
volumes that are not mapped to physical devices
For details on how to assign access attributes, see “
Changing the Access Attributes
While the storage administrator can set access attributes to the volumes in any CUs (Control Units) in
the storage system, the storage partition administrator can set access attributes only to the volumes in
CUs in the SLPR the storage partition administrator manages. Therefore, if you are a storage partition
administrator and using the Data Retention window (see
on page 15), only the CUs in your
SLPR are displayed in the window. The CUs in the SLPRs which are managed by other storage partition
administrators are not displayed.
For detailed information on SLPR, see the HP StorageWorks XP24000 Disk/Cache Partition User’s Guide.
Data Retention Term Function
If you change the access attribute of a volume to Read Only or Protect, you will usually be prohibited
from changing the access attribute to Read/Write for a certain period of time. The Data Retention
window displays the words Retention Term to indicate the period during which attempts to change the
access attribute to Read/Write are prohibited.
You will be prompted to specify a retention term when you change the access attribute of a volume to
Read Only or Protect.
After you specify the retention term, you can extend the term, but cannot shorten the term. For details on
how to extend the retention term, see “
Extending the Data Retention Term
” on page 20. If you need to
shorten the retention term, you must ask your HP service representative to do so.
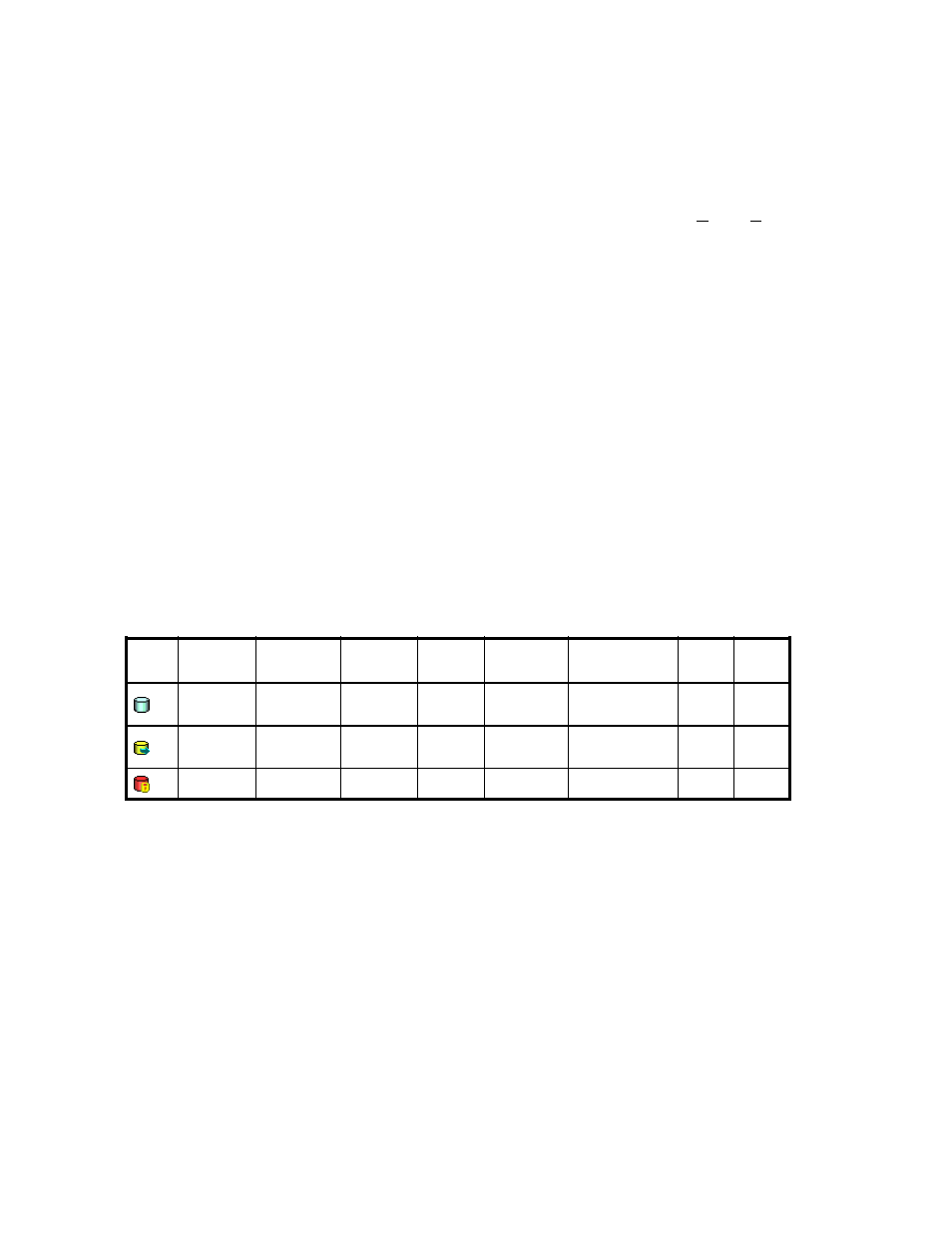
on page 10 is an example of access attributes in the window. This example shows the access
attributes of the volumes 00, 01, and 02.
Table 2 Example of Access Attributes Displayed in the Window
LDEV Attribute Emulation Capacity S-VOL
Reserved
Retention
Term
Paths Mode
00
Read/
Write
OPEN-V
58.59 GB Enable
-
-
0
-
01
Read
Only
OPEN-V
58.59 GB Disable
-
2190 days
0
-
02
Protect
OPEN-V
58.59 GB Disable
-
0 days
0
Inv
on page 10, for example, you cannot change the access attribute of volume #01 to Read/Write
in the next 2,190 days because the retention term for this volume is 2,190 days. If you need to change
the access attribute of this volume to Read/Write, you must ask your HP service representative to do so.
Expiration Lock Function
You will be able to change the access attribute of a volume from Read Only to Read/Write or from
Protect to Read/Write when the retention term ends. Retention Term displays 0 days when the retention
term is over. In
on page 10, for example, you can change the access attribute of volume #02
to Read/Write because the retention term is over. However, if you enable expiration lock in the Data
Retention window, attempts to change Read Only volumes or Protect volumes to Read/Write volumes
will fail even when the retention term is over. Expiration lock is disabled when you start Data Retention
Utility for the first time. To enable expiration lock, see
Prohibiting Changes to Read/Write Even When the
Retention Term is Over (Enabling/Disabling the Expiration Lock Function)
on page 21.
10
About HP StorageWorks XP Data Retention Utility Operations
