5 pass-through state, Pass-through state, Table 4-5: standby registers – PNI SENtral MandM User Manual
Page 21: Nd 4.5
PNI Sensor Corporation
Doc #1020129 revE
SENtral M&M Technical Datasheet
Page 20
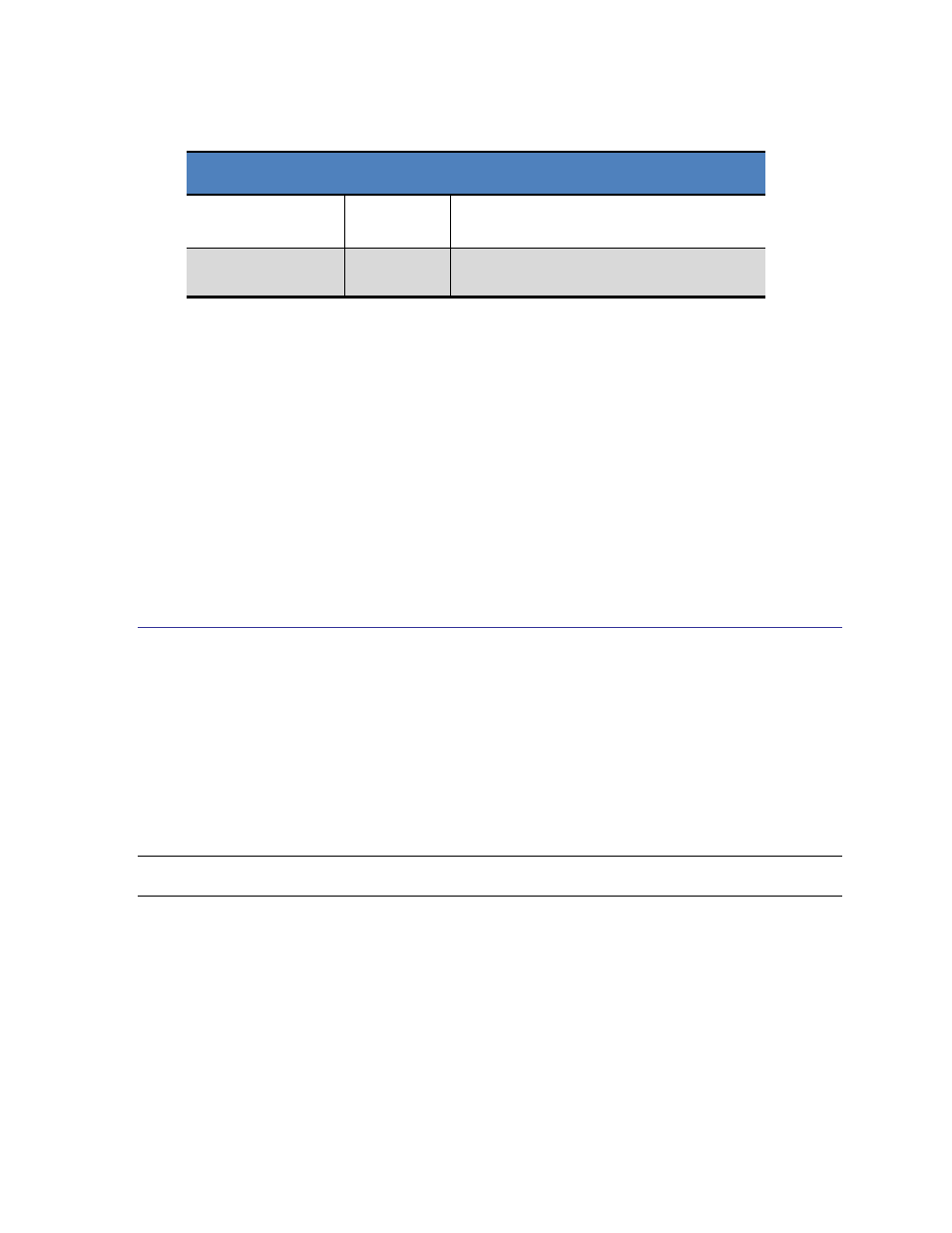
Table 4-5: Standby Registers
Register Name
Address
Register Value
AlgorithmControl
0x54
[0] 1 = StandbyEnable
0 = Disable Standby State
AlgorithmStatus
0x38
[0] 1 = SENtral in Standby State
0 = SENtral not in Standby State
The steps to enter and exit Standby State are given below:
Write 0x01 to the AlgorithmControl register. This places SENtral in Standby State.
Read the AlgorithmStatus register. If bit [0] is ‘1’, then SENtral is in Standby State.
This step is optional.
When you are ready to exit Standby State, write 0x00 to the AlgorithmControl
register. This takes SENtral out of Standby State and normally will place it back into
Normal Operation.
Read the AlgorithmStatus register. If bit [0] is ‘0’, then SENtral is not in Standby
State. This step is optional.
4.5 Pass-Through State
In Pass-Through State, SENtral’s sensor and host interfaces are connected by internal
switches so the host system can communicate directly with the sensors or EEPROM. To
enter Pass-Through State, SENtral first either should be in Standby or Initialized State.
Consequently, in Pass-Through State the SENtral algorithm, host interrupt line, and sensors
are disabled, unless a sensor is directly turned on by the host. When exiting Pass-Through
State, SENtral will return to its prior state.
Note: When entering Pass-Through State
the sensor’s registers retain the values established by
SENtral, and when exiting Pass-Through State any register changes will be retained.
Uses for the Pass-Through State include:
Direct control of sensors, if desired.
Debugging.
Communication with the dedicated EEPROM, if implemented. Specifically, if a new
Configuration File is generated, the host can write this into the EEPROM when in
Pass-Through State, as discussed in the SENtral Motion Coprocessor datasheet.
