LumaSense Technologies M67 User Manual
Page 9
M67, M67S Manual
8
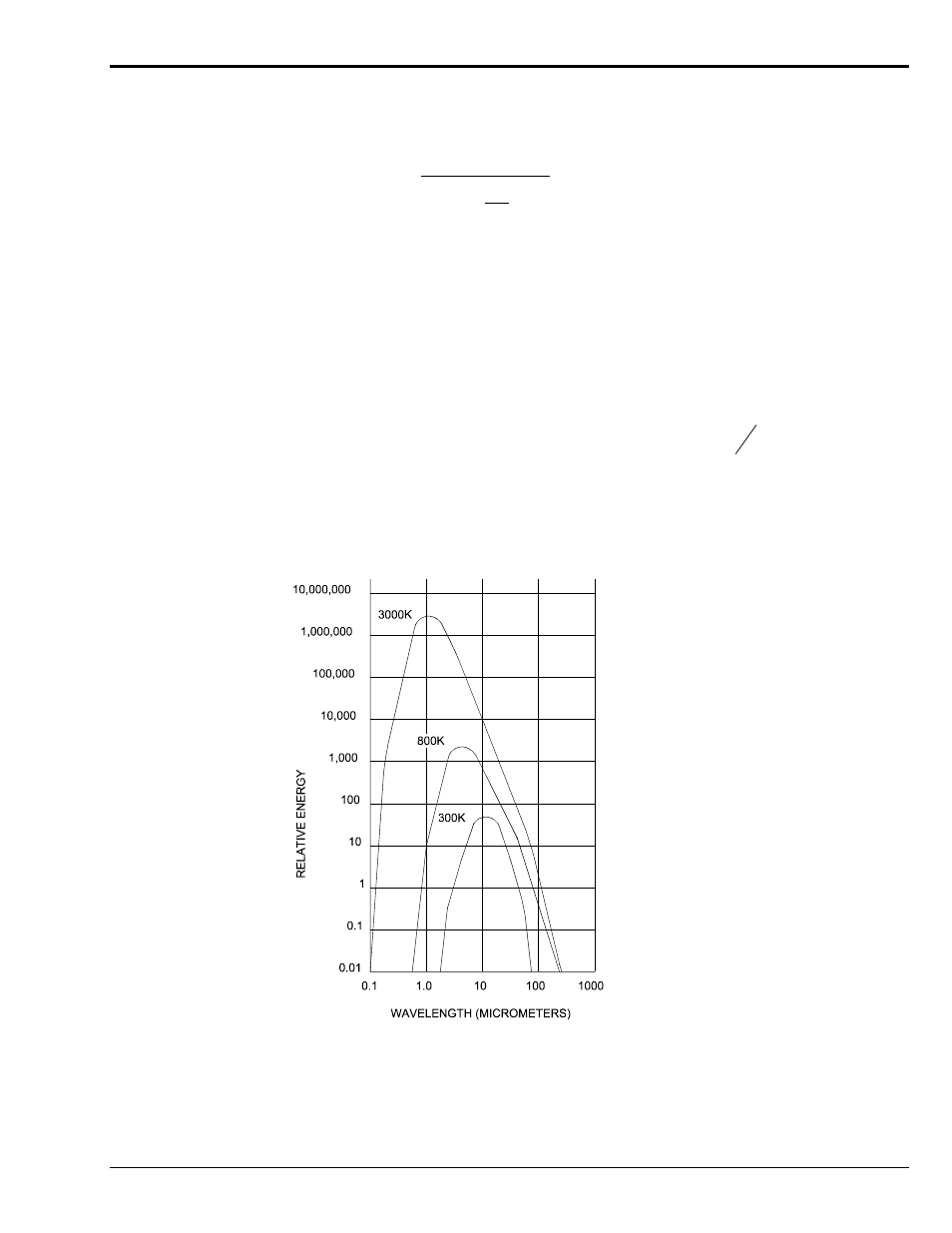
It should be noted that every hot object transmits radiant energy over a spectrum of wavelength. This radiation is of maximum
intensity at a particular wavelength depending on the temperature of the object. In general, the hotter the object, the shorter the
wavelength at which the radiation intensity is highest.
This phenomenon is explained by the following law, which is shown graphically in Figure 3.
1
exp
2
5
1
T
C
e
C
W
: Planck’s Law
where:
W
= radiation intensity at wavelength
, W/cm
2
C
1
= Planck's first radiation constant = 3.75 x 10
-12
W cm
2
e
= emissivity of object at wavelength
C
2
= Planck’s second radiation constant = 1.438 cm K
T
= absolute temperature of object K
and: exp denotes exponetation (natural antilogarithm)
The maximum radiation intensity at a temperature T Kelvin occurs at a wavelength of
max
2890
T
micrometers.
It should be noted that the wavelength of thermal radiation from objects lies in the infrared region of the spectrum. The terms
thermal radiation and infrared radiation are therefore synonymous.
Figure 3 - Variation Of Radiation Intensity With Wavelength At Various Temperatures
