PASCO ES-9060 Charge, Equipotential and Field Mapper User Manual
Page 21
Charge, Equipotential, and Field Mapper
Model No. ES-9060
20
®
2. Zero the Electrometer to remove any residual charge.
3. Roll the large, conductive paper into a cone with a 10 cm diameter
at the base. Make the pointed end with as low a radius as possible.
Stand the cone on the corkboard, and connect the cone to the
2000V output of the power supply (See Figure 2.0).
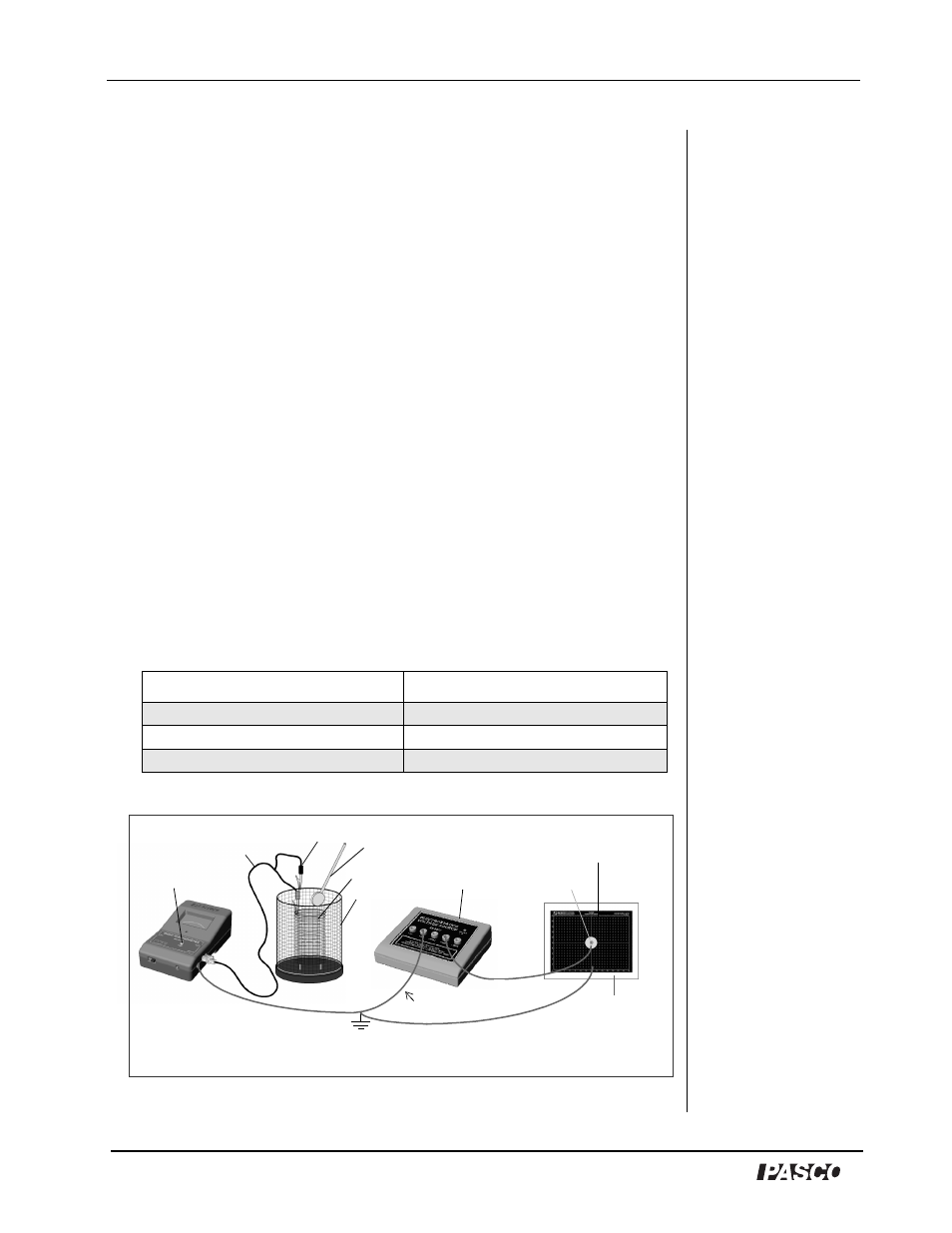
4. Use the Proof Plane, Electrometer, and Faraday Ice Pail to sample
the charge densities at various places on the cone from the 10 cm
diameter base to the point. Be sure to keep yourself grounded
when sampling charges.
Questions:
a) Does there seem to be a ratio between the diameter of the cone
where the proof plane touches and the charge density? (It is best to
use the large end of the cone for this measurement.)
b) Does the size of the proof plane have any effect on measurements
made towards the tip of the cone? If so, why?
Experiment 3: Charge Density on a Plane near a Point
Source
Equipment Required:
Charge Mapping Apparatus ES-9060)
Electrometer (ES-9078)
Proof Plane (ES-9057B)
Electrostatic Voltage Source (ES-9077)
Faraday Ice Pail (ES-9042A)
Conductive
paper
Disk
Figure 3.0: Experiment Setup with Point Source
corkboard
Electrometer
Ice Pail
Power supply
black lead
red lead
Proof Plane
ground
(2000 V)
shield
to COM port
