PASCO ME-6807A Human Arm Model User Manual
Page 16
®
H u m a n A r m M o d e l
E x p e r i m e n t 4 : B i c e p s C u r l
16
3.
Stop data collection.
Analysis
1.
Is the graph linear?
2.
As the elbow flexes does the biceps force increase or decrease?
Part B
Introduction
The motion studied in this part is similar to that of the last part, but the upper arm is
held at an angle rather than vertical.
Hold a mass in your hand. Rest your elbow on the back of a chair so that your upper
arm is at about 45 degrees from vertical. Starting with your elbow straight, flex your
elbow to lift the mass.
Predictions
1.
As you lift the mass, does your biceps force increase or decrease?
2.
Sketch your prediction of the biceps force versus elbow angle graph.
Set-up
1.
Reposition the shoulder and lock it at 45°.
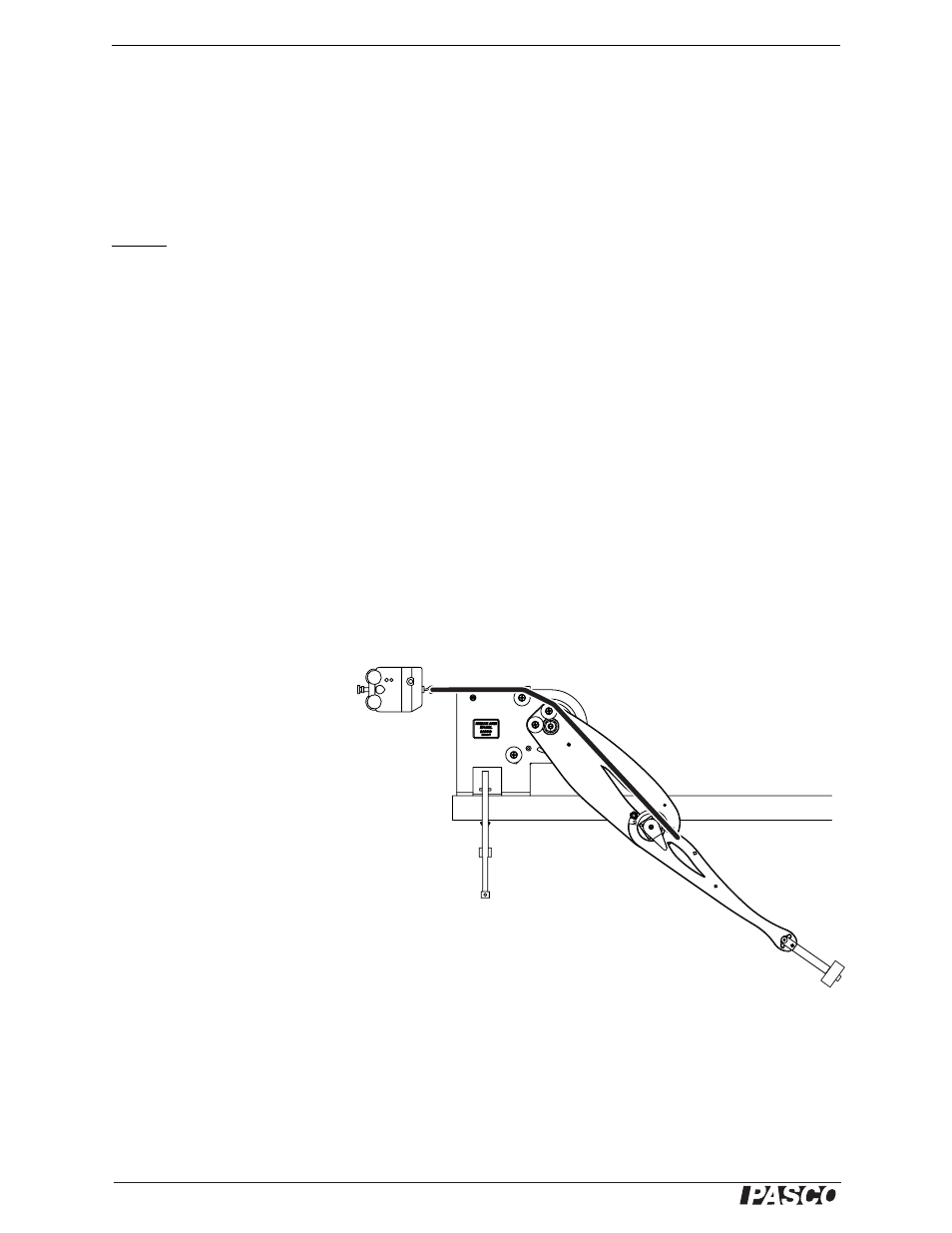
2.
Hold force sensor in the posi-
tion illustrated.
Procedure
1.
Start data collection.
2.
Pull with the force sensor to slowly flex the
elbow from about 5° to 130°.
3.
Stop data collection.
Analysis
1.
Is the graph linear?
2.
As the elbow flexes does the biceps force increase or decrease?
Further Study
Find a shoulder angle for which the biceps force is nearly constant as the elbow flexes
from 10° to 130°.
- UI-5000 850 Universal Interface Quick Start (1 page)
- UI-5000 850 Universal Interface Instruction Manual (24 pages)
- PS-2193 High Current Sensor (2 pages)
- ME-8979 Mass and Hanger Set (1 page)
- ME-9498A Photogate Head (3 pages)
- ME-6821A Photogate Mounting Bracket (2 pages)
- ME-6825A MINI LAUNCHER (39 pages)
- ME-6810 Time of Flight Accessory (24 pages)
- ME-8574 DISCOVER FRICTION ACCESSORY (4 pages)
- PS-2103A Motion Sensor (4 pages)
- PS-2189 High Resolution Force Sensor (2 pages)
- ME-9448B Super Pulley with Clamp (2 pages)
- ME-6955 1.2 m PAScar Dynamics System (27 pages)
- PS-2104 Force Sensor (2 pages)
- ME-8998 Elastic Bumper Kit (2 pages)
- ME-6843 Spring Cart Launcher (9 pages)
- ME-6950 PAScar with Mass (29 pages)
- PS-2120A Rotary Motion Sensor (9 pages)
- PS-2120A Rotary Motion Sensor (17 pages)
- ME-9821 Centripetal Force Pendulum (18 pages)
- ME-8088 Centripetal Force Apparatus (20 pages)
- ME-8735 Large Rod Stand (2 pages)
- CI-6545 Force Accessory Bracket (3 pages)
- ME-9806 Photogate Brackets (1 page)
- CI-6692 IDS MOUNT ACCESSORY (2 pages)
- ME-6569 RMS_IDS KIT (36 pages)
- ME-6829 Mini Launcher Ballistic Pendulum (18 pages)
- ME-9889 Discover Free Fall System (10 pages)
- SE-7256 Motion Sensor Guard (2 pages)
- ME-8973 Discover Collision Bracket (2 pages)
- AP-8214A Stress_Strain Apparatus (12 pages)
- CI-6691 MINI-ROTATIONAL ACCESSORY (2 pages)
- ME-9833 Physical Pendulum Set (30 pages)
- OS-8473 POLARIZER SET (2 pages)
- PS-2343 USB Camera (2 pages)
- AP-8215A Gravitational Torsion Balance (20 pages)
- OS-8526A X-Y ADJUSTABLE DIODE LASER (2 pages)
- Xplorer-GLX Users’ Guide (152 pages)
- PS-2150 Broad Spectrum Light Sensor (2 pages)
- PS-2164 Quad Pressure Sensor (3 pages)
- PS-2200 Load Cell, 100 N (3 pages)
- PS-2205 Dual Load Cell Amplifier (5 pages)
- PS-2107 Absolute Pressure Sensor (2 pages)
- PS-2102 pH Sensor (3 pages)
- PS-2119 Acceleration Sensor (2 pages)
