Introduction, Predictions, Set-up – PASCO ME-6807A Human Arm Model User Manual
Page 13
®
13
Experiment 3: Triceps Force versus Perpendicular Load
Introduction
Hold your arm in front of you with your elbow bent at 90°. Now have your partner
push your hand toward you to try to bend your elbow further. Resist the load force so
that your elbow remains bent at 90°.
Predictions
1.
Which muscle (the biceps or triceps) do you use to resist this load?
How do you know?
2.
Is the muscle force greater, less than, or equal to the load force applied
to your hand?
3.
If you partner pushes your hand with a force of 1 N, how much muscle
force is needed to keep your elbow at 90°?
Set-up
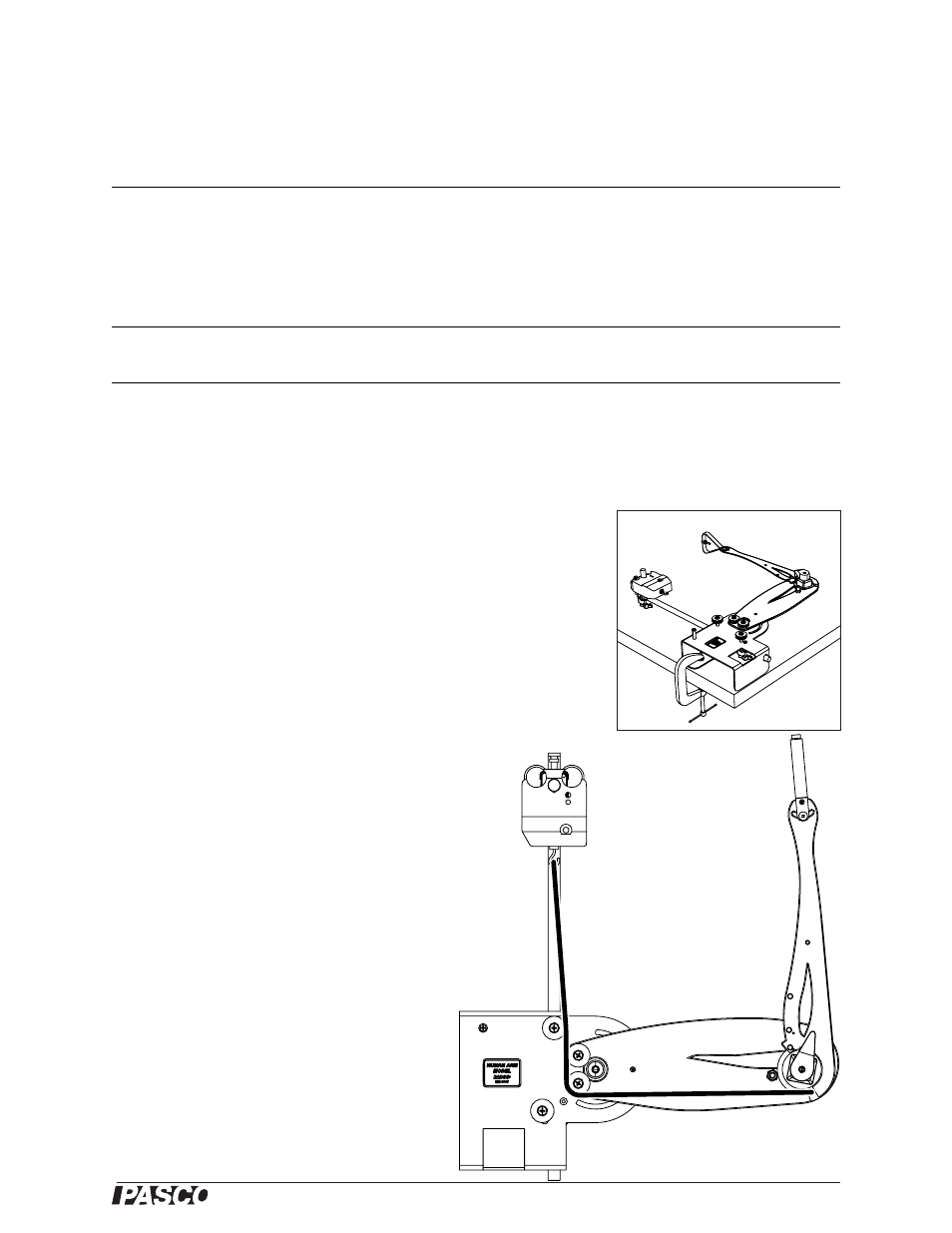
1.
Clamp the arm model horizontally as illustrated.
2.
Clamp the rod to the base of the model as illustrated.
Use the sensor clamp and stud to attach a force sensor
to the rod.
3.
Lock the shoulder at 90°.
4.
Attach a cord as illustrated. Adjust the length of the
cord so that the elbow will be held at about 90°.
5.
Connect two force sensors to your interface. The sec-
ond force sensor will be held in your hand
and apply the load force to the model’s hand.
6.
Set the sampling rate of both force sensors to
20 Hz.
7.
Prepare a graph to plot triceps force versus
load force.
Required Parts of Human Arm Model
Arm
Cord (1 piece)
45 cm rod
Sensor-mounting clamp and stud
Other Required Equipment
2 Force Sensors
PS-2104
or PS-2189
C-clamp
SE-7286 (6-pack)
Force Sensor 1
(Triceps Force)
