Analysis, Questions – PASCO OS-8459 Beginning Optics System User Manual
Page 25
®
M o d e l N o . O S - 8 4 5 9
E x p e r i m e n t 9 : A p p a r e n t D e p t h
25
2.
Mark the place on the paper where the two rays cross each other.
3.
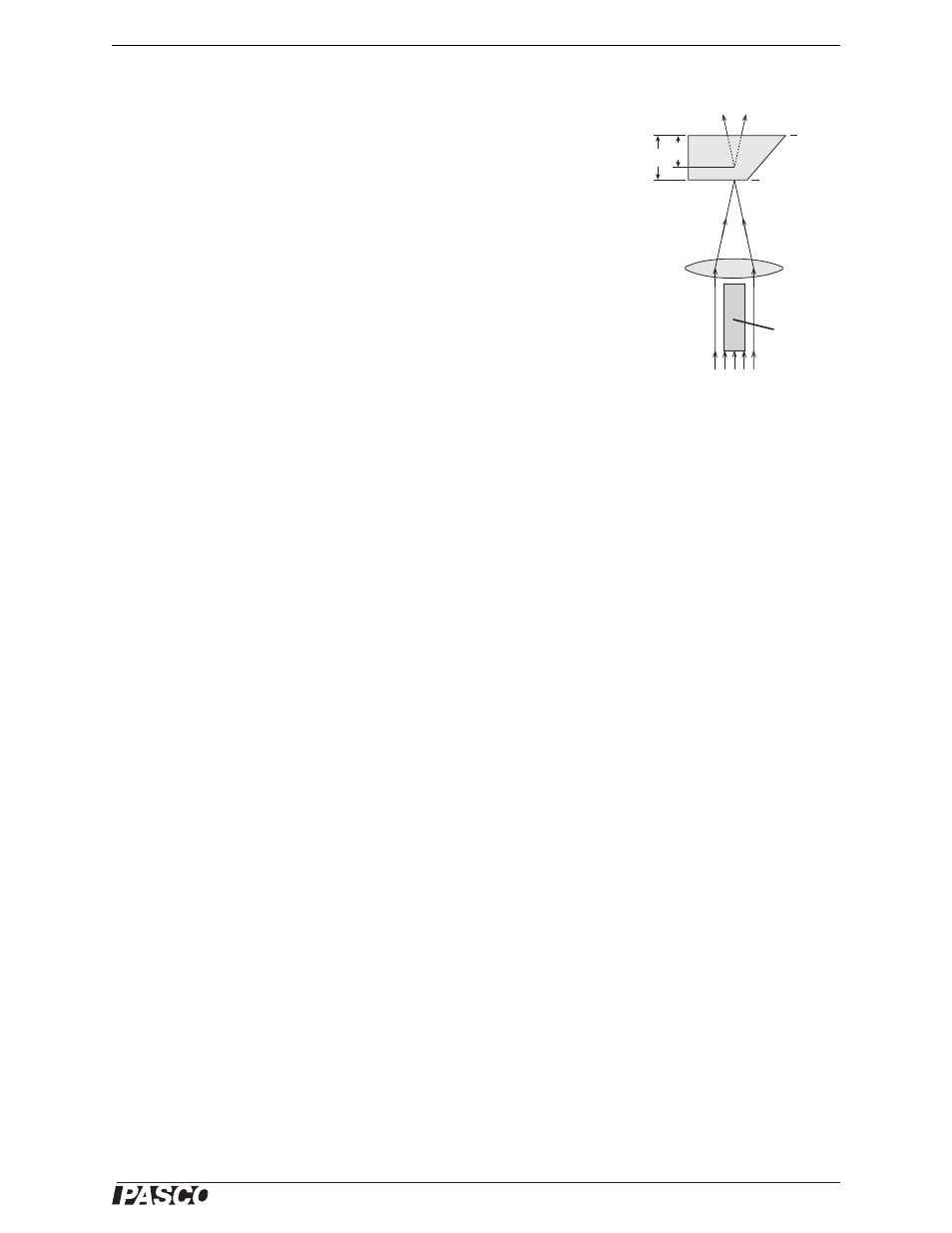
Position the rhombus as shown in Figure 9.4. The “bottom” surface of the
rhombus must be exactly at the point where the two rays cross. The crossed
rays simulate rays that originate at an object on the “bottom” of the block.
4.
Trace the rhombus and trace the rays diverging from the “top” surface.
5.
Remove the rhombus and light source. Trace the diverging rays back into the
rhombus. The point where these rays cross (inside the rhombus) is the appar-
ent position of the “bottom” of the rhombus when viewed through the “top”.
Analysis
1.
Measure the apparent depth, d, and record it in Table 9.1.
2.
Use Equation 9.1 to calculate the index of refraction and record your result
in Table 9.1.
Questions
1.
Of the two methods that you used to determine d, which one is more precise?
Explain.
2.
The accepted value of the index of refraction of acrylic is n = 1.49. What was the
percent difference between the accepted value and each of your two results?
t d
Convex
lens
Mirror
on edge
bottom
surface
top
surface
Figure 9.4
