Table 2. component suppliers, Table 3. k-factor – Rainbow Electronics MAX8720 User Manual
Page 13
Free-Running, Constant-On-Time PWM
Controller with Input Feed-Forward
The quick-PWM control architecture is a pseudo-fixed-
frequency, constant-on-time, current-mode type with
voltage feed-forward (Figure 2). This architecture relies
on the output filter capacitor’s ESR to act as the cur-
rent-sense resistor, so the output ripple voltage pro-
vides the PWM ramp signal. The control algorithm is
simple: the high-side switch on-time is determined sole-
ly by a one-shot whose period is inversely proportional
to input voltage and directly proportional to output volt-
age. Another one-shot sets a minimum off-time (400ns
typ). The on-time one-shot is triggered if the error com-
parator is low, the low-side switch current is below the
current-limit threshold, and the minimum off-time one-
shot has timed out.
On-Time One-Shot (TON)
The heart of the PWM core is the one-shot that sets the
high-side switch on-time. This fast, low-jitter, adjustable
one-shot includes circuitry that varies the on-time in
response to battery and output voltage. The high-side
switch on-time is inversely proportional to the battery
voltage as measured by the V+ input, and proportional
to the output voltage. This algorithm results in a nearly
constant switching frequency despite the lack of a
fixed-frequency clock generator. The benefits of a con-
stant switching frequency are twofold: first, the frequen-
cy can be selected to avoid noise-sensitive regions
such as the 455kHz IF band; second, the inductor rip-
ple-current operating point remains relatively constant,
resulting in easy design methodology and predictable
output voltage ripple.
On-Time = K (V
OUT
+ 0.075V) / V
IN
where K is set by the TON pin-strap connection and
0.075V is an approximation to accommodate the expect-
ed drop across the low-side MOSFET switch (Table 3).
The on-time one-shot has good accuracy at the operat-
ing points specified in the Electrical Characteristics
table (±10% at 200kHz and 300kHz, and ±12% at
550kHz and 1000kHz). On-times at operating points far
removed from the conditions specified in the Electrical
Characteristics table can vary over a wider range. For
example, the 1000kHz setting typically runs approxi-
mately 10% slower with inputs much greater than +5V
due to the very short on-times required.
MAX8720
Dynamically Adjustable 6-Bit VID
Step-Down Controller
______________________________________________________________________________________
13
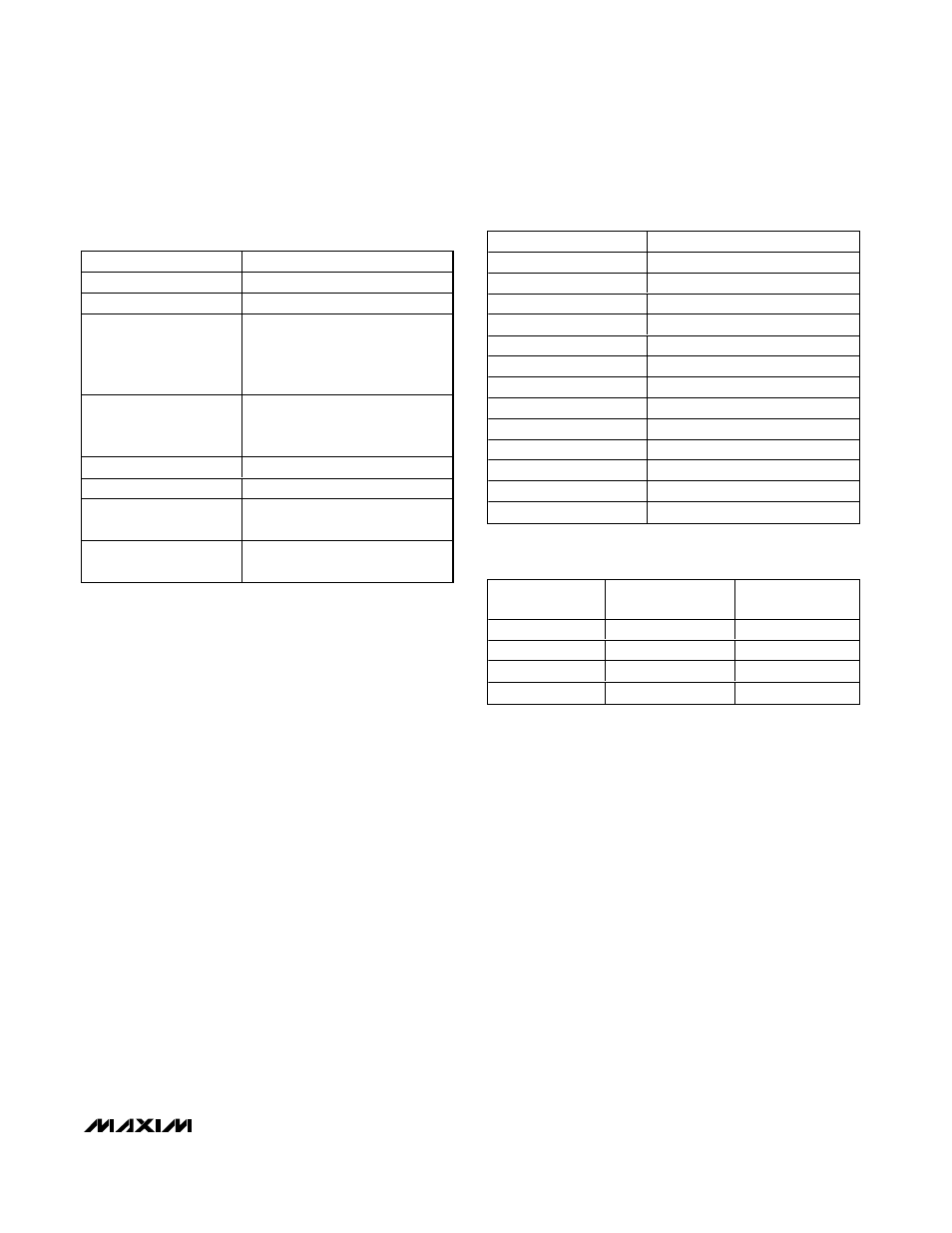
COMPONENT
15A/300kHz
Input Voltage
V
IN
= 7V to 24V
Output Voltage
V
OUT
= 1.25V
C
IN
Input Capacitor
(2) 10µF, 25V
TDK C3225X7R1E106M
AVX 12103D106M
Taiyo Yuden TMK325BJ106MM
C
OUT
Output Capacitor
(3) 470µF, 2.5V, 9m
Ω low-ESR
polymer capacitor
Sanyo 2R5TPE470M9
N
H
High-Side MOSFET
Siliconix SI7390DP
N
L
Low-Side MOSFET
Siliconix SI7356DP
D
L
Schottky Rectifier
3A, 30V, 0.45V
f
Nihon EC31QS03L
L1 Inductor
0.8µH, 20A, 4.9m
Ω
Sumida CDEP104-0R8MC-50
Table 1. Component Selection for
Standard Applications
SUPPLIER
WEBSITE
AVX
www.avx.com
Central Semiconductor
www.centralsemi.com
Coiltronics
www.coiltronics.com
Fairchild Semiconductor
www.fairchildsemi.com
Kemet
www.kemet.com
Nihon
www.niec.co.jp
Panasonic
www.panasonic.com/industrial
Sanyo
www.secc.co.jp
Siliconix (Vishay)
www.vishay.com
Sumida
www.sumida.com
Taiyo Yuden
www.t-yuden.com
TDK
www.component.tdk.com
TOKO
www.tokoam.com
Table 2. Component Suppliers
TON SETTING
TON FREQUENCY
(kHz)
K-FACTOR (µs)
V
CC
200
5 ±10
Open
300
3.3 ±10
REF
550
1.8 ±12.5
GND
1000
1.0 ±12.5
Table 3. K-Factor
