Theory of operation, Power-sonic rechargeable batteries, Discharge – Power-Sonic Sealed Lead Acid Batteries - Technical Manual User Manual
Page 5: Charge
POWER-SONIC Rechargeable Batteries
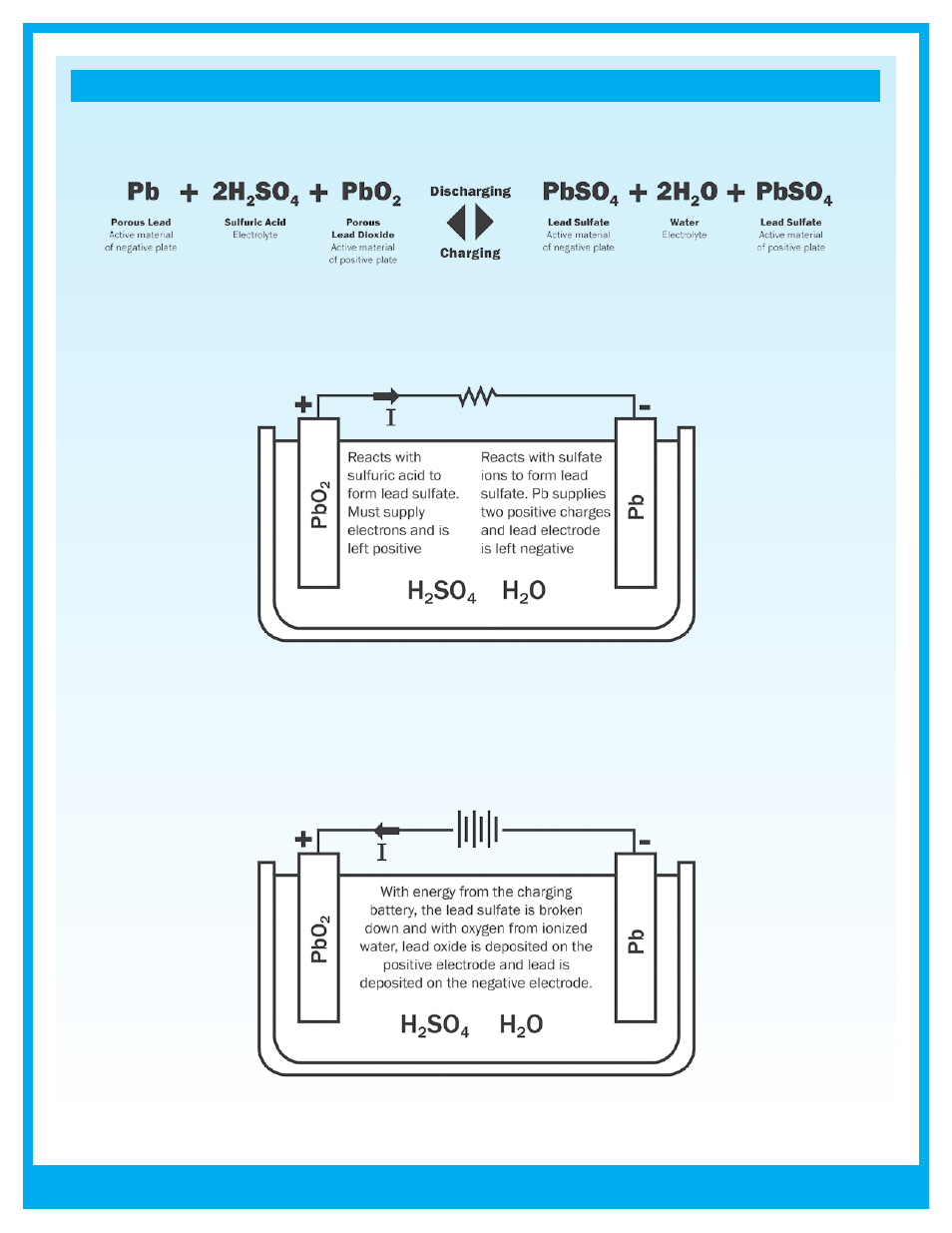
Discharge
During the discharge portion of the reaction, lead dioxide (PbO
2
) is converted into lead sulfate (PbSO
4
) at the positive
plate. At the negative plate sponge lead (Pb) is converted to lead sulfate (PbSO
4
). This causes the sulfuric acid (2H
2
SO
4
)
in the electrolyte to be consumed.
Figure : Chemical reaction when a battery is being discharged
Charge
During the recharge phase of the reaction, the cycle is reversed. The lead sulfate (PbSO
4
) and water are
electrochemically converted to lead (Pb), lead dioxide (PbO
4
) and sulfuric acid (2H
2
SO
4
) by an external electrical charging
source.
Figure : Chemical reaction when a battery is being charged
Theory of Operation
The basic electrochemical reaction equation in a lead acid battery can be written as:
- PG-12V120 (2 pages)
- NH-3000SC (2 pages)
- DCG12-38 (2 pages)
- PS-AA (2 pages)
- PS-12180 (2 pages)
- PS-1229 (1 page)
- PS-621 (2 pages)
- PS-DXF (2 pages)
- PS-610 (2 pages)
- PS-1251FP (2 pages)
- PGFT-12v110 (1 page)
- PS-4-5A (2 pages)
- PG-2v860 (1 page)
- PG-12v220 (1 page)
- 6-OPzV600 (1 page)
- PS-6120FP (2 pages)
- PHR-12350 (1 page)
- PS-62000 (2 pages)
- PS-628 (1 page)
- PG-2v480 (1 page)
- NH-TR7 (2 pages)
- PS-445 (2 pages)
- PCBM-2.4 (2 pages)
- PG-12v130 (1 page)
- PG-12V103 (2 pages)
- PG-12v6 (1 page)
- NH-1250AA (2 pages)
- PS-12120 (1 page)
- PS-1221S (2 pages)
- PG-2v540 (1 page)
- PS-AAXF (2 pages)
- PS-6360 (2 pages)
- 5-OPzV350 (1 page)
- PHR-12500 (1 page)
- PDC-121100 (2 pages)
- PSX12-3.5 (1 page)
- PS-630ST (1 page)
- PS-832 (1 page)
- PDC-121000 (2 pages)
- PS-435 (1 page)
- PSX12-8.5 (1 page)
- PHR-12200 (1 page)
- PG-12v21 (1 page)
- PSC-241000A (6 pages)
- PSGL-12170 (1 page)
