Charging, Power-sonic rechargeable batteries – Power-Sonic Sealed Lead Acid Batteries - Technical Manual User Manual
Page 19
POWER-SONIC Rechargeable Batteries
Charging
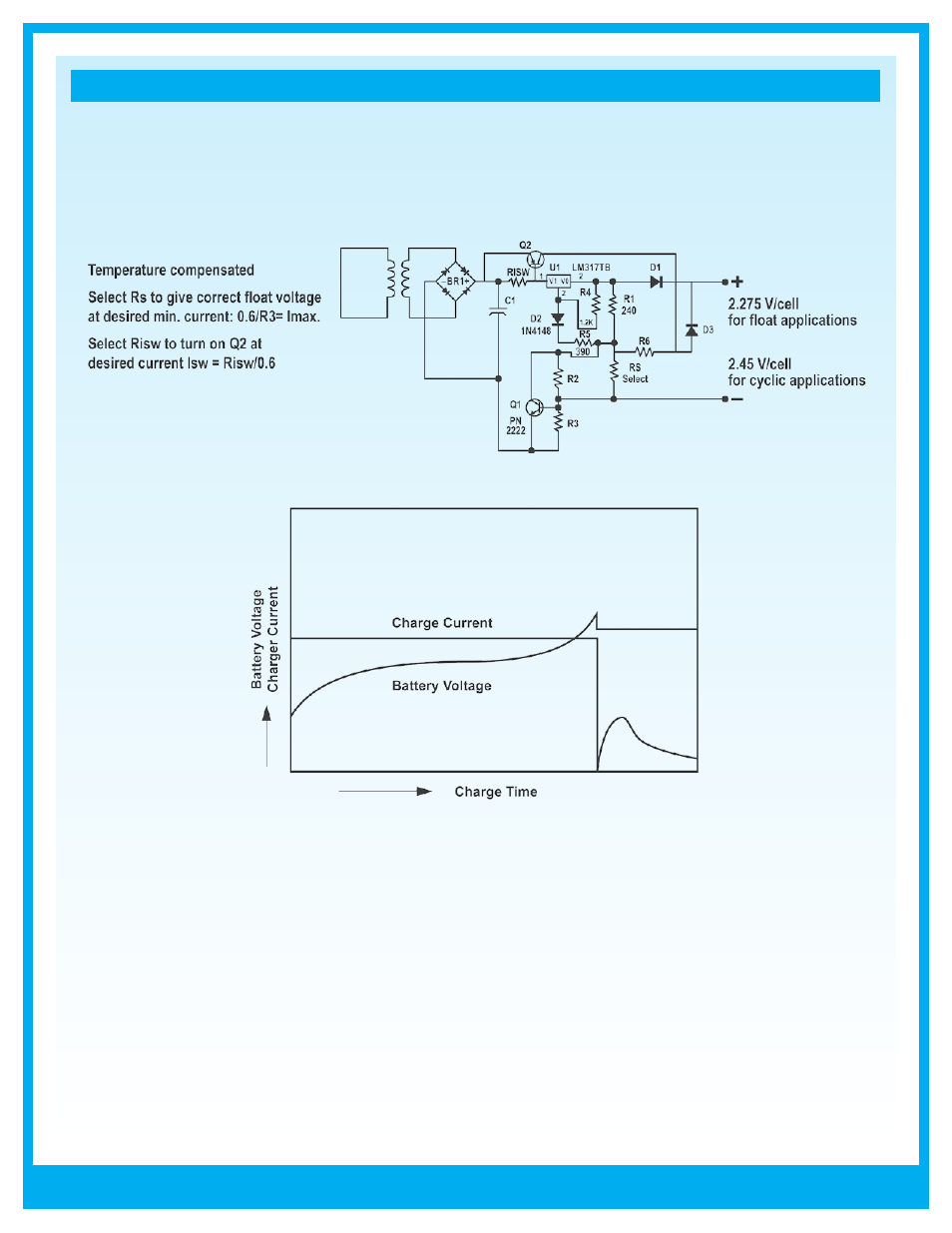
Two-Step Constant Voltage Charging
This method uses two constant voltage devices. In the initial charge phase the high voltage setting is used. When
charging is nearly complete and the charge voltage has risen to a specified value (with the charge current decreased), the
charger switches the voltage to the lower setting. This method allows rapid charging in cycle or float service without the
possibility of overcharging, even after extended charging periods.
Charging in Series
Lead-acid batteries are strings of 2 volt cells connected in series, commonly 2, 3, 4 or 6 cells per battery. Strings of
Power-Sonic batteries, up to 48 volts and higher, may be charged in series safely and efficiently. However, as the number
of batteries in series increases, so does the possibility of slight differences in capacity. These differences can result from
age, storage history, temperature variations or abuse.
Fully charged batteries should never be mixed with discharged batteries when charging in series. The discharged
batteries should be charged before connection.
When a single constant voltage charger is connected across an entire high voltage string, the same current flows through
all cells in the string. Depending on the characteristics of the individual batteries, some may overcharge while others
remain in a slightly undercharged condition.
To minimize the effects of individual battery differences, use batteries of the same age, amp hour, and history and, if
possible, charge in strings of no greater than 24 or 48 volts.
Figure : Dual stage current limited battery charger.
Figure 0: Two-step constant voltage charging characteristics.
