Charging, Power-sonic rechargeable batteries – Power-Sonic Sealed Lead Acid Batteries - Technical Manual User Manual
Page 17
POWER-SONIC Rechargeable Batteries
Charging
Constant Current Charging
Constant current charging is suited for applications where discharged ampere-hours of the preceding discharge cycle are
known. Charge time and charge quantity can easily be calculated, however an expensive circuit is necessary to obtain a
highly accurate constant current. Monitoring of charge voltage or limiting of charge time is necessary to avoid excessive
overcharge.
While this charging method is very effective for recovering the capacity of a battery that has been stored for an extended
period of time, or for occasional overcharging to equalize cell capacities, it lacks specific properties required in today’s
electronic environment.
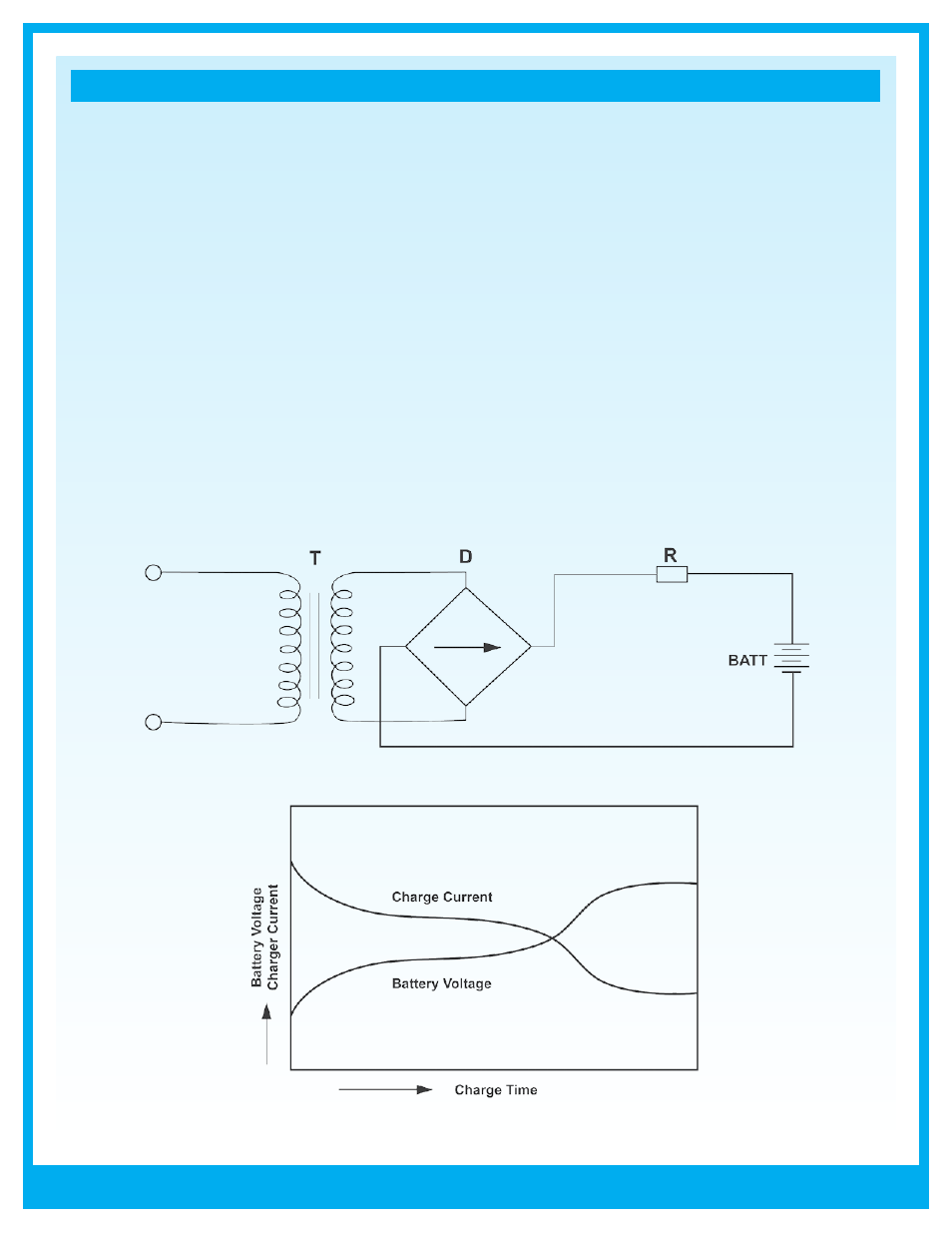
Taper-Current Charging
This method is not recommended as it is somewhat abusive of sealed lead acid batteries and can shorten service
life. However, because of the simplicity of the circuit and low cost, taper-current charging is extensively used to charge
multiple numbers and/or for cyclic charging.
When using a taper-current charger the charger time should be limited or a charging cut-off circuit be incorporated to
prevent overcharge. Please contact our technical department if you need assistance with this.
In a taper-current charging circuit, the current decreases in proportion to the voltage rise. When designing a taper charger
always consider power voltage fluctuations. In this event the internal resistance drop will convert to heat. Heat generated
by the circuit should be measured and if required a heat sink should be incorporated in the design.
Figure : Taper-current charging characteristics for this
type of basically unregulated charger.
Figure : Taper-current charging circuit
