2 planning your raid, Planning your raid, Figure 40: create array with 8 hdds in raid 5 – Accusys ExaSAN B08S2-PS User Manual
Page 59: Figure 41: create array with 8 hdds in raid 6, Figure 42: create array with 16 hdds in two raid5
4. How to Use
User Guide
Page 4-8
4.1.2.2 Planning your RAID
Before using RAIDGuard X to set up your RAID storage, it is a good idea to become familiar with the
variety of configurations, or schemes, that are available for the ExaSAN RAID storage. This section
describes these schemes and illustrates how each RAID level is applied.
RAID Level
Description
Capacity
RAID 0
Striping, the fastest and most efficient
array type but offers no fault-tolerance
Total of all drives
RAID 1
Mirroring, All disks have the same data
Total of one drive
RAID 5
Block-level striping with distributed
parity, one disk fault tolerant
Total of all drives minus one drive
RAID 6
Block-level striping with double
distributed parity, two disks fault tolerant
Total of all drives minus two drives
RAID 0+1
Combines the advantage of R0 and R1,
provides optimal speed and reliability
One-half the total capacity of drives
(Sum of RAID 1 member sets)
When configuring RAID, you may take the follow items into consideration:
1. Are you using a DAS or SAN environment?
2. Do you currently have more than one RAID or JBOD?
3. Which is more important, transfer speed or data security? One or two disk fault tolerance?
4. Do you need multiple volume or single volume on your RAID systems?
5. Do you have to consider the metadata volume for SAN software?
6. Do you consider using Global spare drives?
7. The number of disk drives used determines the speed of the RAID created. Take into account the
desired speed when configuring RAID.
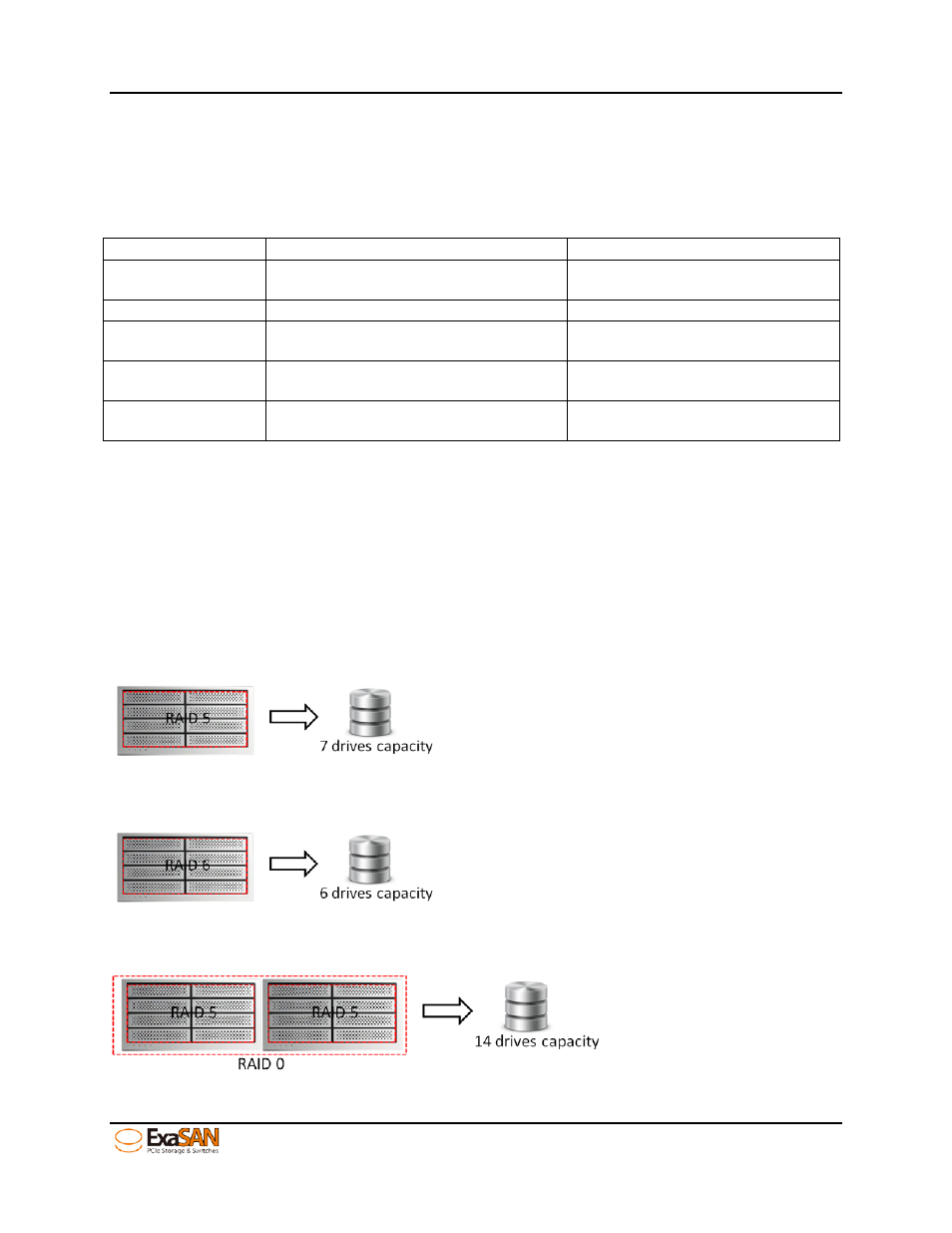
DAS Example 1:
Figure 40: Create array with 8 HDDs in RAID 5
DAS Example 2:
Figure 41: Create array with 8 HDDs in RAID 6
DAS Example 3:
Figure 42: Create array with 16 HDDs in two RAID5
