Table 4-1. platinum rtd types – National Instruments Module SCXI-1503 User Manual
Page 38
Chapter 4
Theory of Operation
4-8
ni.com
Although the resistance-temperature curve is relatively linear, accurately
converting measured resistance to temperature requires curve fitting. The
following Callendar-Van Dusen equation is commonly used to approximate
the RTD curve:
where
R
T
is the resistance of the RTD at temperature T.
R
0
is the resistance of the RTD at 0
°C.
A, B, and C are the Callendar-Van Dusen coefficients shown in
Table 4-1.
T is the temperature in
°C.
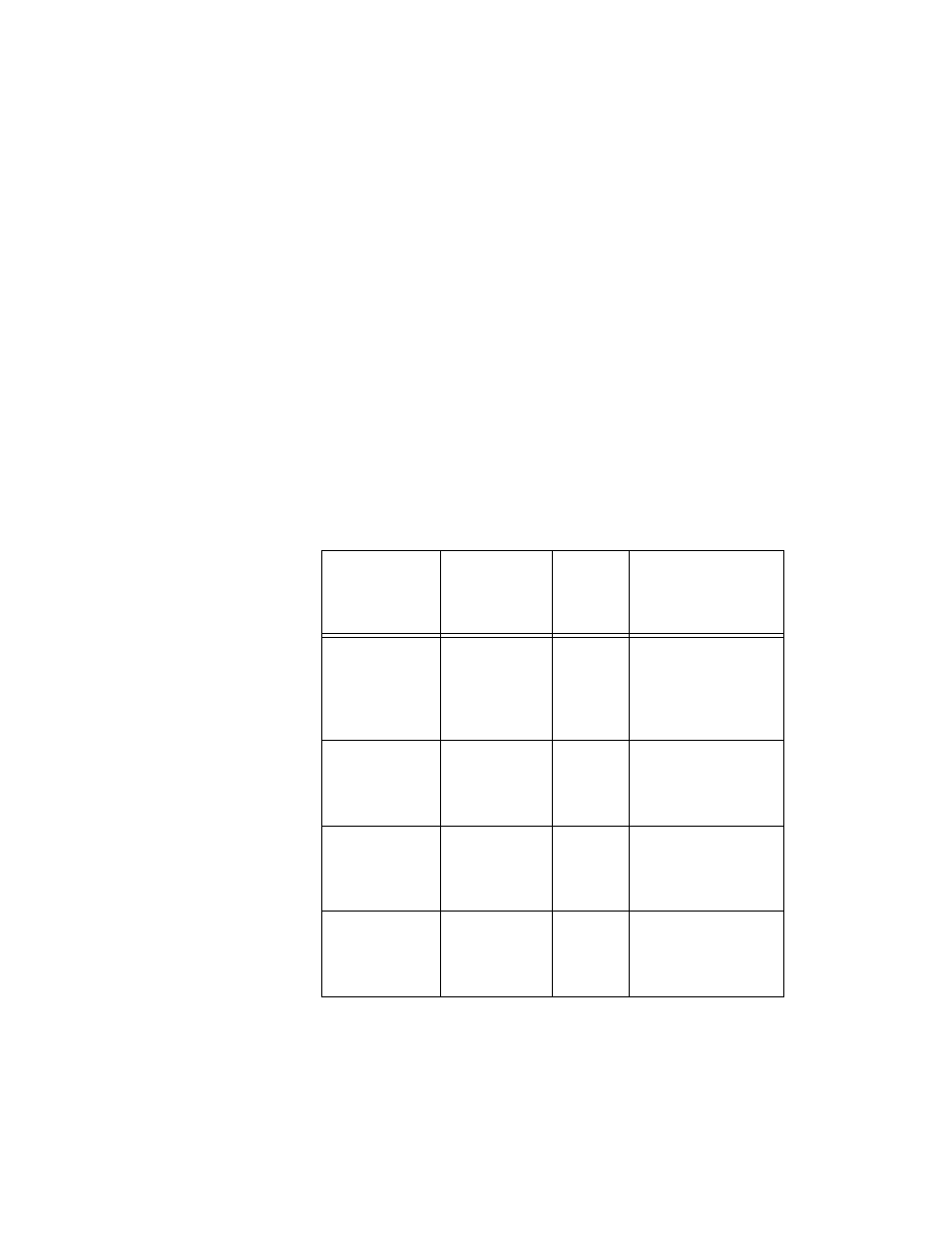
Table 4-1 lists the RTD types and their corresponding coefficients.
Table 4-1. Platinum RTD Types
Standard
Temperature
Coefficient of
Resistance
(TCR, PPM)
Typical
R
0
Callendar-Van
Dusen Coefficient
IEC-751
DIN 43760
BS 1904
ASTM-E1137
EN-60751
3851
100
Ω
1000
Ω
A = 3.9083
× 10
–3
B = –5.775
× 10
–7
C = –4.183
× 10
–12
Low cost
vendor
compliant
1
3750
1000
Ω
A = 3.81
× 10
–3
B = –6.02
× 10
–7
C = –6.0
× 10
–12
JISC 1604
3916
100
Ω
A = 3.9739
× 10
–3
B = –5.870
× 10
–7
C = –4.4
× 10
–12
US Industrial
Standard D-100
American
3920
100
Ω
A = 3.9787
× 10
–3
B = –5.8686
× 10
–7
C = –4.167
× 10
–12
R
T
R
0
1 AT BT
2
C T 100
–
(
)
3
+
+
+
[
]
=
