All configurations, Ip addressing example – Paradyne U8777 User Manual
Page 46
5. IP Addressing
5-2
May 2002
8700-A2-GB20-40
All Configurations
The NTU obtains its IP address when the PPP link is established over the EOC.
Use the ATI to assign:
T
An IP address for each NMS. See
Table A-14, SNMP NMS Security Options,
T
An IP address for the TFTP server you wish to use to upload and download
configurations. See
and Configurations Using TFTP, and the documentation for your TFTP server.
Review the following information in preparation for selecting an IP addressing
scheme.
T
Any legal host address is allowed for a given subnet. The address choice
within the subnet is arbitrary.
T
A single route to a subnet is all that is needed to reach every device on a
subnet. The unit’s routing table supports a maximum of 20 routes.
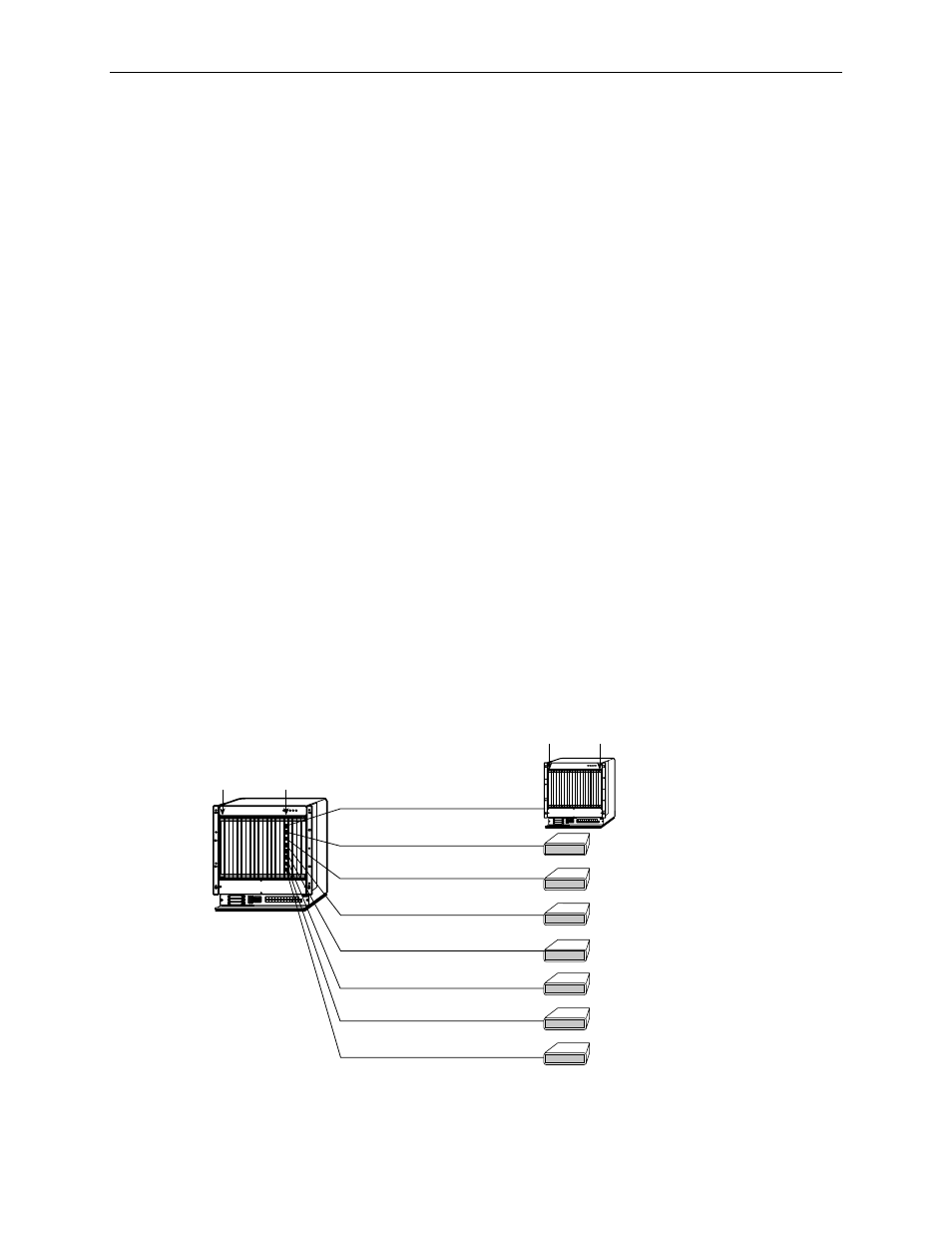
IP Addressing Example
Figure 5-1, Peer IP Address Assignments
, shows IP addressing in a typical
network. Note that the Peer IP Address:
T
Refers to the IP address of the unit configured as an NTU.
T
Is assigned by the LTU.
Figure 5-1.
Peer IP Address Assignments
99-16617
DSLAM
DSLAM
79xx
79xx
79xx
MCC Base
Address = 126.35.50.1
MCC Base Subnet
Mask = 255.255.255.0
Port 1
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.32
MCC
LTU
87xx
Port 2
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.33
Port 3
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.34
Port 4
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.35
NTU
MCC
MCC Backplane
Address = 126.35.1.1
MCC Backplane
Mask = 255.255.255.0
LTU Backplane
Address = 126.35.1.16
NTU Backplane
Address = 126.35.50.17
79xx
79xx
79xx
Port 5
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.36
Port 6
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.37
Port 7
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.38
Port 8
Peer IP Address = 126.35.1.39
79xx
