Net addresses, Group addresses, Special addressing modes – use of wildcards – Motorola MICOM-2ES/2RS/2TS ALE User Manual
Page 22
MICOM-2ES/2RS/2TS ALE Supplement to Owner’s Guide
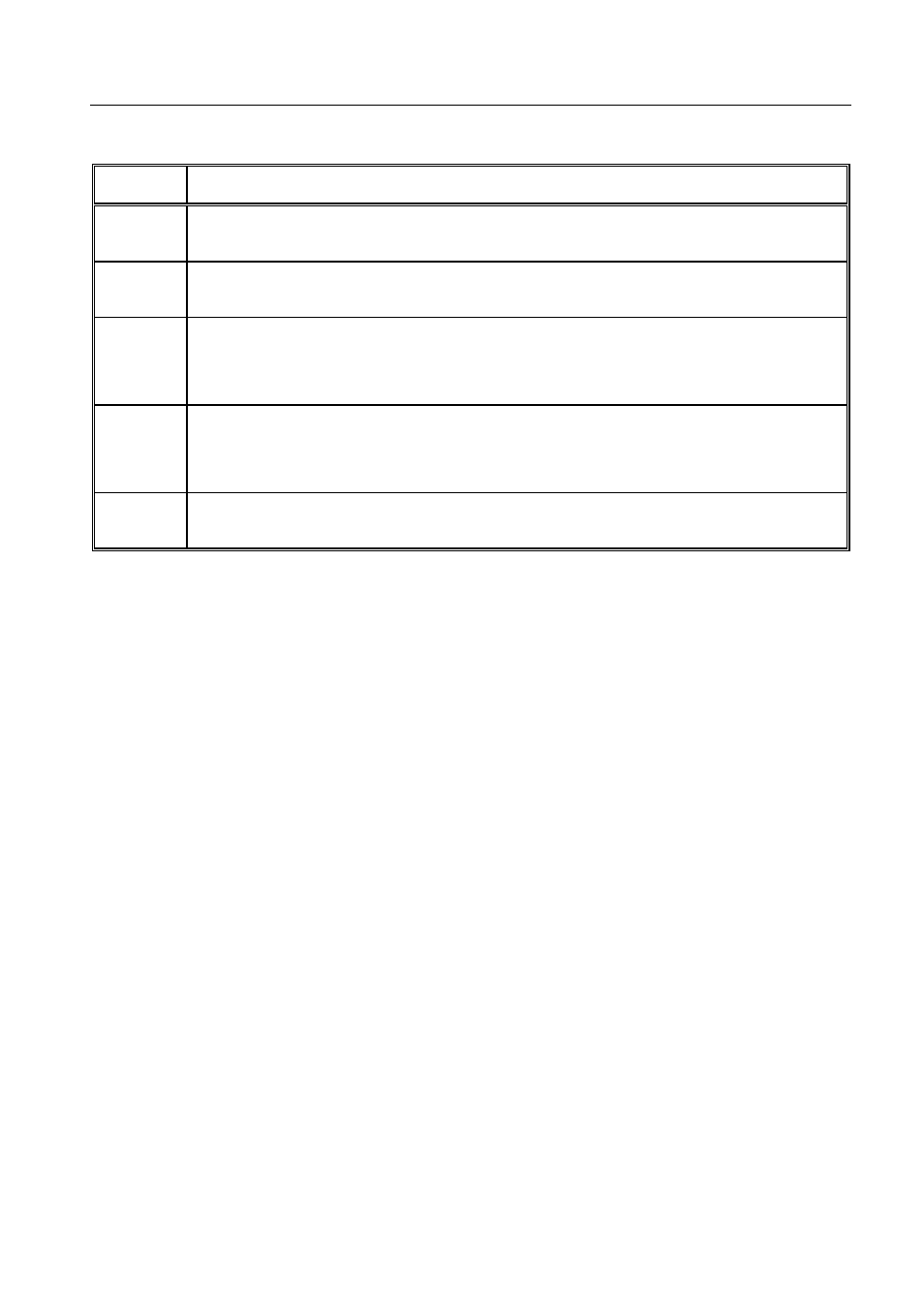
Table 1. Use of “@” Stuffing Symbol (Cont.)
Pattern Interpretation
@ A @ “Selective AllCall” global address: each station with the same last character “A”
stop scanning and listen (unless this function is inhibited
@ @ ?
“AnyCall” global address (see also Table 2): all the stations stop scanning and
respond in randomly selected timeslots (unless this function is inhibited)
@ @ A
@ B@
(option)
“Selective AnyCall” address: each station with same last character(s) “A” (or
“B”) stops scanning and responds in a randomly selected timeslot (unless this
function is inhibited), using its own address
@ A B
@ C D
(option)
“Double selective AnyCall” address: each station with same last characters “AB”
(or “CD”) stops scanning and responds in a randomly selected timeslot (unless
this function is inhibited), using its own address
@ @ @
“Null” address; all the stations ignore this address. The null address intended for
use in test and maintenance, or to create an extra “buffer” timeslot
Net Addresses
The purpose of a net call is to rapidly and efficiently establish contact with multiple
prearranged (net) stations. This is achieved by the use of a single net address.
The net address is actually an additional address assigned in common to all the
stations that are members of a specific net. Its address structure is identical to that
used for individual station addresses (basic or extended, with or without stuffing, as
necessary).
When defining a net, each member station is automatically assigned a timeslot: by
having each station answer a call request in a different timeslot, collisions are
avoided.
Group Addresses
The purpose of a group call is to rapidly and efficiently establish contact with
multiple non-prearranged (group) stations.
To make a group call, a calling ALE station uses a sequence of the actual individual
station addresses of the called stations.
Special Addressing Modes – Use of Wildcards
A “wildcard” is a special character,“?”, that a calling station can use to address
multiple stations with a single call address. The following rules apply:
• The total length of a calling address that includes wildcard(s) must be equal to
that of the called station addresses.
8
_________________________________________________________________________________________________
