Servo motor – MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC MR-E- A/AG User Manual
Page 234
14 - 27
14. SERVO MOTOR
(2) Electromagnetic brake power supply
Prepare the following power supply for use with the electromagnetic brake only.
Switch
Electromagnetic
brake
VAR
24VDC
B1
B2
VAR
: Surge absorber
The surge absorber must be installed across B1-B2. For the selection of the surge absorber, refer to
section 13.2.5.
The electromagnetic brake terminals (B1, B2) have no polarity.
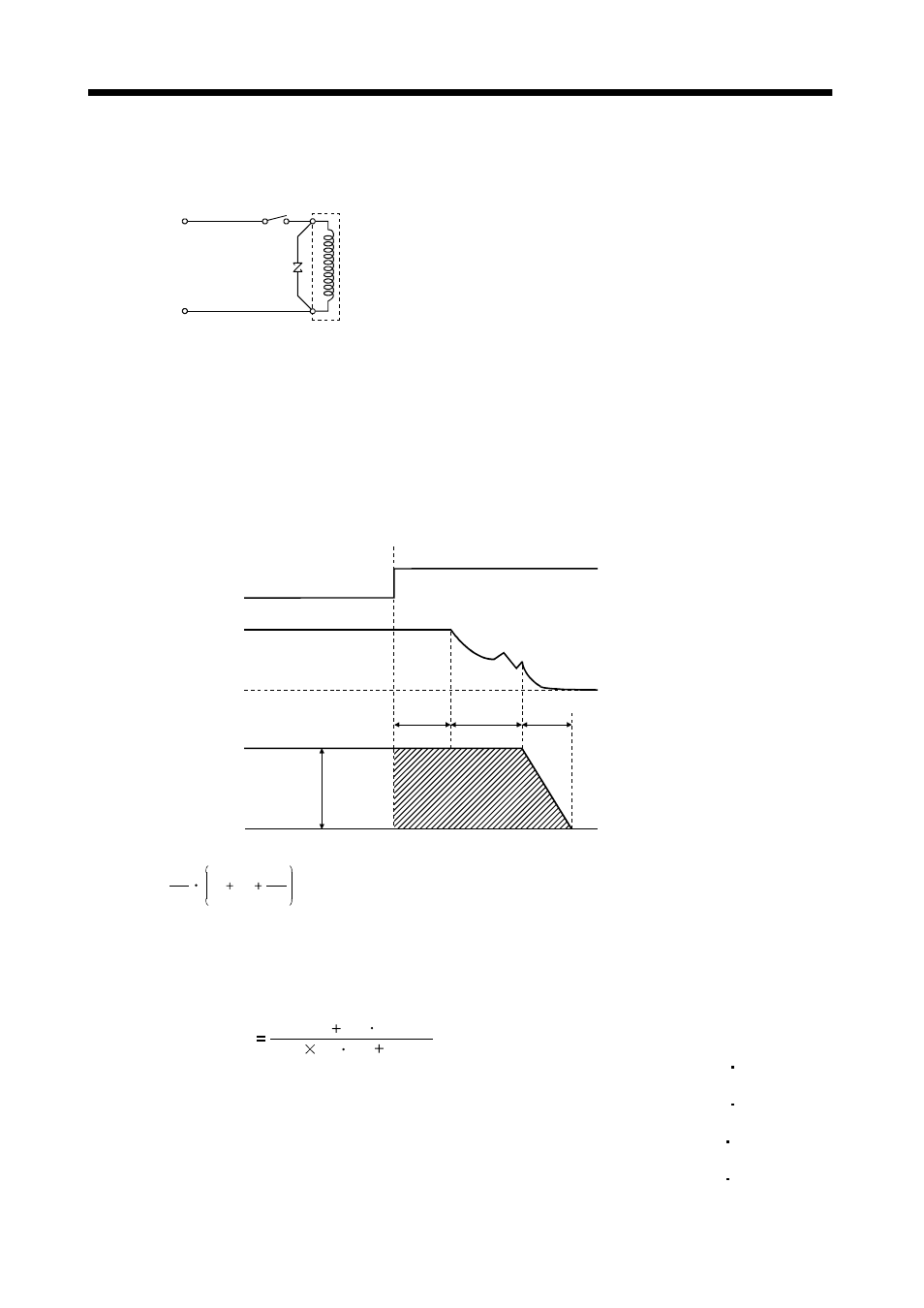
(3) Coasting distance
At an emergency stop, the servo motor will decelerate to a stop in the pattern shown in the following
diagram. Here, the maximum coasting distance (during fast feed), Lmax, will be the area shown with
the diagonal line in the figure and can be calculated approximately with Equation 6.1. The effect of the
load torque is greater near the stopping area. When the load torque is large, the servo motor will stop
faster than the value obtained in the equation.
Emergency stop
Brake current
Machine speed
V
0
t
1
t
2
t
3
L max =60
Vo
t1
t2
2
t3
................................................................................................... (6.1)
Where,
L max : Maximum coasting distance
[mm]
Vo:
Machine's fast feed speed
[mm/min]
t
1
:
Delay time of control section
[s]
t
2
:
Braking delay time of brake (Note)
[s]
t
3
:
Braking time
[s]
9.55 10
4
(T
L
0.8T
B
)
(J
L
J
L
) No
t
3
J
L
: Load inertia moment converted into equivalent
[kg cm
2
]
value on servo motor shaft (Note)
JM
: Servo motor inertia moment
[kg cm
2
]
No
: Servomotor speed during fast feed
[r/min]
T
L
: Load torque converted into equivalent
[N m]
value on servo motor shaft
T
B
: Brake static friction torque (Note)
[N m]
Note: t
2
and TB are the values noted in this section Characteristics. JL is the machine's inertia moment at the servo motor shaft.
