HP Vectra VL 5/xxx Series 5 User Manual
Page 75
75
4 Summary of the HP/Phoenix BIOS
Power Saving and Ergonometry
Advanced Power Management (APM)
The BIOS is APM 1.2 compliant, providing it with facilities for advanced
power management (APM). APM is incorporated in Windows for
Workgroups 3.11, Windows 95 and OS/2, but not Windows NT. A file called
power.exe
is needed for APM under DOS.
APM is a standard, defined by Intel and Microsoft, for a power-saving mode
that is applicable under a wide range of operating systems. It supports the
following modes: Fully-on, Standby, Suspend, Hibernation and Off. Of
these, APM 1.2 supports Fully-on, Standby, Suspend and Off, as
summarized in the following table.
The Suspend mode is managed at the operating system level only, from the
Windows 95 Start menu. There is no longer the inter-activity between the
Setup program and the operating system, and no longer a “sleep at” item on
the Setup program menus, to avoid the BIOS from shutting down the system
at the wrong moment.
RPO defines a variation from the standard Off state. In RPO mode, the main
CPU hardware is off while a RPO function is powered by a power supply
called VStandby. VStandby is active as soon as the computer is plugged in.
RPO hardware can produce a triggering signal which turns on the computer.
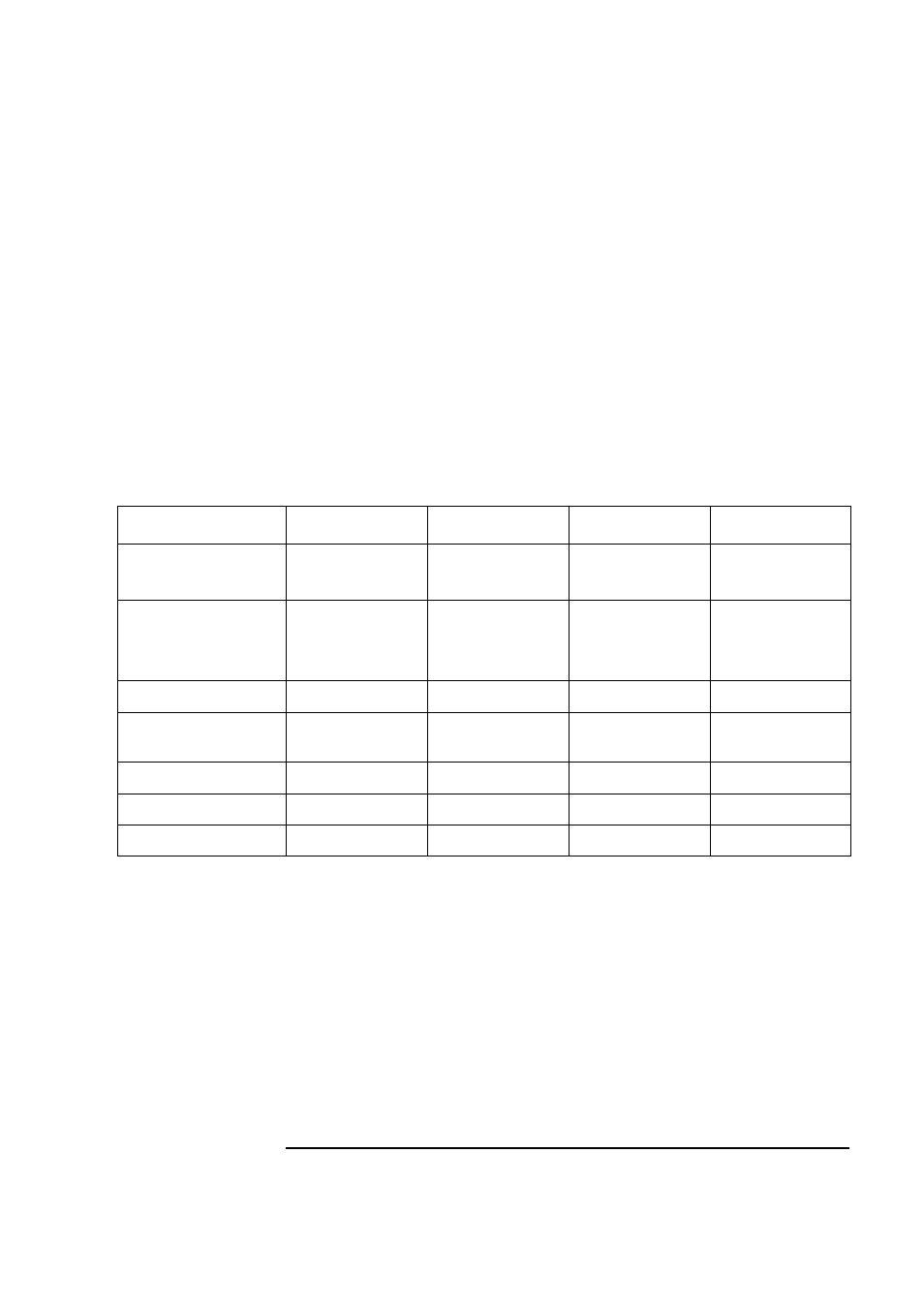
Fully-On
Standby
Suspend
Off
Brought about using:
Setup menu
Operating system
Operating system
Status panel button
Resume events:
Keyboard
Mouse
Keyboard
Fax / Modem
Network (RWU)
Space-bar
Network (RPO)
Resume delay:
Instantaneous
A few seconds
Boot delay
Processor
Normal speed
Clock throttled (divided
by 8)
Halted
Halted
Hard disk drive
Normal speed
Normal speed
Halted
Halted
Display
Normal operation
Blanked (<30 W)
Blanked (<5 W typ)
Blanked (<5 W typ)
Power consumption
24 W to 47 W
< 30 W
< 3 W
