ProSoft Technology RLX2-IFH9E User Manual
Page 51
RLX2-IFHxE ♦ Industrial Wireless
Diagnostics and Troubleshooting
Industrial Frequency Hopping Ethernet Radios
User Manual
ProSoft Technology, Inc.
Page 51 of 81
May 28, 2014
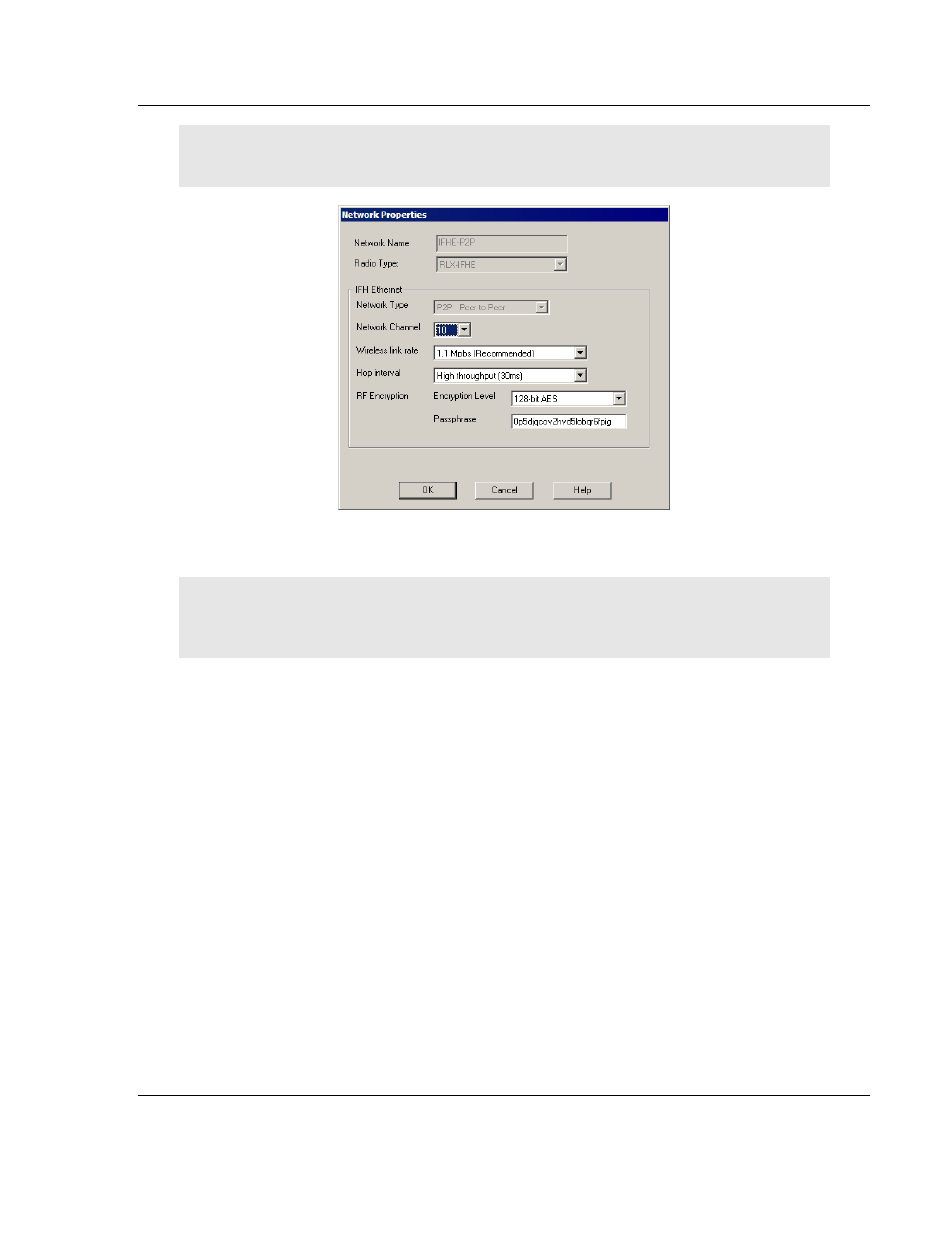
Important: The items in this dialog box depend on the type of radio you select. Click Help or refer
to the user manual of your radio for an explanation of each parameter.
3. Select an unused Network Channel from the drop-down list.
Note: Some fields are unavailable in this dialog box because you cannot change these parameters
here.
Note: See When to Re-Configure Radios (page 33) to ensure all radios are updated.
3.3.2 Monitoring Radio Channel Noise Level
All radio networks experience background noise, known as Electromagnetic
Interference (EMI), that consists of stray signals from other radios on the same
frequency, or random interference generated by non-radio devices that leak or
emanate EMI as a side effect of their operation. There are also natural sources of
EMI, including atmospheric disturbances and sunspots. The snow on an unused
or distant television channel, or static on a car radio when passing under high
voltage power lines, are two common examples of background noise.
Unwanted noise, or EMI, on a data network can cause data transmission errors,
or stop a radio network from functioning at all. Most modern devices, including
RLX2-IFHxE radios, are designed to prevent unwanted emanation of EMI from
the device. Radios are also typically designed to tolerate a certain amount of
interference from other devices; however when the amount of noise reaches a
certain threshold, typically within 10dB of a link's RSSI, the radio may be unable
to distinguish between wanted and unwanted signals.
ControlScape FH can help you diagnose transmission problems with a graphical
representation of radio channel noise. You can use this diagnostic information
during a site survey to check for RF signals already present in an area, or to
detect network issues caused by RF interference.
