Relationship of task mode and task rate – Avago Technologies 3ware 9650SE-12ML (Channel) User Manual
Page 12
Working with the Background Task Mode
8
9.5.2 Addendum to the 3ware SAS/SATA RAID Software User Guide
Low Latency
mode minimizes the latency (delay) in reading data from the
RAID unit by slowing down the background task process. In contrast,
Adaptive
mode allows the firmware to adjust the interaction of background
tasks with host I/Os to maximize the speed of both host I/O and background
tasks.
If latency is not an issue in the applications you use, then using the Adaptive
Background Task Mode will probably meet your needs and will result in
background tasks that complete faster.
Relationship of Task Mode and Task Rate
The Background Task Mode works in conjunction with the Background Task
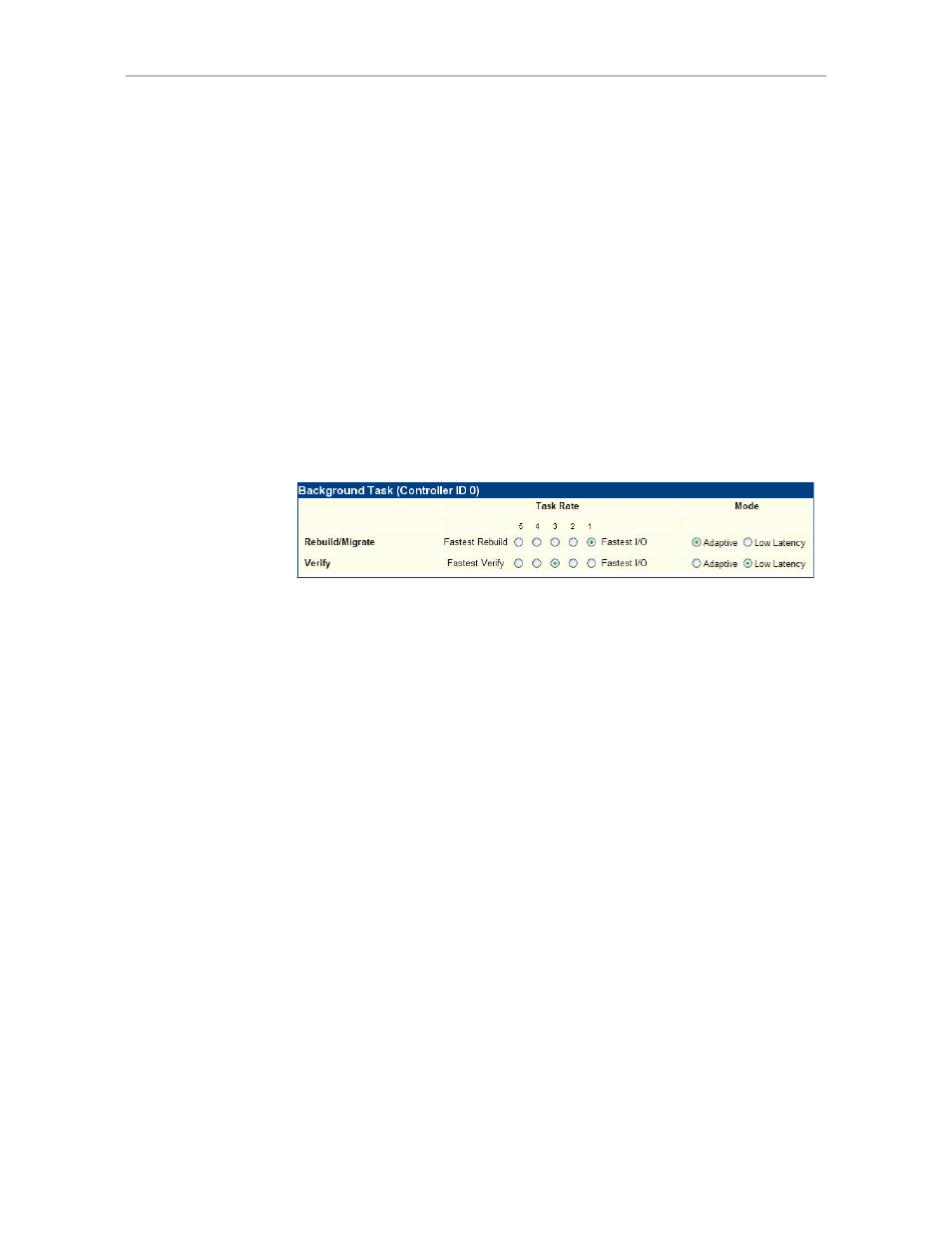
Rate. The settings are shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5. Background Task Settings on Controller Settings page
Background Task Rate
lets you set the relative performance of background
tasks in relation to host I/O activity on a scale of
1 to 5
, with 5 being the
fastest background task and slowest I/O, while 1 is the fastest I/O and the
slowest background task, as shown in Figure 5. Separate settings are available
for Rebuild/Migrate and for Verify. (Initialization occurs at the Rebuild/
Migrate rate.)
5 = fastest background task; slowest host I/O
4 = faster background task; slower host I/O
3 = balanced between background tasks and host I/O
2 = faster host I/O; slower background task
1 = fastest host I/O; slowest background task
If you set the
Background Task Mode
to
Low Latency
, it slows down the
background task process in the context of the current Task Rate setting, with a
graduated pacing of host I/O versus background task I/O, 2 through 5.
Important:
It is recommended that if you use the Background Task Mode of
Low Latency, you always set the Background Task Rate to at least
2
on the
scale of 1 to 5. When used in conjunction with a rate of
1
(fastest host I/O;
slowest background task), Low Latency Mode can create a situation in which
background tasks never complete, if there is continuous host I/O activity on
the unit.
