Circular path g12/g13/g15 around pole i, j, 5 p a th cont ours—p o lar coor dinat e s – HEIDENHAIN iTNC 530 (340 49x-04) ISO programming User Manual
Page 244
244
6 Programming: Programming Contours
6.5 P
a
th Cont
ours—P
o
lar Coor
dinat
e
s
Straight line at rapid traverse G10
Straight line with feed rate G11 F. . .
The tool moves in a straight line from its current position to the
straight-line end point. The starting point is the end point of the
preceding block.
Programming
Polar coordinates radius R: Enter distance from the
straight line end point to the pole I, J
Polar-coordinates angle H: Angular position of the
straight-line end point between –360° and +360°
The sign of H depends on the angle reference axis:
Angle from angle reference axis to R is counterclockwise: H >0
Angle from angle reference axis to R is clockwise: H <0
Example NC blocks
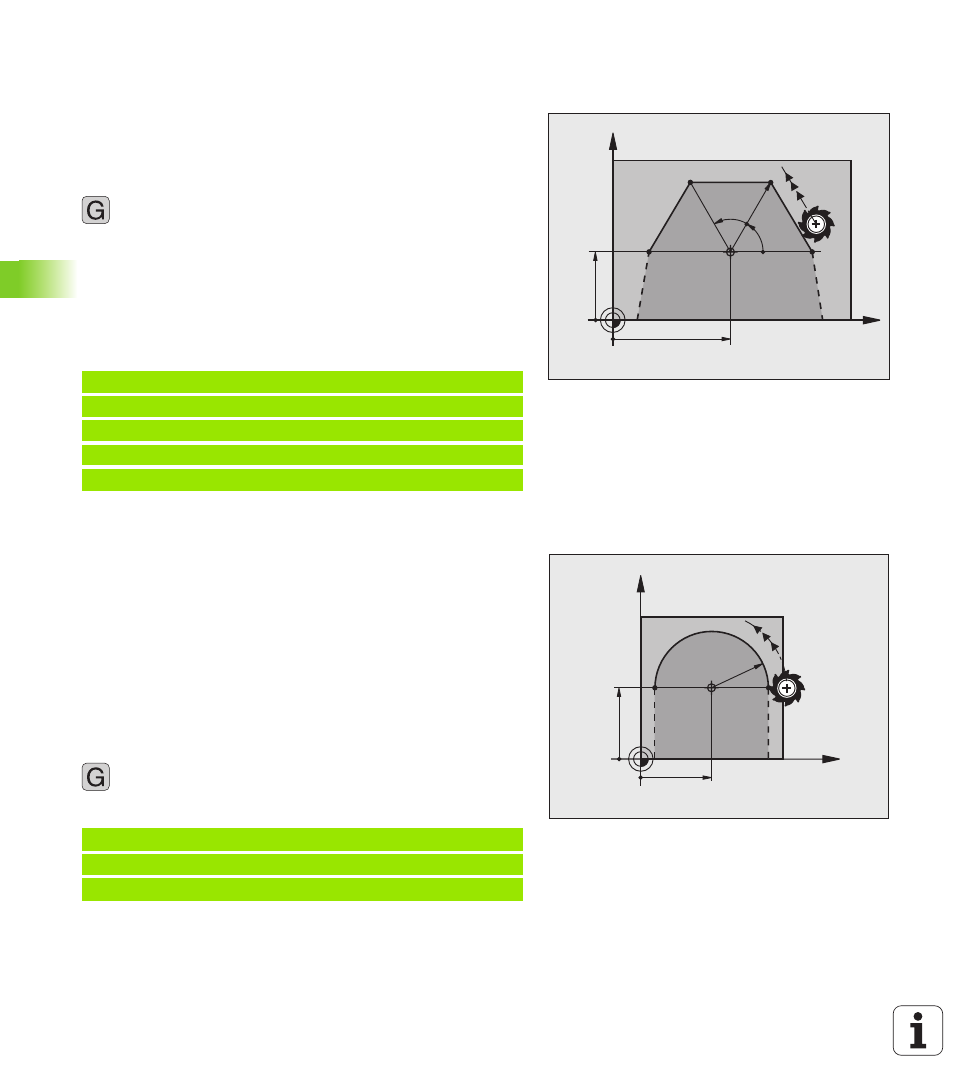
Circular path G12/G13/G15 around pole I, J
The polar coordinate radius R is also the radius of the arc. It is defined
by the distance from the starting point to the pole I, J. The last
programmed tool position before the G12, G13 or G15 block is the
starting point of the arc.
Direction
In clockwise direction: G12
In counterclockwise direction: G13
Without programmed direction: G15. The TNC traverses the circular
arc with the last programmed direction of rotation.
Programming
Polar-coordinates angle H: Angular position of the arc
end point between -99,999.9999° and +99,999.9999°
Example NC blocks
X
Y
45
25
60°
60°
30
CC
N120 I+45 J+45 *
N130 G11 G42 R+30 H+0 F300 M3 *
N140 H+60 *
N150 G91 H+60 *
N160 G90 H+180 *
11
X
Y
25=I
25=J
R20
N180 I+25 J+25 *
N190 G11 G42 R+20 H+0 F250 M3 *
N200 G13 H+180 *
13
