Basic concepts in igmp snooping, Igmp snooping related ports – H3C Technologies H3C S3100V2 Series Switches User Manual
Page 21
13
•
Reducing Layer 2 broadcast packets, saving network bandwidth
•
Enhancing the security of multicast traffic
•
Facilitating the implementation of per-host accounting
Basic concepts in IGMP snooping
IGMP snooping related ports
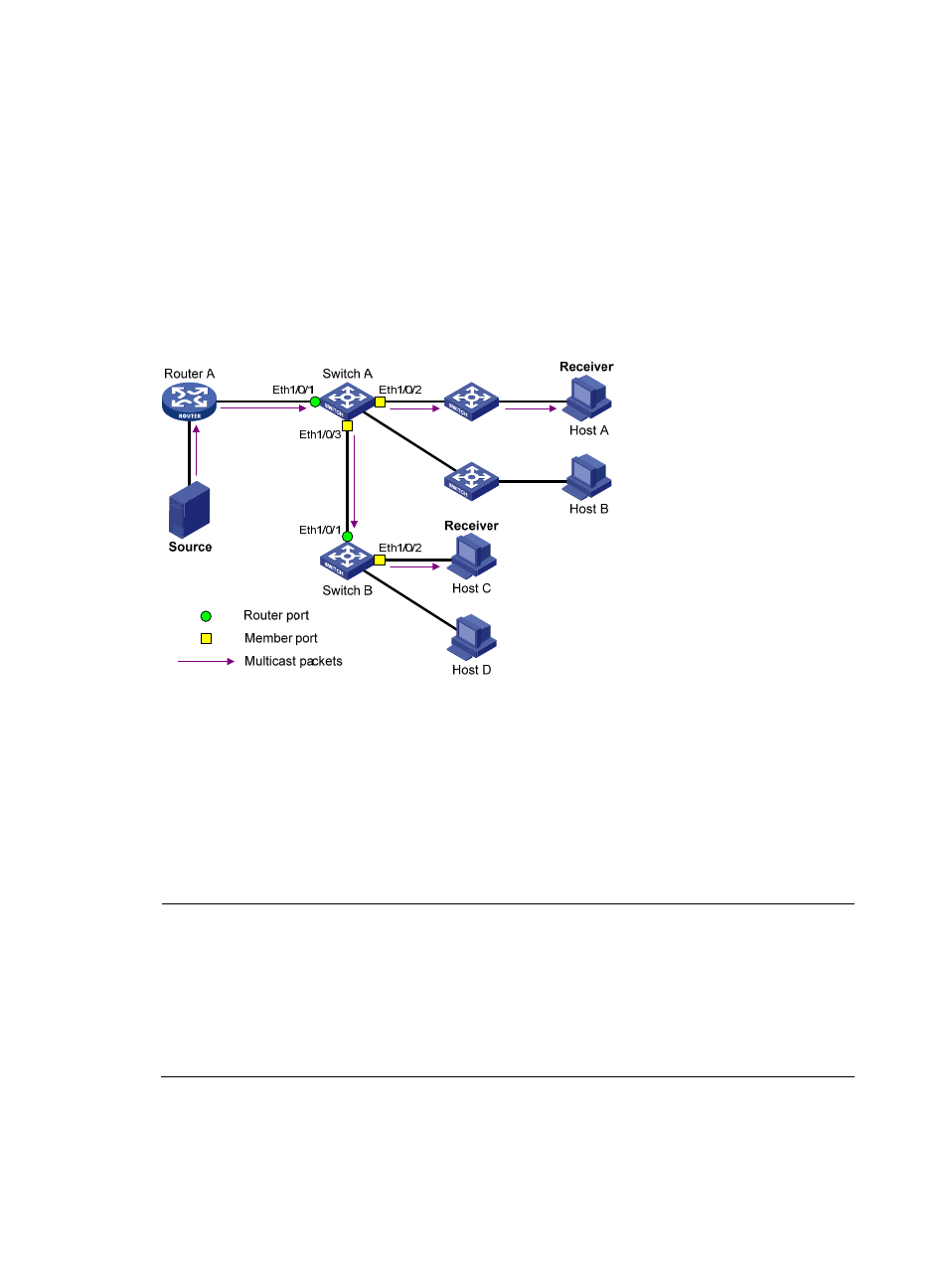
, Router A connects to the multicast source, IGMP snooping runs on Switch A and Switch B,
and Host A and Host C are receiver hosts—also called “multicast group members.”
Figure 11 IGMP snooping related ports
IGMP snooping involves the following ports:
•
Router port—A router port is a port on a Layer 2 switch that leads toward a Layer 3 multicast
device—DR or IGMP querier. In
, Ethernet 1/0/1 of Switch A and Ethernet 1/0/1 of
Switch B are router ports. Each switch registers all its local router ports in its router port list.
•
Member port—A member port is a port on a Layer 2 switch that leads toward multicast group
members. In
, Ethernet 1/0/2 and Ethernet 1/0/3 of Switch A and Ethernet 1/0/2 of
Switch B are member ports. Each switch registers all the member ports on the local device in its
IGMP snooping forwarding table.
NOTE:
•
Whenever mentioned in this document, a router port is a port on the switch that leads the switch to a
Layer 3 multicast device, rather than a port on a router.
•
Unless otherwise specified, router/member ports mentioned in this document include static and
dynamic ports.
•
An IGMP-snooping-enabled switch deems that all its ports on which IGMP general queries with the
source IP address other than 0.0.0.0 or PIM hello messages are received are dynamic router ports.
