Multicycle custom instructions, Multicycle custom instructions –5 – Altera Nios II Custom User Manual
Page 9
Chapter 1: Nios II Custom Instruction Overview
1–5
Custom Instruction Types
January 2011
Altera Corporation
Nios II Custom Instruction User Guide
describes the combination custom instruction ports.
The only required port for combinational custom instructions is the
result
port. The
dataa
and
datab
ports are optional. Include them only if the custom instruction
functionality requires input operands. If the custom instruction requires only a single
input port, use
dataa
.
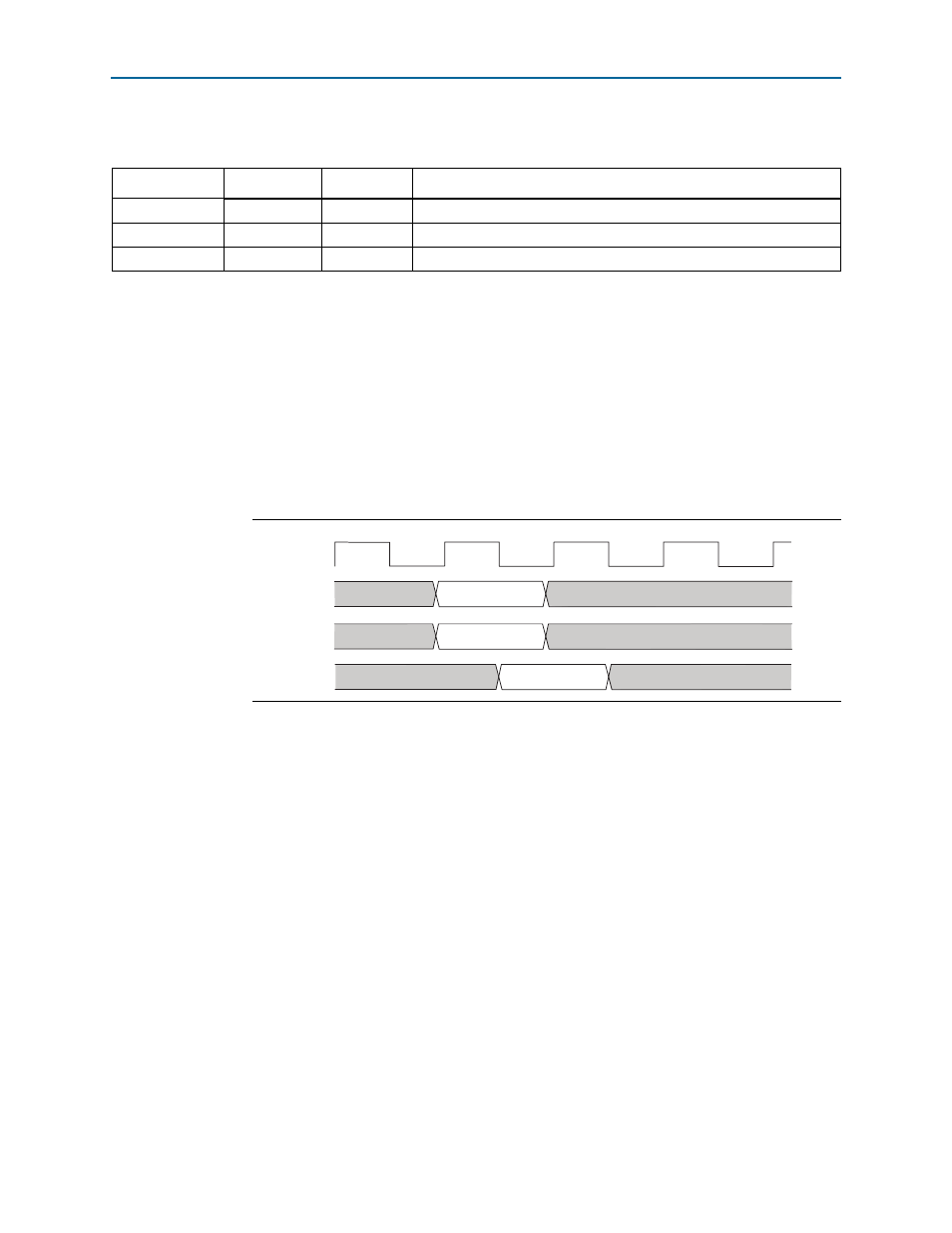
shows the combinational custom instruction hardware port timing
diagram.
, the processor presents the input data on the
dataa
and
datab
ports on
the rising edge of the processor clock. The processor reads the
result
port on the
rising edge of the following processor clock cycle.
The Nios II processor issues a combinational custom instruction speculatively; that is,
it optimizes execution by issuing the instruction before knowing whether it is
necessary, and ignores the result if it is not required. Therefore, a combinational
custom instruction must not have side effects. In particular, a combinational custom
instruction cannot have an external interface.
You can further optimize combinational custom instructions by implementing the
extended custom instruction. Refer to
“Extended Custom Instructions” on page 1–7
.
Multicycle Custom Instructions
Multicycle or sequential, custom instructions consist of a logic block that requires two
or more clock cycles to complete an operation. Additional control ports are required
for multicycle custom instructions, as shown in
.
Table 1–2. Combinational Custom Instruction Ports
Port Name
Direction
Required
Description
dataa[31:0]
Input
No
Input operand to custom instruction
datab[31:0]
Input
No
Input operand to custom instruction
result[31:0]
Output
Yes
Result of custom instruction
Figure 1–4. Combinational Custom Instruction Timing Diagram
clk
T0
T1
T3
T2
T4
dataa[ ]
datab[ ]
result[ ]
dataa[ ] valid
datab[ ] valid
result valid
