Internal register file custom instructions, Internal register file custom instructions –9, Internal register file custom – Altera Nios II Custom User Manual
Page 13
Chapter 1: Nios II Custom Instruction Overview
1–9
Custom Instruction Types
January 2011
Altera Corporation
Nios II Custom Instruction User Guide
Internal Register File Custom Instructions
The Nios II processor allows custom instruction logic to access its own internal
register file. This provides you the flexibility to specify if the custom instruction reads
its operands from the Nios II processor’s register file or from the custom instruction’s
own internal register file. In addition, a custom instruction can write its results to the
local register file rather than to the Nios II processor’s register file.
Custom instructions containing internal register files use
readra
,
readrb
, and
writerc
signals to determine if the custom instruction should use the internal register file or
the
dataa
,
datab
, and
result
signals. Ports
a
,
b
, and
c
specify the internal registers
from which to read or to which to write. For example, if
readra
is deasserted
(specifying a read operation from the internal register), the
a
signal value provides an
index to the internal register file. Ports
a
,
b
, and
c
are five bits each, allowing you to
address as many as 32 registers.
f
For further details of Nios II custom instruction implementation, refer to the
chapter of the Nios II Processor Reference Handbook.
lists the internal register file custom instruction-specific optional ports. Use
the optional ports only if the custom instruction functionality requires them.
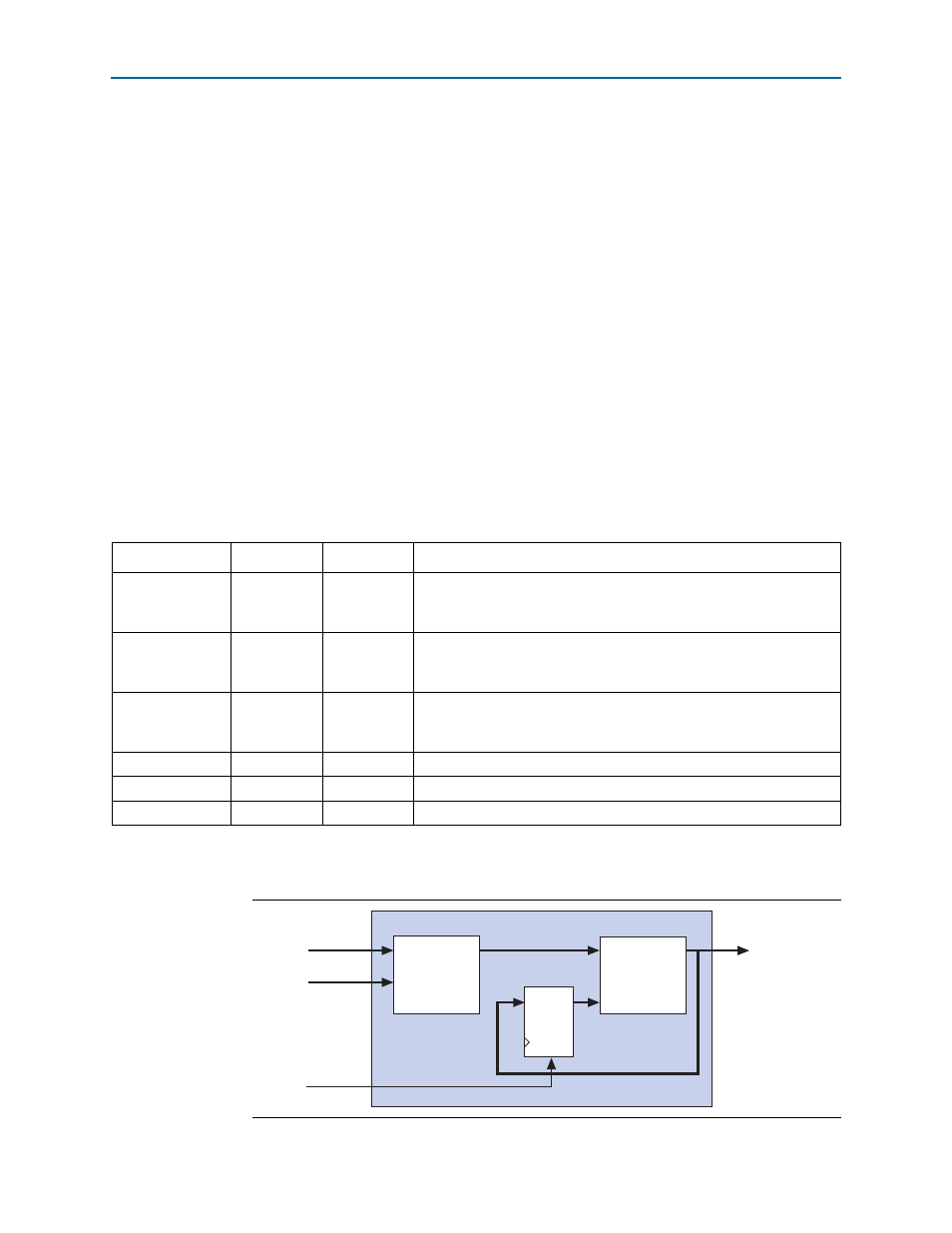
shows a simple multiply-accumulate custom logic block.
Table 1–4. Internal Register File Custom Instruction Ports
Port Name
Direction
Required
Description
readra
Input
No
If
readra
is high, the Nios II processor supplies
dataa
;
if
readra
is low, custom instruction logic reads the internal register file
indexed by
a
.
readrb
Input
No
If
readrb
is high, the Nios II processor supplies
datab
;
if
readrb
is low, custom instruction logic reads the internal register file
indexed by
b
.
writerc
Input
No
If
writerc
is high, the Nios II processor writes to the
result
port;
if
writerc
is low, custom instruction logic writes to the internal
register file indexed by
c
.
a[4:0]
Input
No
Custom instruction internal register file index
b[4:0]
Input
No
Custom instruction internal register file index
c[4:0]
Input
No
Custom instruction internal register file index
Figure 1–8. Multiply-accumulate Custom Logic Block
dataa[31..0]
datab[31..0]
writerc
result[31..0]
Multiplier
Adder
D
Q
CLR
