Combinational custom instructions, Combinational custom instructions –4 – Altera Nios II Custom User Manual
Page 8
1–4
Chapter 1: Nios II Custom Instruction Overview
Custom Instruction Types
Nios II Custom Instruction User Guide
January 2011
Altera Corporation
The following sections discuss the basic functionality and hardware interface of each
of the custom instruction types listed in
.
Combinational Custom Instructions
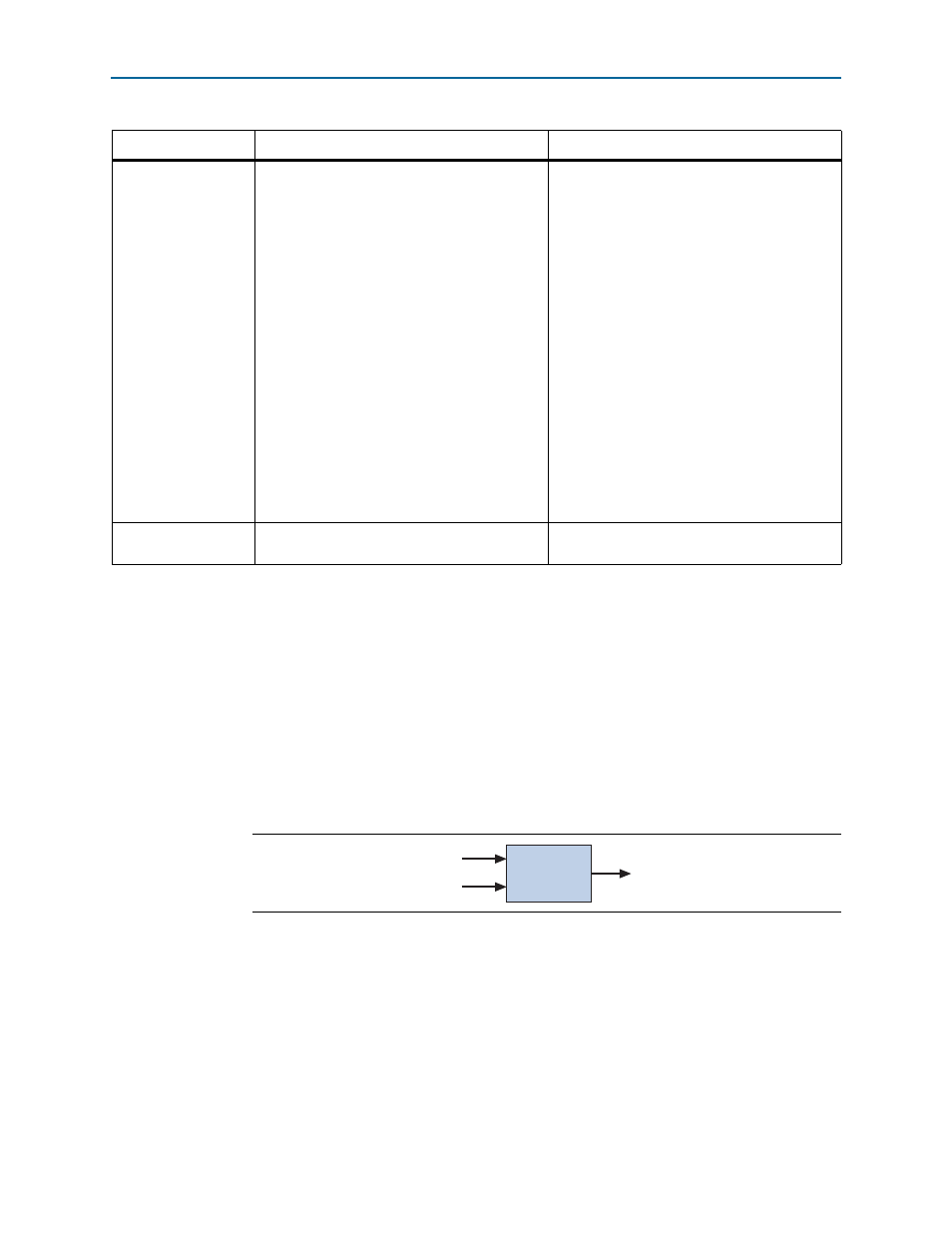
A combinational custom instruction is a logic block that completes its logic function in
a single clock cycle.
shows a block diagram of a combinational custom
instruction.
the
dataa
and
datab
ports are inputs to the logic block, which drives the
results on the
result
port. Because the logic function completes in a single clock cycle,
a combinational custom instruction does not require control ports.
Internal register file
Custom logic blocks that access internal register
files for input or output or both.
■
dataa[31:0]
■
datab[31:0]
■
result[31:0]
■
clk
■
clk_en
■
start
■
reset
■
done
■
n[7:0]
■
a[4:0]
■
readra
■
b[4:0]
■
readrb
■
c[4:0]
■
writerc
External interface
Custom logic blocks that interface to logic
outside of the Nios II processor’s datapath
Standard custom instruction ports, plus
user-defined interface to external logic.
Note to
(1) The
clk_en
input signal must be connected to the
clk_en
signals of all the registers in the custom instruction, in case the Nios II processor
needs to stall the custom instruction during execution.
Table 1–1. Custom Instruction Types, Applications, and Hardware Ports (Part 2 of 2)
Type
Application
Hardware Ports
Figure 1–3. Combinational Custom Instruction Block Diagram
dataa[31..0]
datab[31..0]
Combinational
result[31..0]
