Altera Device-Specific Power Delivery Network User Manual
Page 4
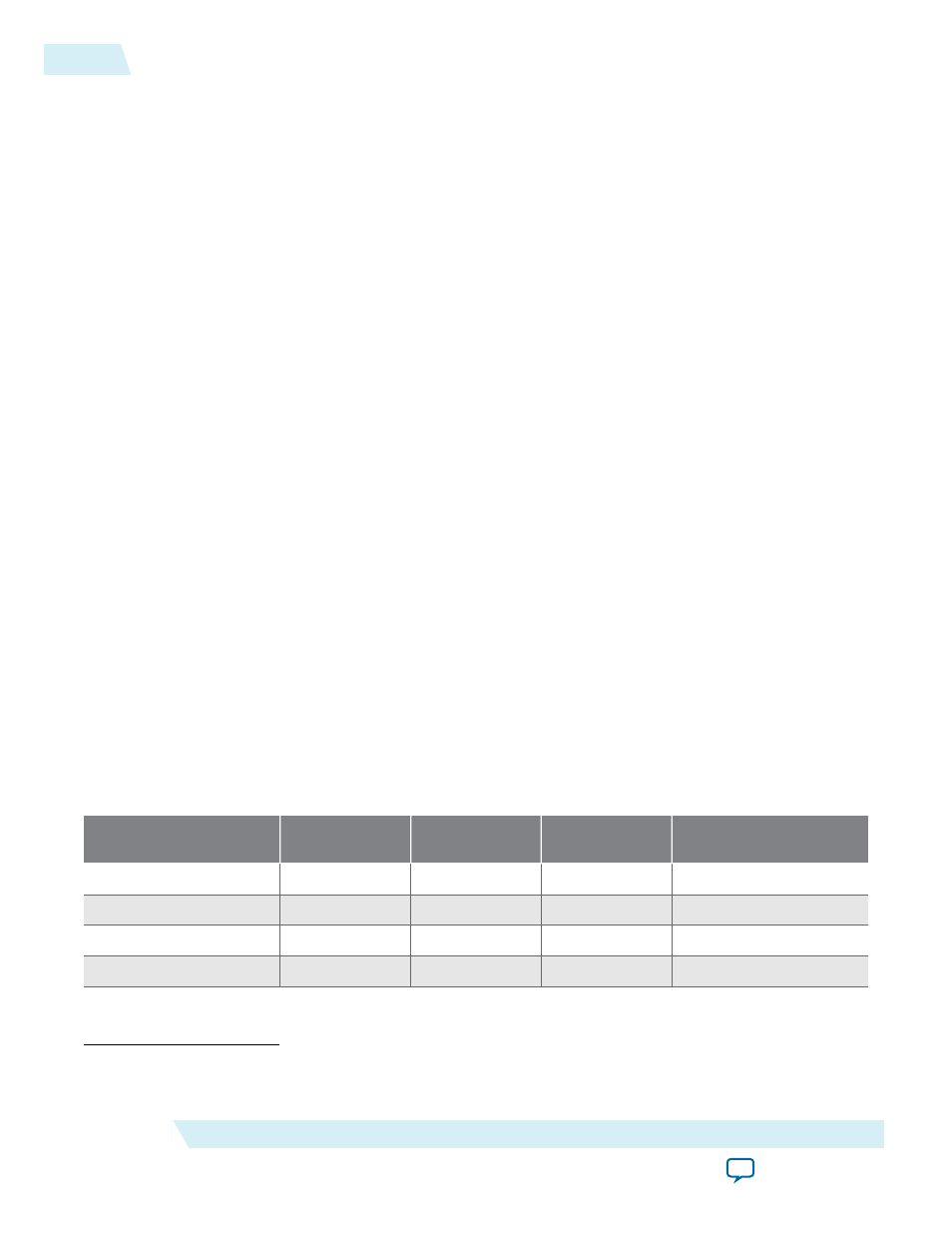
To accurately calculate the Z
TARGET
for any power rail, you must know the following information:
• The maximum dynamic current change requirements for all devices in the system that are powered by
the power rail under consideration. You can obtain this information from manufacturers of the
respective devices. You can calculate the maximum dynamic current change of a device using the
maximum total current and the dynamic current change percentage.
Note: The dynamic current change is intended to parameterize the high-frequency current draws
required to provide the energy for CMOS transistors changing state. In the case of the core rail,
the transients are generated by switching inside the FPGA core. Thus, a design which involves
extensive logical switching generates higher % transients (dynamic current change) than a more
static design. For information about recommended settings, refer to the table in the Introduc‐
tion tab of the PDN tool 2.0.
Note: You can obtain accurate estimations on the maximum total current for Altera devices using the
Altera PowerPlay Early Power Estimator (EPE) tool or the Quartus
®
II PowerPlay Power
Analyzer tools.
• The maximum allowable die noise tolerance on the power rail is given as a percentage of the supply
voltage.
Device switching activity leads to transient noise (high frequency spikes) seen on the power supply rails.
This noise can cause functionality issues if they are too high. The noise must be damped within a range
defined as a percentage of power supply voltage. The recommended values for the maximum allowable
AC die noise tolerance are listed in the Introduction tab of the PDN tool 2.0. Different rails have different
specifications because of their sensitivity to the transient voltage noise as well as how much current is used
by the power rail.
This AC die noise tolerance differs from the minimum and maximum voltage specifications in the device
datasheet in that the voltage specifications in the device datasheet are DC values. The (DC) ripple of the
voltage regulator module (VRM) is the change in the power supply voltage level. Altera devices are
designed to operate within a specific voltage range, which is considered the DC specification. The DC
specification is, in turn, translated to the requirement for the VRM ripple specification. This DC specifica‐
tion is not included in the die noise tolerance field in the PDN tool 2.0.
Refer to the Introduction tab of the PDN tool 2.0 for more information about Z
TARGET
.
Table 2: Settings for the Arria 10 Device Power Rails
This information is from the PDN tool 2.0 for an Arria 10 device.
Rail Name
(1)
Voltage (V)
Die Noise
Tolerance (%)
Dynamic Current
Change (%)
Description
VCC
0.85 - 0.9
5
50
Core
VCCIO
1.2 - 3.0
5
100
I/O Bank
VCCPT
1.8
5
50
I/O Pre-Drivers
VCCPGM
1.2/1.5/1.8
5
50
Programming Power
(1)
For more information about power rail functions, refer to the Pin Connection Guidelines for the selected
device family.
4
Z
TARGET
UG-01157
2015.03.06
Altera Corporation
Device-Specific Power Delivery Network (PDN) Tool 2.0 User Guide
