About your snap circuits, Xp parts, Base grid snap wires & jumper wires motor – Elenco XP&trade User Manual
Page 4: Battery holder
-3-
About Your Snap Circuits
®
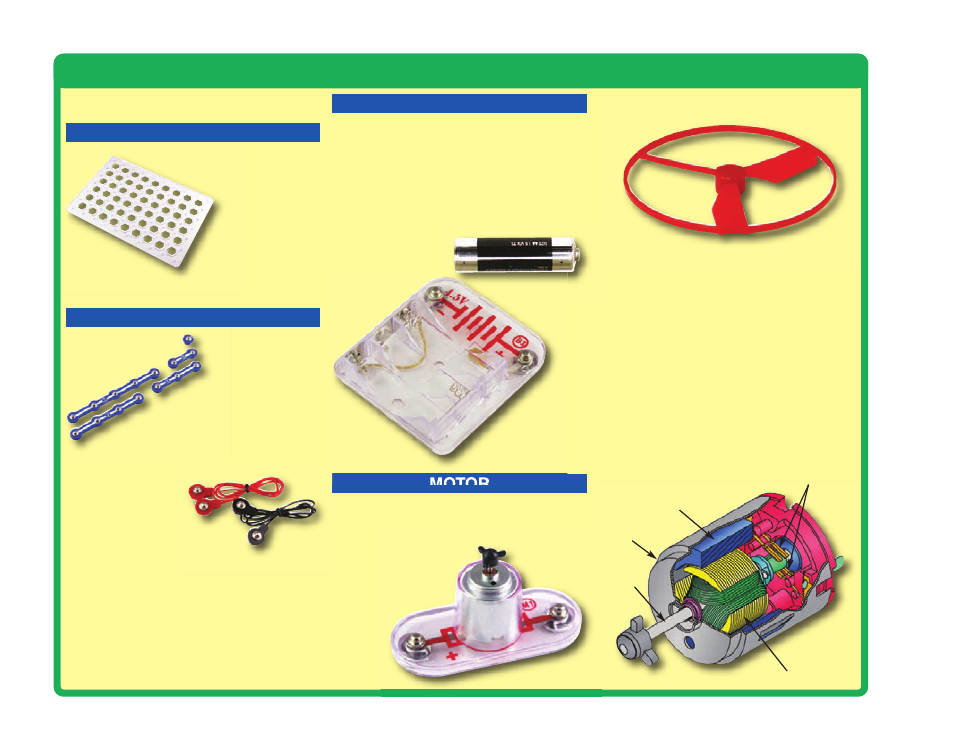
XP Parts
(Part designs are subject to change without
notice).
BASE GRID
SNAP WIRES & JUMPER WIRES
MOTOR
Magnet
Electromagnet
Shaft
Power Contacts
Shell
Motor (M1)
BATTERY HOLDER
Battery Holder (B3)
The batteries (B3) produce an electrical
voltage
using a chemical reaction. This “voltage” can be
thought of as electrical pressure, pushing
electricity through a circuit just like a pump
pushes water through pipes. This voltage is
much lower and much safer than that used in
your house wiring. Using more batteries
increases the “pressure”, therefore, more
electricity flows.
The blue snap wires
are wires used to
connect components.
They are used to
transport electricity and do
not affect circuit performance.
They come in different lengths to
allow orderly arrangement of connections
on the base grid.
The red and black
jumper wires make
flexible connections for
times when using the snap wires
would be difficult. They also are
used to make connections off the base grid.
Wires transport electricity just like pipes are used
to transport water. The colorful plastic coating
protects them and prevents electricity from
getting in or out.
The base grid is a platform for
mounting parts and wires.
It functions like the
printed circuit
boards used in
most electronic
products, or like how
the walls are used for
mounting the electrical
wiring in your home.
The motor (M1)
converts electricity into
mechanical motion. An electric current in the
motor will turn the shaft and the motor blades,
and the fan blade if it is on
the motor.
Fan
How does electricity turn the shaft in the motor?
The answer is magnetism. Electricity is closely
related to magnetism, and an electric current
flowing in a wire has a magnetic field similar to
that of a very, very tiny magnet. Inside the motor
is a coil of wire with many loops wrapped around
metal plates. This is called an electromagnet. If
a large electric current flows through the loops, it
will turn ordinary metal into a magnet. The motor
shell also has a magnet on it. When electricity
flows through the electromagnet, it repels from
the magnet on the motor shell and the shaft
spins. If the fan is on the motor shaft, then its
blades will create airflow.
