Echelon Neuron C User Manual
Page 86
66
Functions
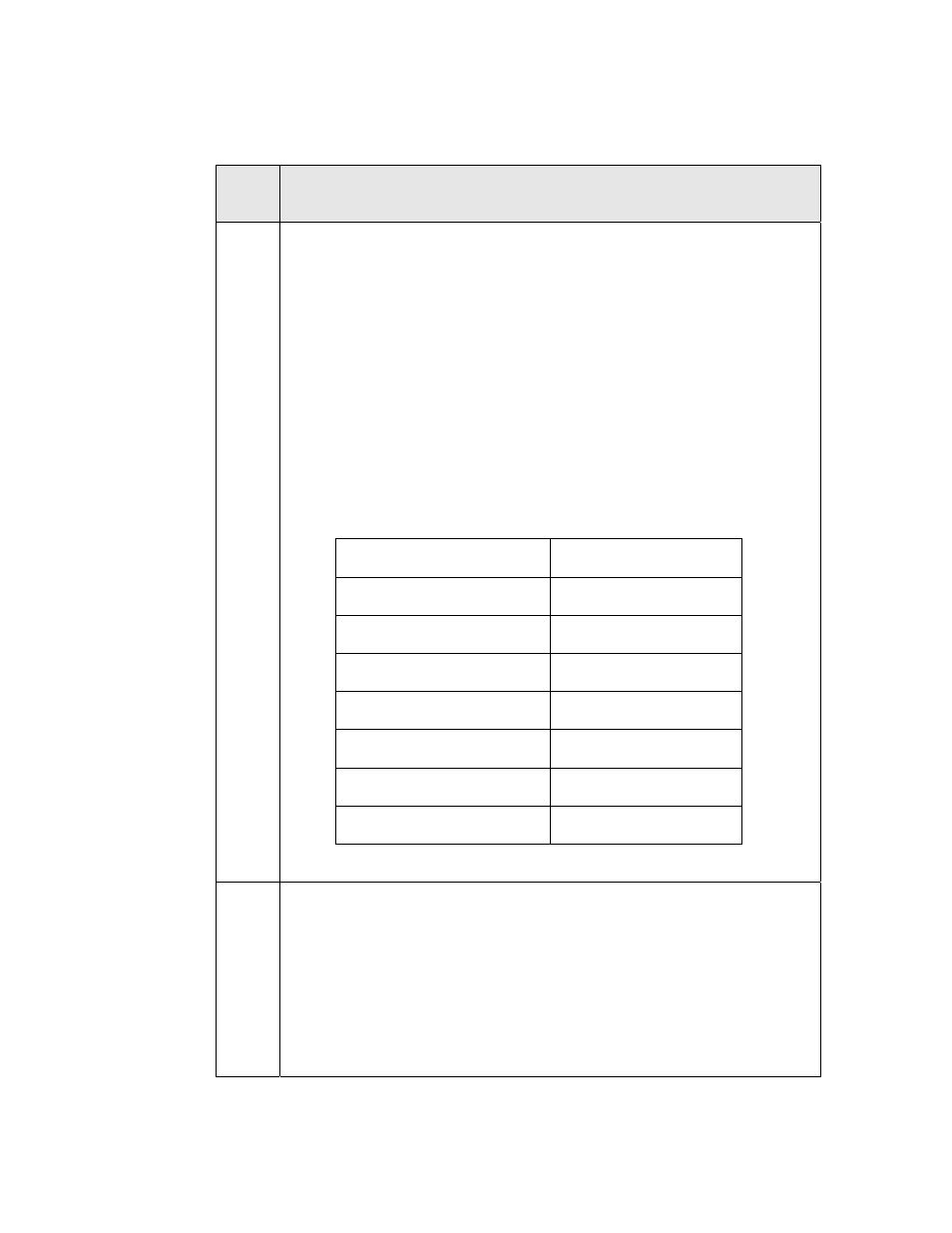
Table 26. Conversions of Floating-Point Numbers to ASCII Strings
Short
Name Function
to
ascii
void fl_to_ascii(const float_type *arg1, char *arg2,
int decimals, unsigned buf_size);
Converts a floating-point number *arg1 to an ASCII string followed by a
terminating NUL character. The decimals value is the required number
of decimal places after the point. The buf_size value is the length of the
output buffer pointed to by arg2, including the terminating null. If
possible, the number is converted using non-scientific notation, for
example [-]xxx.xxxxx. If the result would not fit in the buffer provided,
the number is converted using scientific notation, for example [-
]x.xxxxxxE[-]nn. This function uses repeated multiplication and
division, and can be time-consuming, depending on the input data. If
decimals
is 0, the buffer includes a trailing decimal point. If
decimals
is
-1, there is no trailing decimal point. The number is rounded to the
specified precision.
Example: Converting the number -12.34567, with a buf_size of 10.
decimals output
string
5 -12.34567
4 -12.3457
3 -12.346
2 -12.35
1 -12.3
0 -12.
-1 -12
to
ascii
fmt
void fl_to_ascii_fmt(const float_type *arg1, char *arg2,
int decimals, unsigned buf_size,
format_type
format);
Converts the *arg1 floating-point number to an ASCII string followed by
a terminating null. This function operates in the same way as
fl_to_ascii(), except that the caller specifies the output format. The
format parameter can be set to FMT_DEFAULT, FMT_FIXED or
FMT_SCIENTIFIC to specify the default conversion (same as
fl_to_ascii()), non-scientific notation or scientific notation respectively.
