Spanning tree algorithm, 4 related documentation -4 – Cabletron Systems SmartSTACK 100 User Manual
Page 20
1-10
Introduction
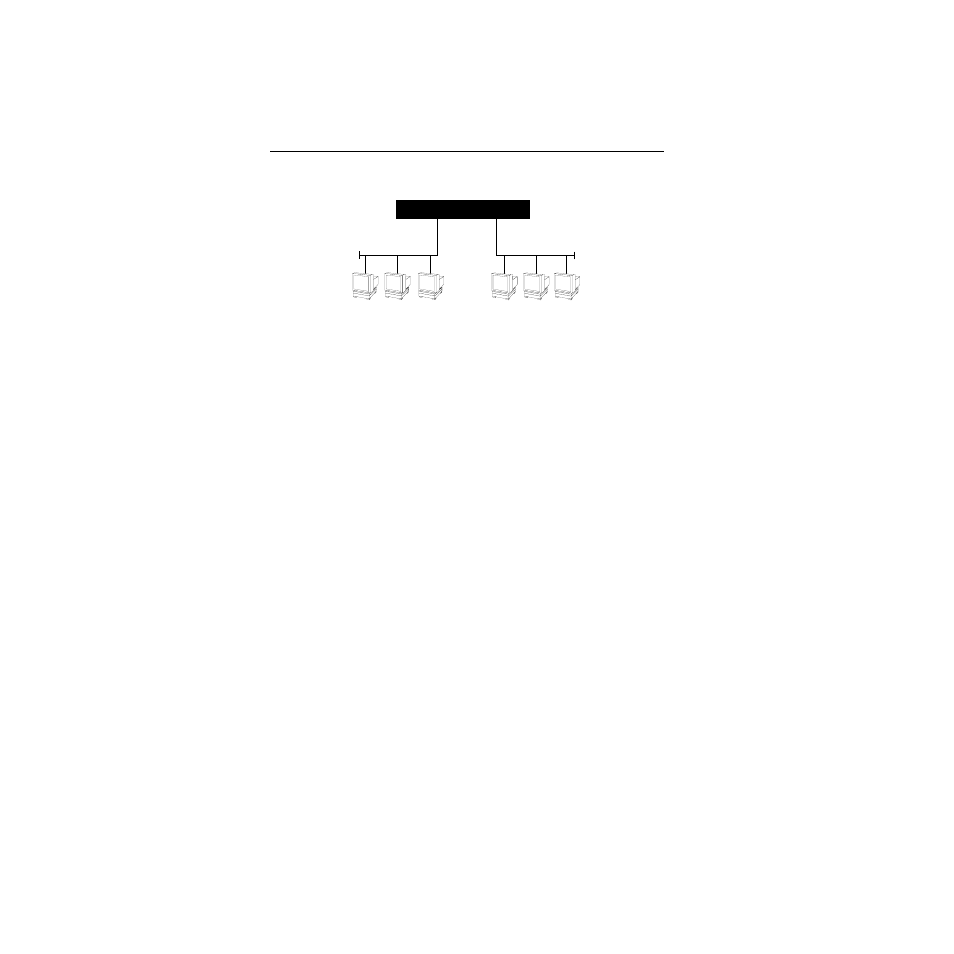
Figure 1-3. Typical Switching Application
By forwarding only packets addressed to devices on other network
segments, the SmartSTACK 100 ELS100-16TX reduces unnecessary
traffic and thereby enhances the overall performance of the
network.
Note:
If the packet address is not found in the Bridge Address Table, it
will be forwarded (flooded) to all network segments.
Spanning Tree Algorithm
The SmartSTACK 100 ELS100-16TX supports the IEEE 802.1d
Spanning Tree algorithm. The Spanning Tree algorithm converts
multiple LANs into a “spanning tree” of networks. It is used to
prevent bridging loops. This standard defines a logical (not
physical) network configuration consisting of one extended LAN
without active duplicate paths between spanning tree bridges.
The SmartSTACK 100 ELS100-16TX, along with other IEEE 802.1d
Spanning Tree compliant bridges in the network, dynamically
configure the network topology into a single Spanning Tree by
exchanging Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs). Typically, each
LAN segment is sent one BPDU every two seconds (this is the
default setting).
When there are multiple SmartSTACK 100 ELS100-16TXs
connecting LANs in a loop, the Spanning Tree algorithm
determines which SmartSTACK 100 ELS100-16TX should forward
LAN 1
LAN 2
A
B
C
FastNet 10
ELS100-16TX
