Quality of service – Interlogix MCR205-1T/1S User Manual User Manual
Page 43
IFS MCR205-1T/1S User Manual
37
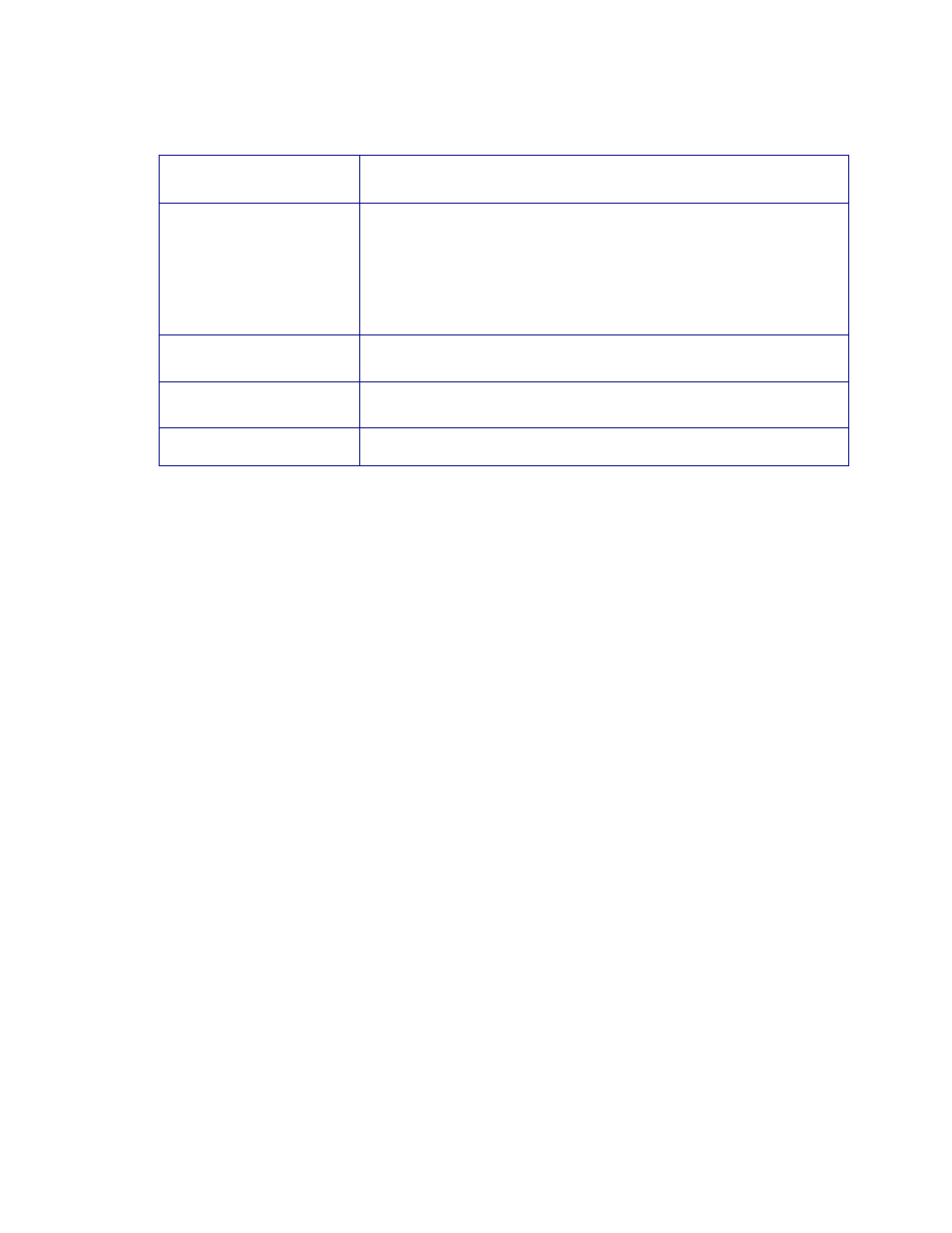
The Q-in-Q VLAN setting Web page includes the following configurable data:
Q-in-Q Enable
Disable or enable the Q-in-Q VLAN function. Default mode is
Disable.
Q-in-Q Direction
Provides two directions for Q-in-Q function, the available options
are:
UTP is customer port, Fiber is main port
Fiber is customer port, UTP is main port
Default mode is UTP is customer port, Fiber is main port.
Out Layer VLAN Tag
EtherType (HEX)
Defines the Out Layer VLAN Tag Ether Type and default mode is
0x8100.
Out Layer VLAN VID
(DEC)
Defines the Out Layer VLAN VID and default mode is 1.
Apply Button
Press this button to save current configuration of MCR205-1T/1S.
Quality of Service
Quality of Service (QoS) is an advanced traffic prioritization feature that allows
you to establish control over network traffic. QoS enables you to assign various
grades of network service to different types of traffic, such as multi-media, video,
protocol-specific, time critical, and file-backup traffic.
QoS reduces bandwidth limitations, delay, loss, and jitter. It also provides
increased reliability for delivery of data and allows you prioritization of certain
applications across the network. You can define exactly how you want the switch
to treat selected applications and types of traffic.
You can use QoS on your system to control a wide variety of network traffic by:
• classifying traffic based on packet attributes.
• Assigning priorities to traffic (for example, to set higher priorities to time-
critical or business-critical applications).
• Applying security policy through traffic filtering.
• Provide predictable throughput for multimedia applications such as video
conferencing or voice over IP by minimizing delay and jitter.
• Improve performance for specific types of traffic and preserve performance as
the amount of traffic grows.
• Reduce the need to constantly add bandwidth to the network.
• Manage network congestion.
