Digilent Basys Board Rev.E User Manual
Page 2
Digilent
Basys Reference Manual
www.digilentinc.com
Copyright Digilent, Inc.
Page 2/12
Doc: 502-107
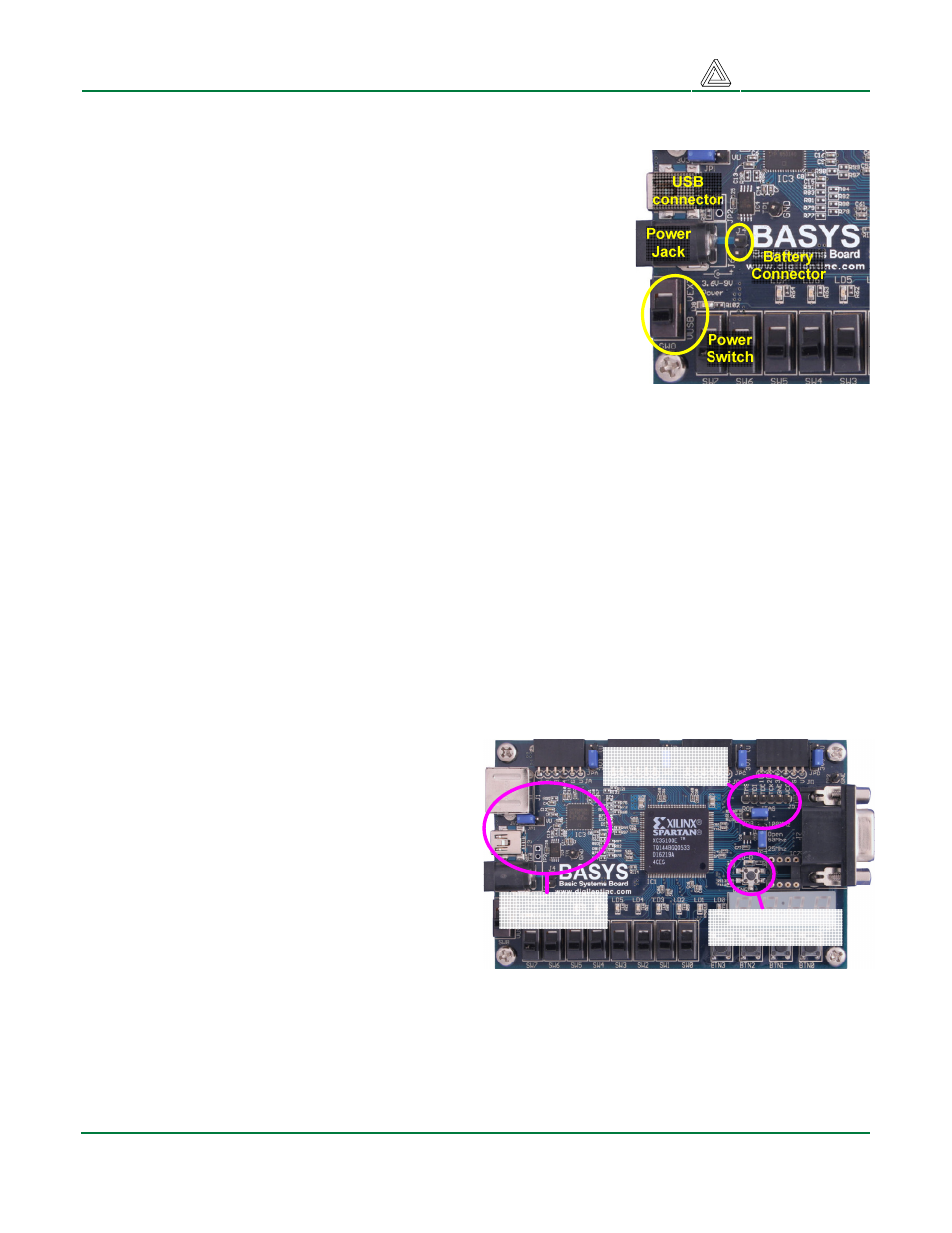
Board Power
The Basys board is typically powered from a USB cable, but a
power jack and battery connector are also provided so that external
supplies can be used. To use USB power, set the power source
switch (SW8) to USB and attach the USB cable. To use an external
wall-plug power supply, set SW8 to EXT and attach a 5VDC to
9VDC supply to the center-positive, 2.1/5.5mm power jack. To use
battery power, set SW8 to EXT and attach a 4V-9V battery pack to
the 2-pin, 100-mil spaced battery connector (four AA cells in series
make a good 6+/- volt supply). Voltages higher than 9V on either
power connector may cause permanent damage. SW8 can also be
used to turn off main power by setting it to the unused power input
(e.g., if USB power is used, setting SW8 to EXT will shut off board
power without unplugging the USB cable).
Input power is routed through the power switch (SW8) to the four 6-
pin expansion connectors and to a National Semiconductor LP8345 voltage regulator. The LP8345
produces the main 3.3V supply for the board, and it also drives secondary regulators to produce the
2.5V and 1.2V supply voltages required by the FPGA. Total board current is dependant on FPGA
configuration, clock frequency, and external connections. In test circuits with roughly 20K gates
routed, a 50MHz clock source, and all LEDs illuminated, about 100mA of current is drawn from the
1.2V supply, 50mA from the 2.5V supply, and 50mA from the 3.3V supply. Required current will
increase if larger circuits are configured in the FPGA, or if peripheral boards are attached.
The Basys board uses a four layer PCB, with the inner layers dedicated to VCC and GND planes. The
FPGA and the other ICs on the board have large complements of ceramic bypass capacitors placed
as close as possible to each VCC pin, resulting in a very clean, low-noise power supply.
Configuration
After power-on, the FPGA on the Basys board
must be configured before it can perform any
useful functions. During configuration, a “bit” file
is transferred into memory cells within the
FPGA to define the logical functions and circuit
interconnects. The free ISE/WebPack CAD
software from Xilinx can be used to create bit
files from VHDL, Verilog, or schematic-based
source files.
Digilent’s PC-based program called Adept can
be used to configure the FPGA with any
suitable bit file stored on the computer. Adept
uses the USB cable to transfer a selected bit
file from the PC to the FPGA (via the FPGA’s
JTAG programming port). Adept can also
program a bit file into an on-board non-volatile ROM called “Platform Flash”. Once programmed, the
Platform Flash can automatically transfer a stored bit file to the FPGA at a subsequent power-on or
reset event if the Mode Jumper is set to ROM. The FPGA will remain configured until it is reset by a
Figure 2. Basys power circuits
FPGA Reset button
and Done LED
USB Connector
and circuit
JTAG Header and
Mode jumper
Figure 3. Basys programming circuit locations
