Digilent 410-155P-KIT User Manual
Page 8
Basys2 Reference Manual
Digilent
www.digilentinc.com
VGA Port
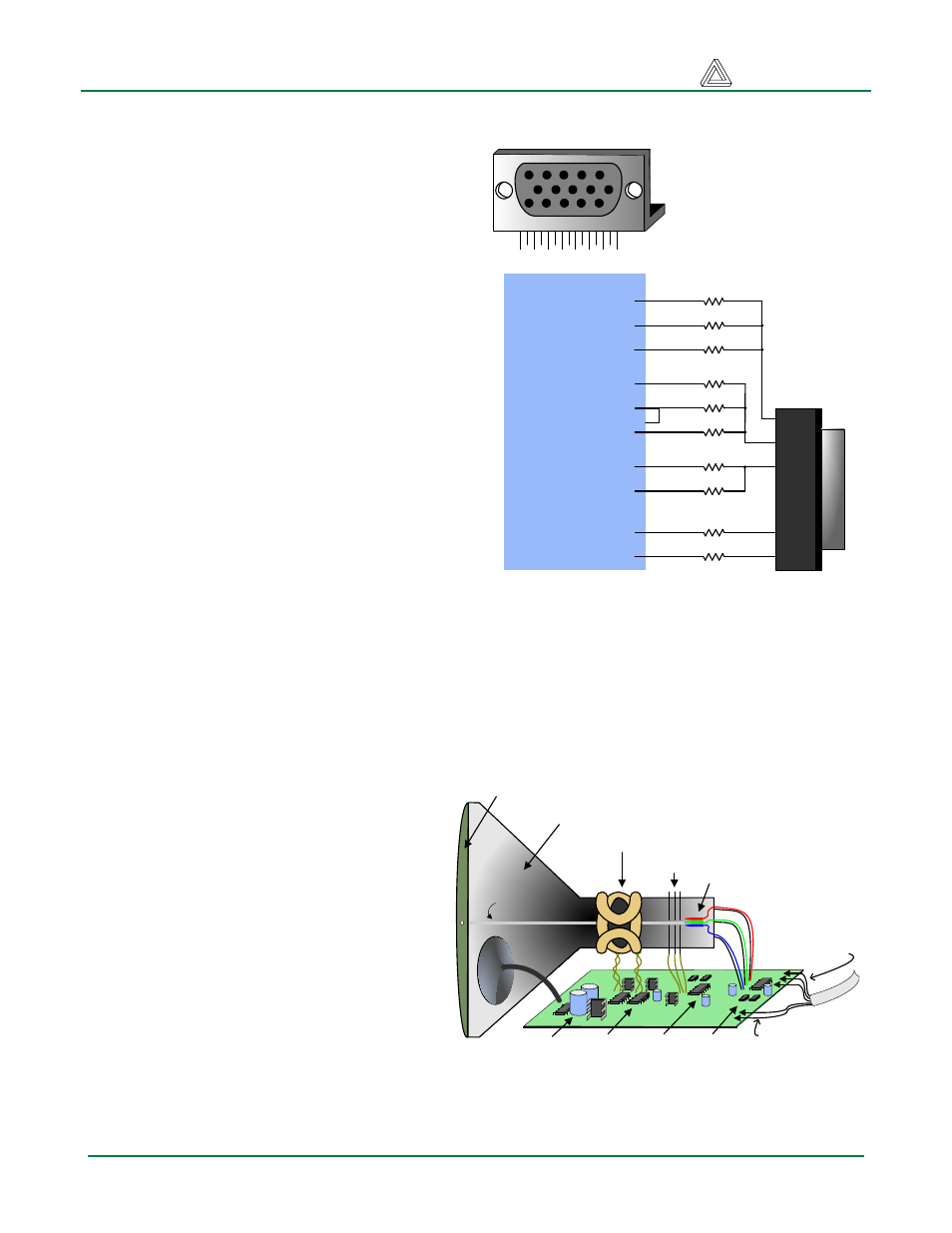
The Basys2 board uses 10 FPGA signals to
create a VGA port with 8-bit color and the two
standard sync signals (HS – Horizontal Sync,
and VS – Vertical Sync). The color signals use
resistor-divider circuits that work in conjunction
with the 75-ohm termination resistance of the
VGA display to create eight signal levels on the
red and green VGA signals, and four on blue
(the human eye is less sensitive to blue levels).
This circuit, shown in figure 13, produces video
color signals that proceed in equal increments
between 0V (fully off) and 0.7V (fully on). A
video controller circuit must be created in the
FPGA to drive the sync and color signals with
the correct timing in order to produce a working
display system.
VGA System Timing
VGA signal timings are specified, published,
copyrighted and sold by the VESA organization
(www.vesa.org). The following VGA system
timing information is provided as an example of
how a VGA monitor might be driven in 640 by
480 mode. For more precise information, or for
information on other VGA frequencies, refer to documentation available at the VESA website.
CRT-based VGA displays use amplitude-modulated moving electron beams (or cathode rays) to
display information on a phosphor-coated screen. LCD displays use an array of switches that can
impose a voltage across a small amount of liquid crystal, thereby changing light permittivity through
the crystal on a pixel-by-pixel basis. Although the following description is limited to CRT displays, LCD
displays have evolved to use the same signal
timings as CRT displays (so the “signals”
discussion below pertains to both CRTs and
LCDs). Color CRT displays use three electron
beams (one for red, one for blue, and one for
green) to energize the phosphor that coats
the inner side of the display end of a cathode
ray tube (see illustration). Electron beams
emanate from “electron guns” which are
finely-pointed heated cathodes placed in
close proximity to a positively charged
annular plate called a “grid”. The electrostatic
force imposed by the grid pulls rays of
energized electrons from the cathodes, and
those rays are fed by the current that flows
into the cathodes. These particle rays are
initially accelerated towards the grid, but they
soon fall under the influence of the much
larger electrostatic force that results from the
C14
Spartan 3E
FPGA
HD-DB15
D13
F13
J14
K13
2K
Ω
1K
Ω
510
Ω
200
Ω
200
Ω
15
10
5
11
6
1
Pin 1: Red
Pin 2: Grn
Pin 3: Blue
Pin 13: HS
Pin 14: VS
Pin 5: GND
Pin 6: Red GND
Pin 7: Grn GND
Pin 8: Blu GND
Pin 10: Sync GND
RED0
RED1
RED2
F14
G13
G14
2K
Ω
1K
Ω
510
Ω
GRN0
GRN1
GRN2
H13
J13
1K
Ω
510
Ω
BLUE0
BLUE1
RED
GRN
BLU
HS
VS
Figure 13. VGA pin definitions and Basys2 circuit
Anode (entire screen)
High voltage
supply (>20kV)
Deflection coils
Grid
Electron guns
(Red, Blue, Green)
gun
control
grid
control
deflection
control
R,G,B signals
(to guns)
Cathode ray tube
Cathode ray
VGA
cable
Figure 14. CRT deflection system
Doc: 502-138
page 8 of 12
