1 how to read the diagram, 2 airflow, Figure 4-2: operational limits for the am4220 – Kontron AM4220 User Manual
Page 43
28
www.kontron.com
4.2.2.1
How to read the diagram
The diagram contains one curve for 80% thermal load and one for 100%. Full thermal load is not expected to
be reached under real operating conditions. For a given flow rate there is a maximum airflow input
temperature (= ambient temperature) provided. Below this operating point, a safe operation is guaranteed.
Above this operating point, the chassis thermal management must become active and take the necessary
steps to protect the AMC from thermal destruction.
4.2.2.2
Airflow
At a given cross-sectional area and a required flow rate, an average, homogeneous airflow speed can be
calculated using the following formula:
Airflow = Volumetric flow rate / area.
The airflow is specified in m/s = meter-per-second or in LFM = linear-feet-per-minute, respectively.
Conversion: 1 LFM = 0.00508 m/s; 1 m/s = 196.85 LFM
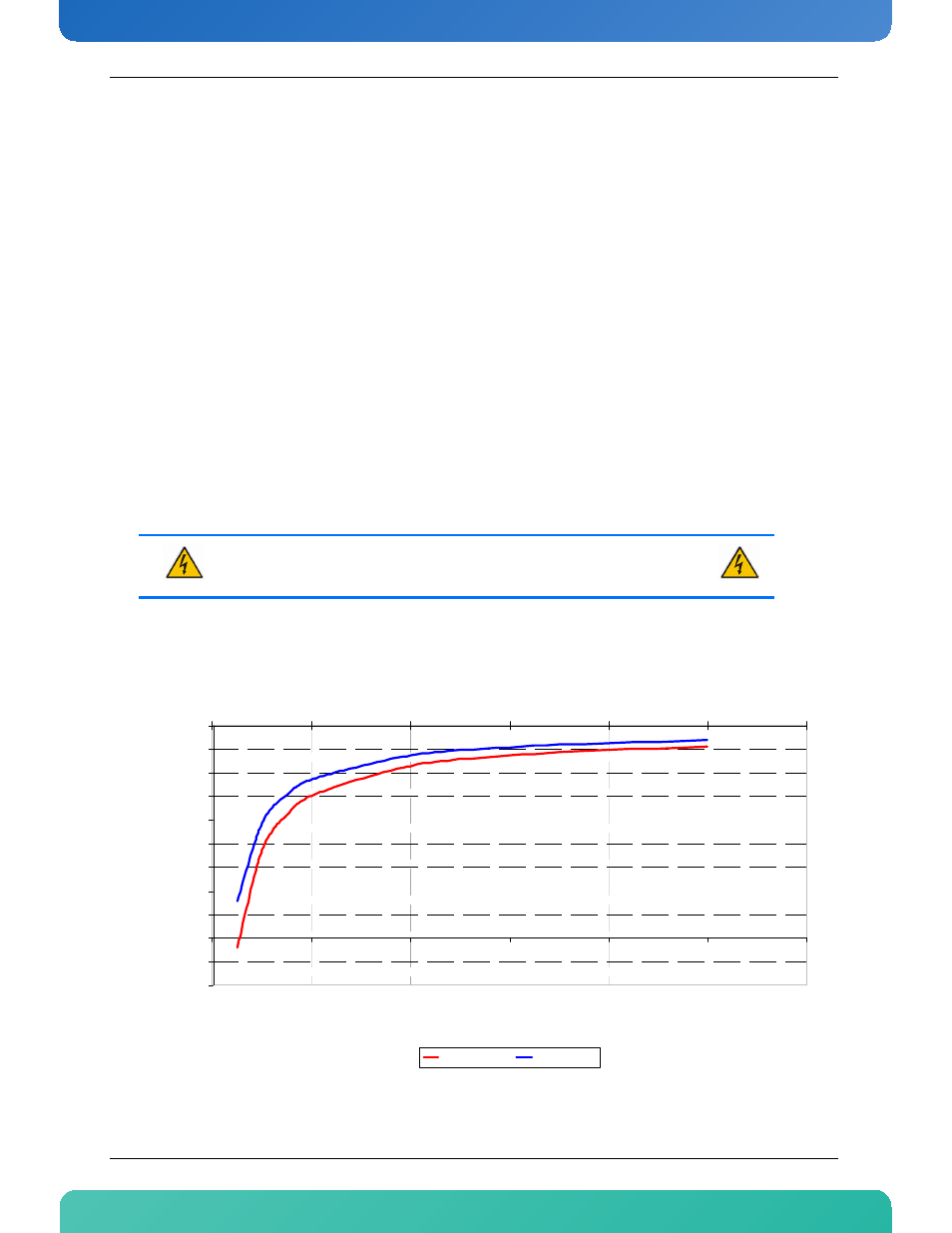
The following figure illustrates the operational limits of the AM4220 taking into consideration power
consumption vs. ambient air temperature vs. airflow rate. The values are based on simulation data taking
into account the actual power values of all components.
Figure 4-2:Operational Limits for the AM4220
WARNING
In all situations, the maximum specified case temperature of the components must
be kept below the maximum allowable temperature.
-20,00
-10,00
0,00
10,00
20,00
30,00
40,00
50,00
60,00
70,00
80,00
90,00
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
FLOW (LFM)
M
A
X
. I
N
L
E
T
TE
M
P
. (
°C
)
0,00
0,50
1,00
1,50
2,00
2,50
3,00
FLOW (m/s)
100% TDP
80% TDP
