6 terms and definitions – Baumer BA Scatec10 15 User Manual
Page 8
User manual Scatec-10 / -15
8 / 44
Baumer Electric AG
Version 2011-03
www.baumer.com
Frauenfeld, Switzerland
6 Terms and definitions
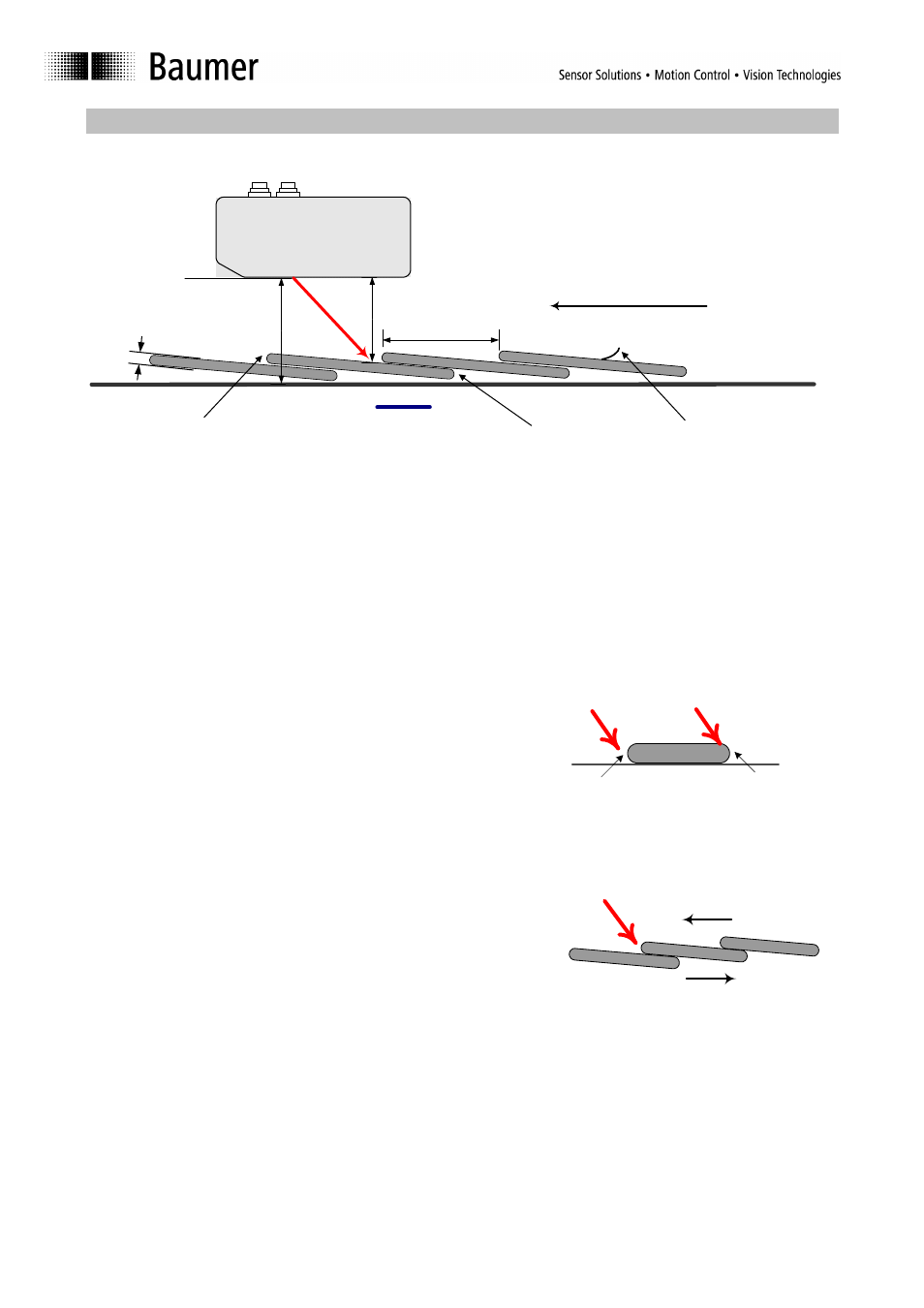
Mounting height
h
Distance between the lower edge of the sensor and the conveying plane.
Working distance
d
Distance between the lower edge of the sensor and the plane where the edge
lies on. Note that the working distance equals the mounting height only if the
edge lies directly on the conveying plane.
Overlap
a
Interval between two successive edges, measured along the conveying plane.
Edge thickness
k
Thickness of the copy at the point where the edge is to be detected.
Front edge
The edge of an object which faces the laser beam. In principle, edges facing
the laser beam can be detected
by the Scatec, independently of
the running direction.
Tail edge
The edge of an object which
faces away from the laser beam.
Edges facing away from the
laser beam cannot be detected
by the Scatec and do not initiate
output pulses no matter the
running direction is.
Running direction
For Scatec-10 / -15 both running
directions are allowed, with the
front edge leading (a) or trailing
(b). A front edge is detected
independently of the running
direction. However, for certain
false pulse suppression modes to
operate properly, the running
direction must be set correctly.
Interfering edge
Folds, fissures, creases, or other imperfections on a newspaper can form
edges which will be detected by the Scatec but should not be counted. Such
edges are termed “interfering edges” and cause so called “false pulses”.
Scatec-10 / -15 offers several possibilities to efficiently suppress these false
pulses.
Front edge:
detectable
Tail edge:
non-detectable
Laser beam
Running direction of copy:
(a) leading
(b) trailing
Laser beam
k
d
h
a
Beam blocker
Conveying plane
Front edge
Tail edge
Interfering edge
Scatec-1x
Running direction
