Correct voltage, Page – Tweco Dynamics Automation User Manual
Page 8
Kerf
– Kerf width is specified in the cut charts and can be calculated into cut programs.
The kerf width is related to tip orifice size and higher current cutting will produce a wider kerf.
Higher torch height will also result in a wider kerf.
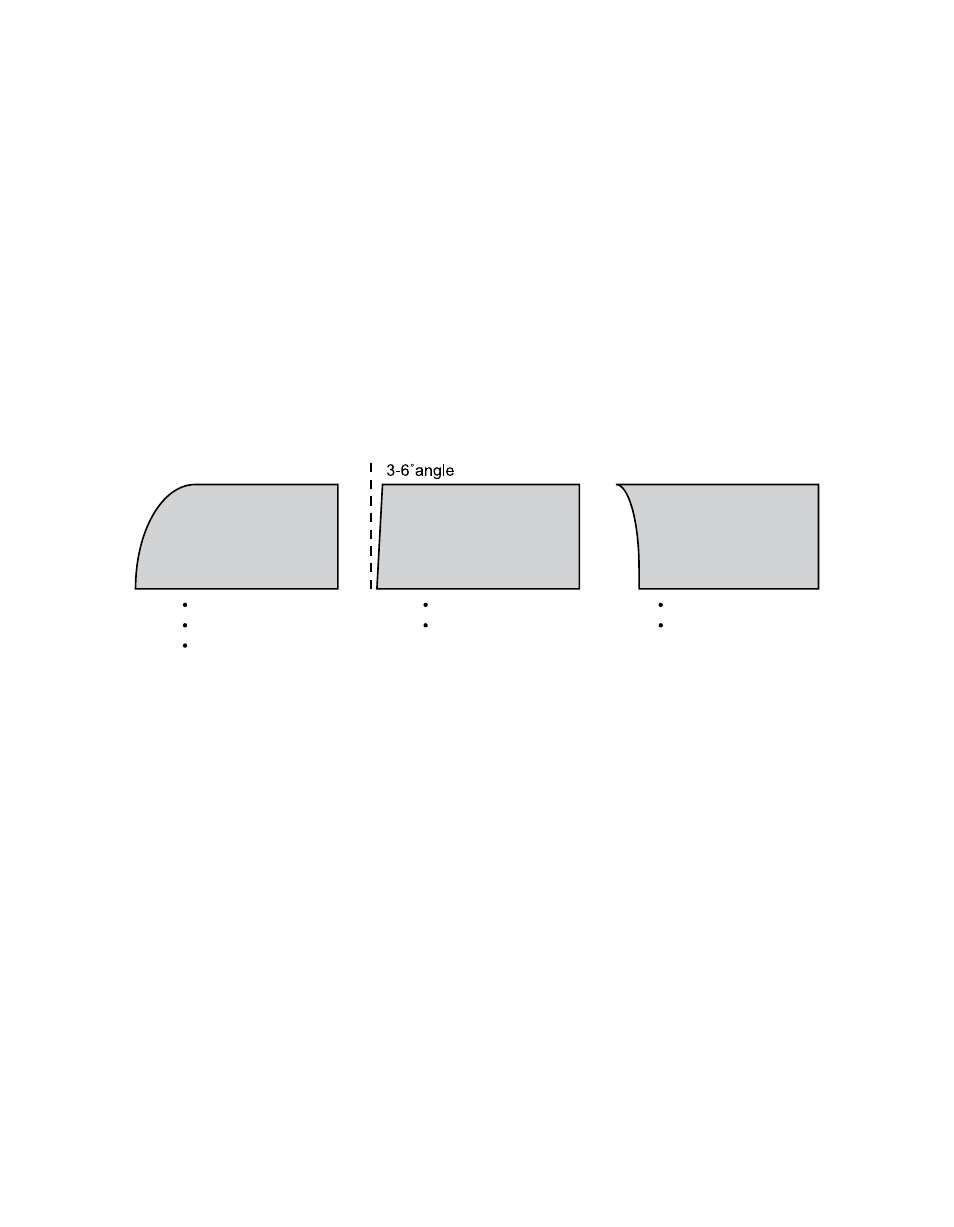
Bevel angle
– Precision cut processes produce bevel angle in the 0-3° range. Conventional
plasma cutting will produce larger bevel angles. Proper torch height control will produce the
smallest bevel angle, as well as improved kerf width and minimal top edge rounding. A slower
cut speed can be used when cutting circles and corners to reduce bevel.
Effect of Height Control Settings – General Purpose Cut
Nitride contamination
– Air plasma cutting will produce nitride contamination of the cut face
on carbon steel and stainless steel. Nitride contaminated surfaces will require grinding before
welding to eliminate weld porosity. The depth of the contamination will be close to the Heat
Affected Zone, between .005 and .010” in depth.
Nitride contamination can be eliminated by using a process other than air plasma;
oxygen plasma for carbon steel, H35 or nitrogen/WMS for non-ferrous materials.
Cut speed
– Cut charts specify a cut speed that will produce high quality cut performance.
Any plasma system can cut at faster or slower speeds, but cut performance will be affected.
Cut speed should be reduced for corners and tight curves to reduce bevel and corner rounding.
Optimum cut speeds produce a trailing arc which will be visible in the slight arc lines
visible in the cut face. Arc lines are useful for evaluating cut speed on mild steel, but less so
for aluminum and stainless steel. Arc lines that trail at less than 15° indicate that cut speed is
in the optimum range when air or oxygen plasma processes are used. Optimum cut quality in
precision cutting processes will result in arc lines that are near vertical. A slow cut speed may
show arc lines that angle forward and a fast cut speed will show arc lines at a sharper angle
relative to the top of the plate.
Correct Voltage
High Voltage
Low Voltage
Minimal Bevel
Normal Kerf
Negative Bevel
Wide Kerf
Positive Bevel
Wide Kerf
Top Dross
page
