Overview, 7 gain setting – Banner EZ-ARRAY USB Serial Adapter User Manual
Page 8
6
P/N 126701
Banner Engineering Corp.
•
Minneapolis, U.S.A.
www.bannerengineering.com • Tel: 763.544.3164
A-GAGE EZ-ARRAY
QuickStart Guide
Overview
Single-edge scan is used for single, solid objects that block the
first beam. The receiver always checks the beam closest to the
display first, and only if that beam is blocked does the binary
search continue. Therefore, single-edge scan will not work in
instances where the item to be measured does not block the first
beam. Single-edge scan is also ineffective if the object does not
present a continuous blocked pattern.
Single-edge scan will work only when the high-excess-gain
setting is enabled. When single-edge scan is selected, the
sensor object detection size will be 10 mm and edge resolution
will be 2.5 mm.
Double-Edge Scan is used to detect two edges of a single
object, for example, to determine box width measurements.
Double-edge scan requires the selection of a step size: 1, 2,
4, 8, 16 or 32 beams. The sensor uses the steps to “skip” over
beams.
Double-edge scan works as follows:
1. The sensor activates beam 1 (the beam closest to the sensor
display end).
2. The sensor activates the next beam, determined by the step
size. (For example, if the step size is 2, beam 3 is next; if the
step size is 8, beam 9 is next.)
3. As long as the activated beam is unblocked (or “made”), the
sensor will continue the stepping routine until a blocked beam
is found.
4. When a blocked beam is found, a binary search is conducted
to find the object’s “bottom edge.”
5. When the bottom edge is found, the sensor begins “stepping”
again through the array until the sensor finds the next
unblocked beam.
6. A binary search is again performed to find the second edge.
Similar to single-edge scan, double-edge scan has some
restrictions: the object should provide a solid obstruction; the
size of the object will determine the maximum step size (Figure
1-5). Double-edge scan can be used to detect up to three
objects. Like single-edge scan, double-edge scan will work only
when the high-excess-gain setting is selected. When double-
edge scan is selected, the sensor object detection size will vary
depending on the step size, but edge resolution will be 2.5 mm.
Sensor response time is a function of sensor length and
scanning method. Maximum scan times are shown in Figure 1-7.
1.7 Gain Setting
The EZ-ARRAY provides two gain options: high excess gain
and low contrast. The gain option can be selected using the
push button on the receiver interface, the receiver remote teach
wire, or the software GUI, and is available for straight scan
applications only.
High (maximized) excess gain is best suited for detecting
opaque objects and to provide reliable sensing in dirtier
environments where objects to be detected are 10 mm or larger.
The low-contrast setting is excellent for sensing semi-transparent
materials and for detecting objects as small as 5 mm.
When using the GUI, low-contrast sensing allows a fine-tune
sensitivity setting of 15% to 50%. When using the receiver
interface, low-contrast sensitivity is always 30%. The push button
may be disabled, using the GUI.
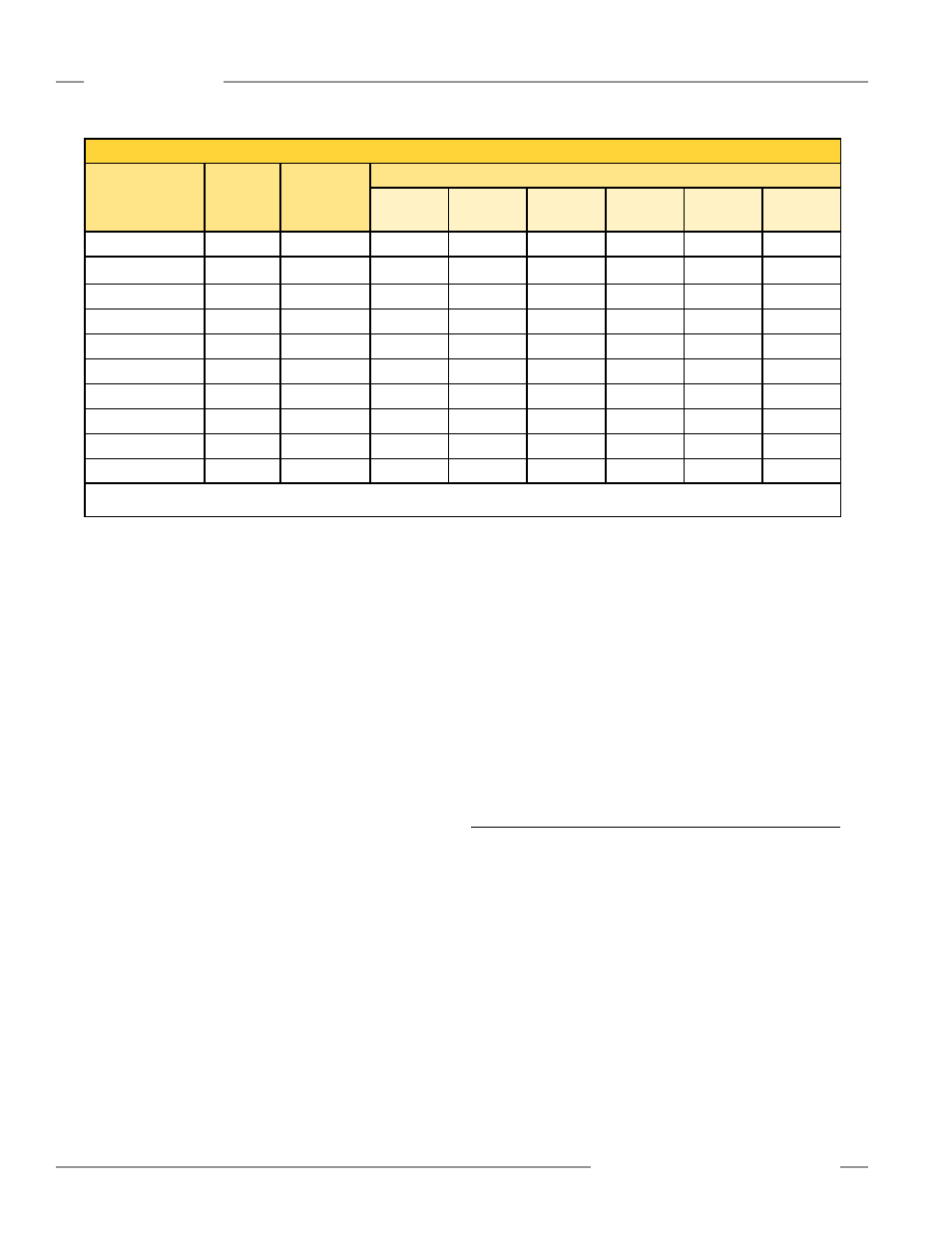
Maximum Scan Times (in milliseconds)
Array Length
Straight
Scan
Single-Edge
Scan
Double-Edge Scan
Step
1 Beam
Step
2 Beams
Step
4 Beams
Step
8 Beams
Step
16 Beams
Step
32 Beams
150 mm (5.9")
2.8
1.5
3.4
2.8
2.5
2.4
1.9
N/A
300 mm (11.8")
5.0
1.5
5.9
4.1
3.2
2.8
2.3
2.1
450 mm (17.7")
7.1
1.6
8.5
5.5
4.2
4.0
3.2
2.5
600 mm (23.6")
9.3
1.6
11.0
6.8
4.9
4.2
4.0
2.8
750 mm (29.5")
11.4
1.7
13.5
8.1
5.7
4.6
4.5
4.5
900 mm (35.4")
13.6
1.7
16.0
9.5
6.1
4.7
4.6
4.6
1050 mm (41.3")
15.7
1.8
18.6
10.8
6.8
5.2
4.8
4.8
1200 mm (47.2")
17.9
1.8
21.1
12.2
7.4
5.5
4.9
4.9
1500 mm (59.1")
22.2
1.9
26.1
14.8
9.0
6.4
5.3
4.9
1800 mm (70.9")
26.5
2.0
31.2
17.5
10.5
7.3
6.0
5.6
NOTE: Scan times are exclusive of serial communication transmission times.
Figure 1-7. Maximum scan times for straight, single-edge and double-edge scanning
