Series operation, Parallel use to increase output power, Parallel use for redundancy – Rockwell Automation 1606-XLP50E Power Supply Reference Manual User Manual
Page 18
All parameters are specified at 24V, 2.1A, 230Vac input, 25ªC ambient and after a 5 minutes run-in time unless noted otherwise.
18
Rockwell Automation Publication 1606-RM034A-EN-P — March 2014
Bulletin 1606 Switched Mode Power Supplies
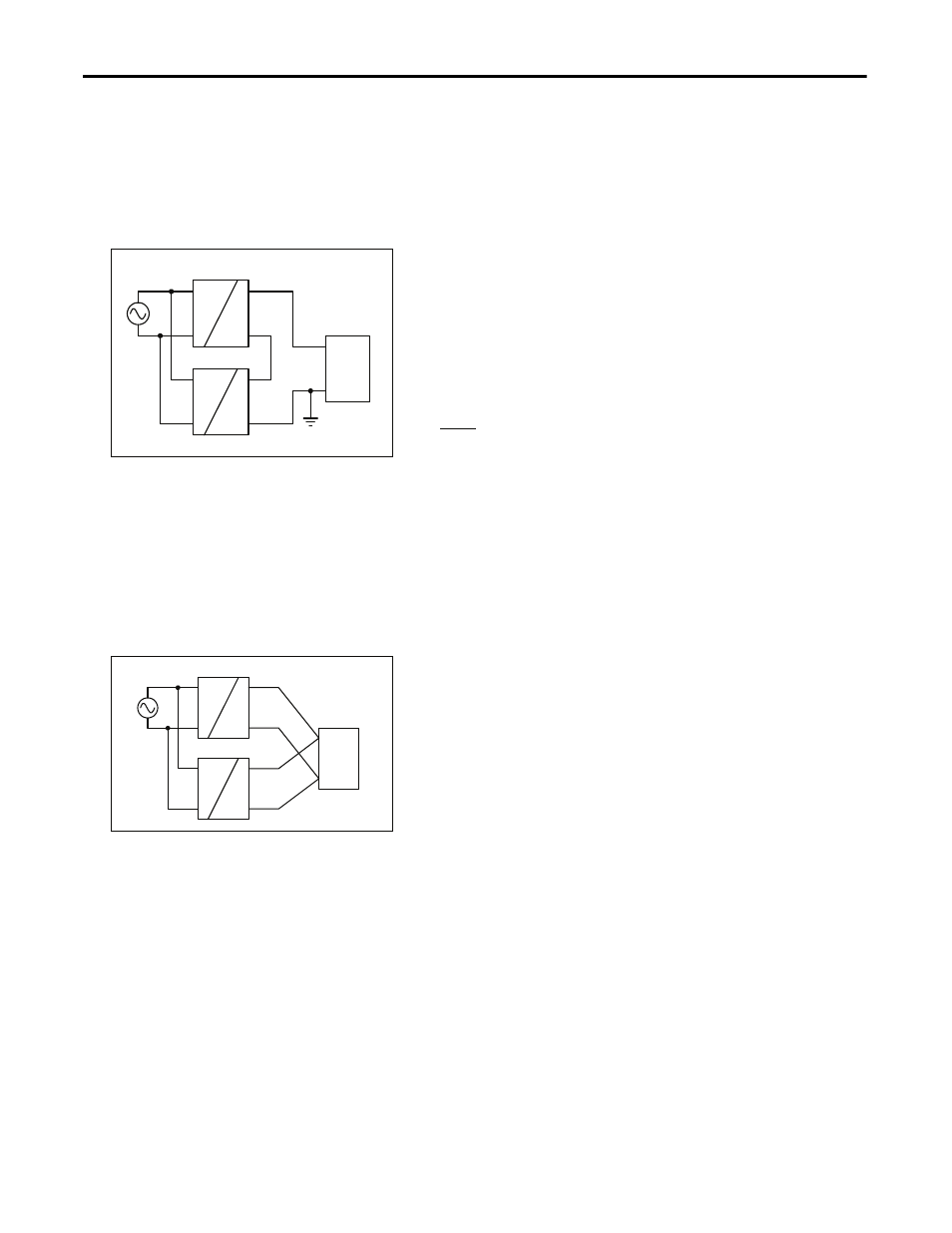
26.3. Series Operation
The power supply can be put in series to increase the output voltage.
Fig. 26-3 Schematic for series operation
Instructions for use in series:
Earth
Unit A
AC
DC
Unit B
AC
DC
-
+
-
+
Load
+
-
a)
It is possible to connect as many units in series as needed,
providing the sum of the output voltage does not exceed
150Vdc.
b)
Voltages with a potential above 60Vdc are no longer SELV
and can be dangerous. Such voltages must be installed
with a protection against touching.
c)
For serial operation use power supplies of the same type.
d)
Earthing of the output is required when the sum of the
output voltage is above 60Vdc.
Note: Avoid return voltage (e.g. from a decelerating motor or
battery) which is applied to the output terminals.
26.4. Parallel Use to Increase Output Power
Several power supplies can be paralleled to increase the output power. The 1606-XLP50E does not include a feature
to balance the load current between the power supplies. Usually the power supply with the higher adjusted output
voltage draws current until it goes into current limitation. This causes no harm to the power supply as long as the
ambient temperature stays below 50°C.
Fig. 26-4 Schematic for parallel operation
Instructions for parallel use:
Unit A
AC
DC
Unit B
AC
DC
-
+
-
+
Load
+
-
a)
Use only power supplies from the same series.
b)
Adjust the output voltages of all power supplies to
approximately the same value (±200mV).
c)
A fuse (or diode) on the output is only required if more than
three units are connected in parallel.
d)
Do not load terminals with more than 13A. Follow wiring
instructions according to section 27.6.
e)
Ensure that the ambient temperature of the power supply
does not exceed 50°C.
26.5. Parallel Use for Redundancy
Power supplies can be paralleled for redundancy to gain a higher system reliability. Redundant systems require a
certain amount of extra power to support the load in case one power unit fails. The simplest way is to put to
power supplies in parallel. This is called a 1+1 redundancy. Should one power supply fail, the second
is automatically able to support the load current without any interruption. Redundant systems for a higher power
demand are usually built in a N+1 method. E.g. Five power supplies, each rated for 2.1A are paralleled to build a 8A
redundant system. If one unit fails, the 8A can still be drawn.
