Aerovent IM-745 User Manual
Page 8
8
Aerovent IM-745
Bearing Problems
Generally speaking, Aerovent uses three types of bearings:
1. Ball bearings with setscrew lock;
2. Spherical roller bearing with setscrew lock;
3. Spherical roller bearing with adapter sleeve/taper lock
feature to attach them to the shaft.
Ball Bearings with setscrew lock - These are self-aligning
bearings and should present no alignment problems with
one exception: i.e., on Sealmaster bearings, there is a pin
beneath the grease fitting which prevents the bearing outer
race from rotating. Should this pin jam, the bearing loses
its alignment feature.
Common failure causes are (a) setscrews loosening and
shaft turning within the bearing inner race, and (b) crowned
bearing supports. Loosen one bolt and measure the clear-
ance between the bearing foot and the support. Add shims
to compensate.
Spherical Roller Bearings with setscrew lock - The self-
aligning characteristic of these bearings are inherent in the
spherical roller design. The closer that these bearings are
to perfect alignment, the cooler they will operate.
Common failure causes are the same as with the ball
bearings, mainly setscrews loosening and crowned bearing
supports.
Spherical Roller Bearings with adapter lock - Again, the self-
aligning feature is inherent in the spherical design. Good
alignment results in a cooler operating bearing. The faster
the bearing operates the more critical this becomes.
A common cause of failure is improper installation
practice. Removing too much radial internal clearance from
the bearing can cause preloading of the bearing with the
result of premature failure; and removing not enough inter-
nal clearance can allow the shaft to rotate within the
adapter sleeve with the result of noise, heat, and failure.
Properly tightened, this method of attaching a bearing to
a shaft is second only to an interference fit. Crowned
bearing supports can also preload these bearings and
should be checked by loosening one bolt and checking
the clearance between the bearing foot and the support.
Add shims to compensate.
Lubrication - The major cause of bearing failure is con-
tamination of grease, insufficient grease, or incompatibility
of grease. If a fan is to be stored for any length of time
at the job site, the bearings immediately should be filled
with grease while rotating the shaft and then the bearings
should be regreased and shaft rotated monthly. This will
prevent moisture, which condenses within the bearing, from
corroding the raceways. Most of the grease used on fan
pillow block bearings are lithium base. Use the greases
shown on the bearing decal. Do not mix greases with dif-
ferent type of bases, but always purge out the initial grease
having one base with the new grease having a different
base.
Initially, follow the lubrication instruction on the side of
the fan. The frequency of lubrication should be adjusted
depending on the condition of the old grease being
purged. This is the responsibility of the user. If the grease
is dirty, the lubrication frequency should be more often.
Bearing Noise – If a bearing is increasing in noise inten-
sity and/or vibration, it will probably result in failure.
Bearing Temperature – If a bearing temperature begins to
gradually rise, it will generally result in failure. A bearing
can operate up to 200°F and perform satisfactorily as long
as the temperature remains constant and the bearing
receives adequate lubrication. Remember that a roller bear-
ing under the same load and speed will be somewhat
noisier and run warmer than a ball bearing. This is normal.
Rough handling and /or dropping a fan can result in
brinelling the bearing. This appears as a clicking noise at
first, and then gradually worsens until failure occurs.
When replacing a bearing, always align the bearings first,
then bolt the pillow blocks to their support, rotate the
shaft, fasten the bearing to it. If the bearing is fastened to
the shaft first, tightening the pillow block blocks may bind
the shaft and preload the bearings.
Drive Problems
1. Belts improperly tensioned.
2. Drive alignment is poor. Check belts or coupling.
3. Coupling lubrication.
Motor Problems
1. Incorrect wiring.
2. Speed of fan is too high.
3. Parts improperly installed or binding.
4. Bearings improperly lubricated.
5. WR2 capability of motor is too low for application.
6. VFD compatible.
7. Cable and grounding correct.
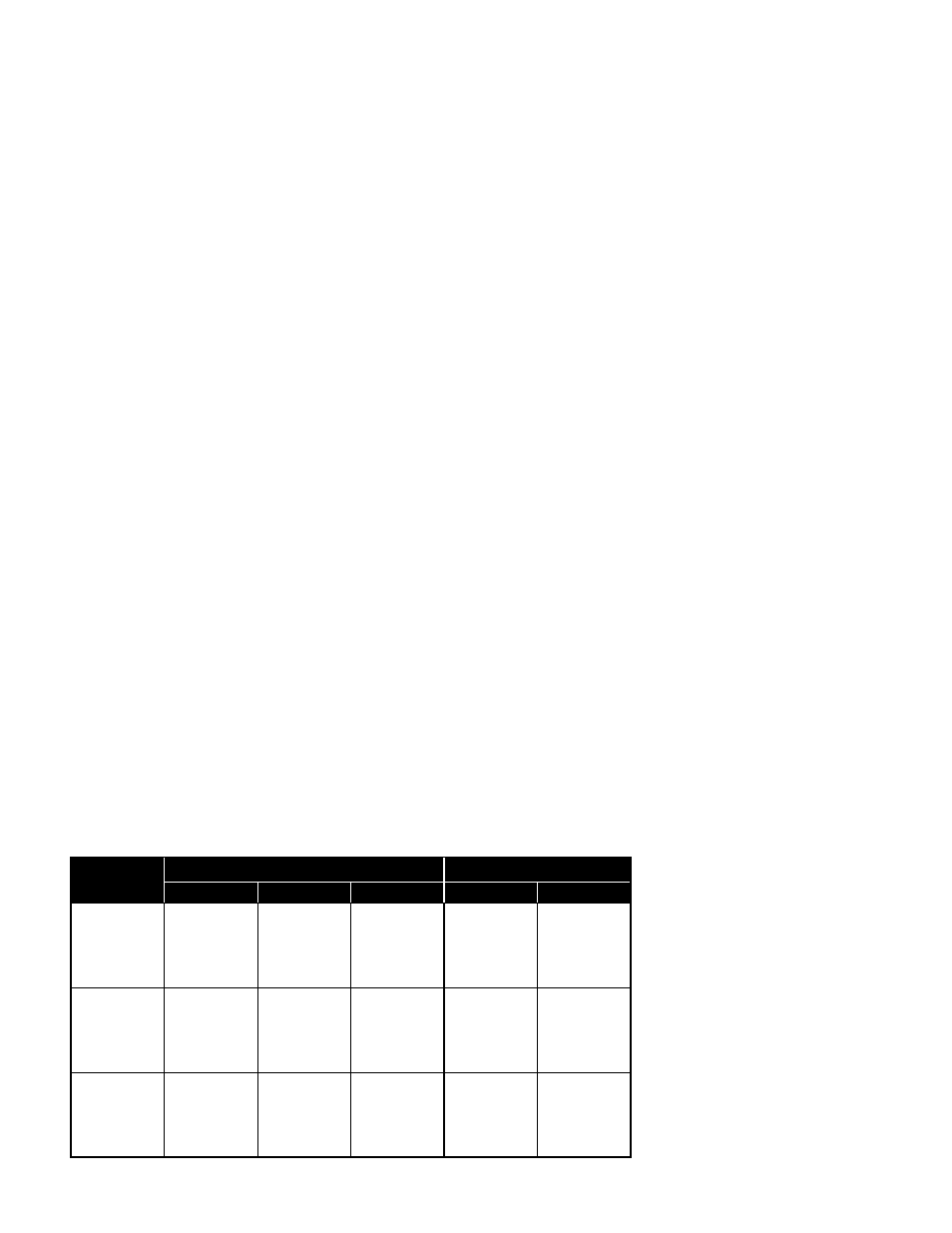
The torque values are for nonlubricated
fasteners and Browning Bushings.
For bearing setscrews, use manufacturer’s
recommendations.
If other bushings are used, utilize bushing
manufacturer's specifications.
Tolerance: /-
5%
For wheel setscrews use Grade 2 values.
+
Table 1. Tightening Torques (in lb-ft)
SIZE
FASTENER
TAPER BUSHINGS (DRIVE)
GRADE 2
GRADE 5
GRADE 8
SPLIT
QD
#10
—
—
—
—
6
1
⁄
4
-20
5.5
8
12
7.9
9
5
⁄
16
-18
11
17
25
16
15
3
⁄
8
-16
22
30
45
29
30
7
⁄
16
-14
30
50
70
—
—
1
⁄
2
-13
55
75
110
70
60
9
⁄
16
-12
—
—
—
—
75
5
⁄
8
-11
100
150
200
140
135
3
⁄
4
-10
170
270
380
250
225
7
⁄
8
-9
165
430
600
—
300
1-8
250
645
900
600
450
1
1
⁄
4
-7
500
1120
1500
—
—
