Chapter 3 – safety, Danger – Snorkel AB46JE User Manual
Page 11
AB46JE – 0260072
7
Chapter 3 – Safety
Knowledge of the information in this manual, and proper
training, provide a basis for safely operating the aerial plat-
form. Know the location of all controls and how they oper-
ate to act quickly and responsibly in an emergency.
Safety devices reduce the likelihood of an accident.
Never disable, modify, or ignore any safety device.
Safety alerts in this manual indicate situations where
accidents may occur.
If any malfunction, hazard or potentially unsafe condi-
tion relating to capacity, intended use, or safe operation
is suspected, stop aerial platform operation and seek
assistance.
The operator bears ultimate responsibility for following
all manufacturer’s instructions and warnings, regulations
and safety rules of their employer and/or any state or
federal law.
Electrocution Hazards
The aerial platform is made of metal components and is
not insulated. Regard all conductors as energized. Do
not operate outside during a thunderstorm.
•
•
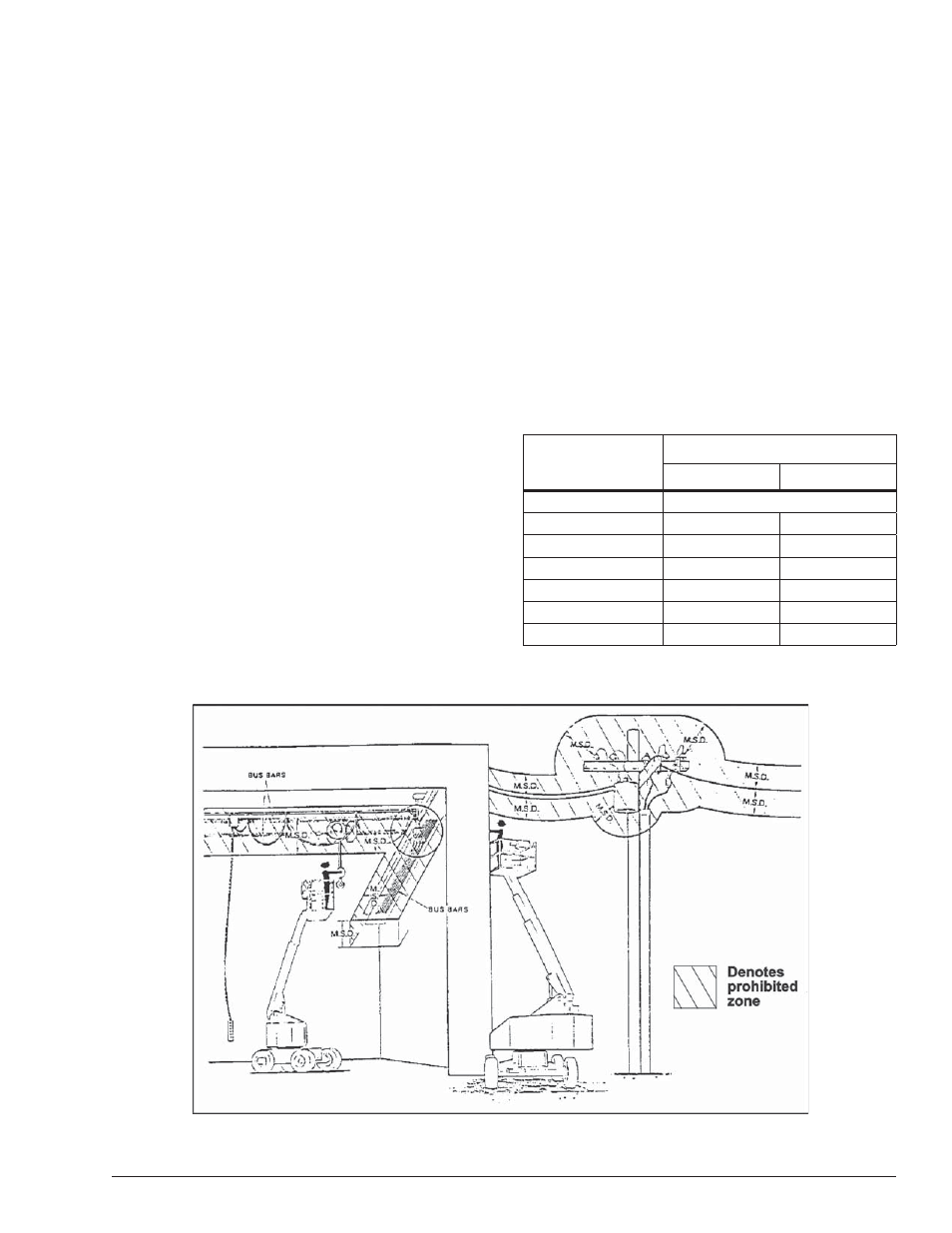
Minimum Safe Approach Distance
Minimum safe approach distances to energized power
lines and their associated parts must be observed while
operating the aerial platform.
A
Danger
The aerial platform is not electrically insulated. Death
or serious injury will result from contact with, or in-
adequate clearance from, an energized conductor.
Do not go closer than the minimum safe approach
distance as defined by ANSI.
ANSI publications define minimum distances that must
be observed when working near bus bars and energized
power lines. Table 1 and Figure 3 are reprinted courtesy
of Scaffold Industry Association, ANSI/SIA A92.5.
Table 1 – Minimum Safe Approach Distance
Figure 3 – Minimum Safe Approach Distance
Voltage Range
(Phase to Phase)
Minimum Safe Approach Distance
Feet
Meters
0 to 300V
Avoid Contact
Over 300V to 50kV
10
3.05
Over 50kV to 200kV
15
4.60
Over 200kV to 350kV
20
6.10
Over 350kV to 500kV
25
7.62
Over 500kV to 750kV
35
10.67
Over 750kV to 1000kV
45
13.72
