Modbus rtu communications, Introduction, Modbus rtu specification – Beijer Electronics Industrial Inverter E2 User Manual
Page 27: Rj45 connector configuration, Modbus telegram structure, Modbus register map
27
8. Modbus RTU Communications
8.1. Introduction
The drive can be connected to a Modbus RTU network via the RJ45 connector on the front of the drive.
8.2. Modbus RTU Specification
Protocol
Modbus RTU
Error check
CRC
Baud rate
9600bps, 19200bps, 38400bps, 57600bps, 115200bps (default)
Data format
1 start bit, 8 data bits, 1 stop bits, no parity.
Physical signal
RS 485 (2-wire)
User interface
RJ45 (see section 5.2 for more information)
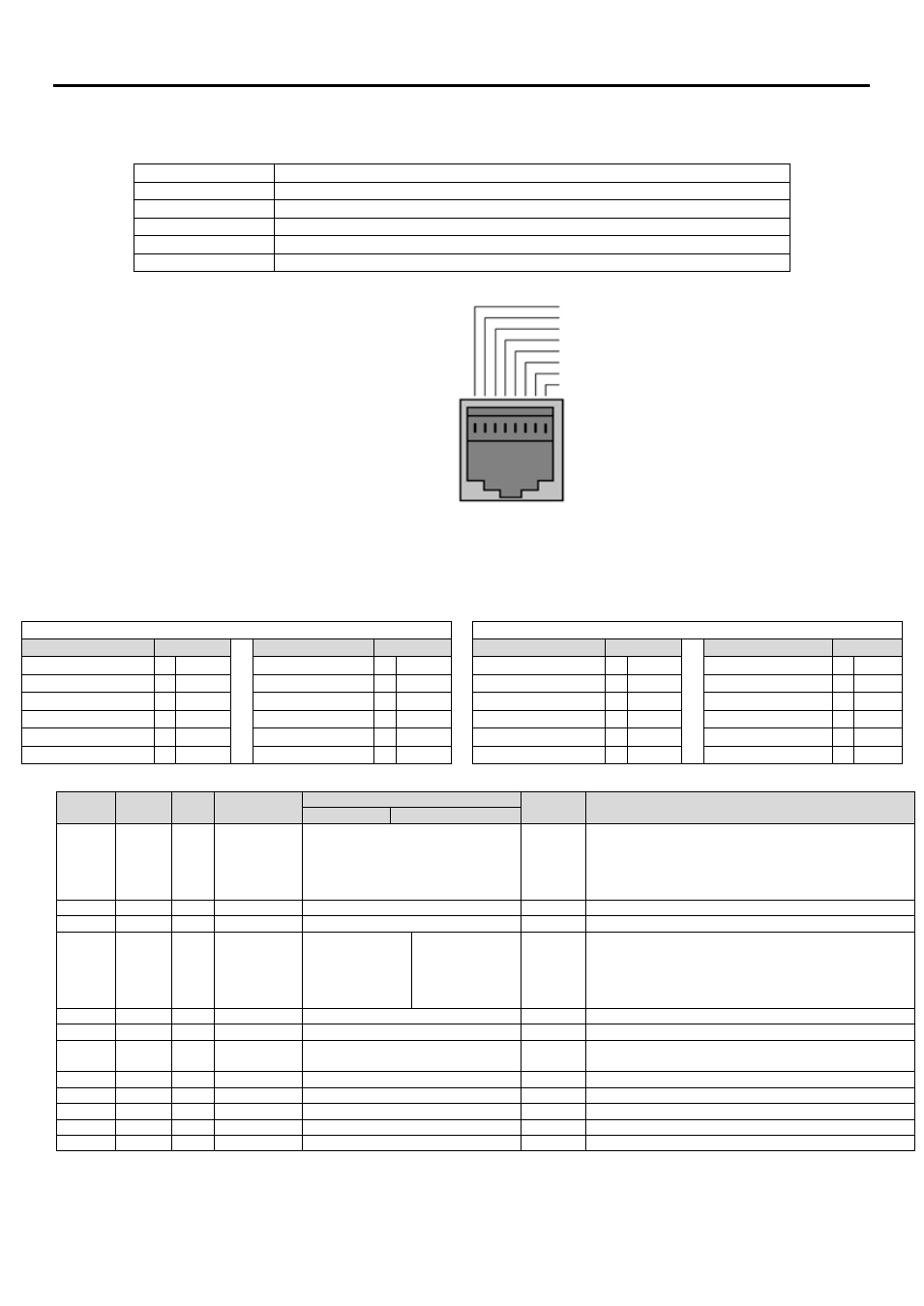
8.3.
RJ45 Connector Configuration
For full MODBUS RTU register map
information please refer to Beijer Electronics.
When using MODBUS control the Analog and
Digital Inputs
can be configured as shown in section 7.3
1
No Connection
2
No Connection
3
0 Volts
4
-RS485 (PC)
5
+RS485 (PC)
6
+24 Volt
7
-RS485 (Modbus RTU)
8
+RS485 (Modbus RTU)
Warning:
This is not an Ethernet
connection. Do not connect
directly to an Ethernet port.
8.4. Modbus Telegram Structure
The drive supports Master / Slave Modbus RTU communications, using the 03 Read Holding Registers and 06 Write Single Holding Register
commands. Many Master devices treat the first Register address as Register 0, therefore it may be necessary to convert the Register Numbers
detail in section 8.5 by subtracting 1 to obtain the correct Register address. The telegram structure is as follows:-
Command 03 – Read Holding Registers
Command 06 – Write Single Holding Register
Master Telegram
Length
Slave Response
Length
Master Telegram
Length
Slave Response
Length
Slave Address
1 Byte
Slave Address
1 Byte
Slave Address
1 Byte
Slave Address
1 Byte
Function Code (03)
1 Byte
Starting Address
1 Byte
Function Code (06)
1 Byte
Function Code (06)
1 Byte
1
st
Register Address
2 Bytes
1
st
Register Value
2 Bytes
Register Address
2 Bytes
Register Address
2 Bytes
No. Of Registers
2 Bytes
2
nd
Register Value
2 Bytes
Value
2 Bytes
Register Value
2 Bytes
CRC Checksum
2 Bytes
Etc...
CRC Checksum
2 Bytes
CRC Checksum
2 Bytes
CRC Checksum
2 Bytes
8.5.
Modbus Register Map
Register
Number
Par.
Type
Supported
Commands
Function
Range
Explanation
Low Byte
High Byte
1
-
R/W
03,06
Drive Control Command
0..3
16 Bit Word.
Bit 0 : Low = Stop, High = Run Enable
Bit 1 : Low = Decel Ramp 1 (P-04), High = Decel Ramp 2 (P-24)
Bit 2 : Low = No Function, High = Fault Reset
Bit 3 : Low – No Function, High = Coast Stop Request
2
-
R/W
03,06
Modbus Speed reference setpoint
0..5000
Setpoint frequency x10, e.g. 100 = 10.0Hz
4
-
R/W
03,06
Acceleration and Deceleration Time
0..60000
Ramp time in seconds x 100, e.g. 250 = 2.5 seconds
6
-
R
03
Error code
Drive status
Low Byte = Drive Error Code, see section 10.1
High Byte = Drive Status as follows :-
0 : Drive Stopped
1: Drive Running
2: Drive Tripped
7
R
03
Output Motor Frequency
0..20000
Output frequency in Hz x10, e.g. 100 = 10.0Hz
8
R
03
Output Motor Current
0..480
Output Motor Current in Amps x10, e.g. 10 = 1.0 Amps
11
-
R
03
Digital input status
0..15
Indicates the status of the 4 digital inputs
Lowest Bit = 1 Input 1
20
P00-01
R
03
Analog Input 1 value
0..1000
Analog input % of full scale x10, e.g. 1000 = 100%
21
P00-02
R
03
Analog Input 2 value
0..1000
Analog input % of full scale x10, e.g. 1000 = 100%
22
P00-03
R
03
Speed Reference Value
0..1000
Displays the setpoint frequency x10, e.g. 100 = 10.0Hz
23
P00-08
R
03
DC bus voltage
0..1000
DC Bus Voltage in Volts
24
P00-09
R
03
Drive temperature
0..100
Drive heatsink temperature in ºC
All user configurable parameters are accessible as Holding Registers, and can be Read from or Written to using the appropriate Modbus
command. The Register number for each parameter P-04 to P-047 is defined as 128 + Parameter number, e.g. for parameter P-15, the register
number is 128 + 15 = 143. Internal scaling is used on some parameters, for further details, please contact Beijer Electronics.
