Rotation, Final steps, Operation – COOK TCN User Manual
Page 5: Inspection, Maintenance, Wheel rotation, Final installation steps, Start up
5
• Improper motor amperage or voltage.
If a problem is discovered, immediately shut the fan
off. Lock out all electrical power and check for the
cause of the trouble. See Troubleshooting.
Inspection
Inspection of the fan should be conducted at the first 30
minute, 8 hour and 24 hour intervals of satisfactory opera-
tion. During the inspections, stop the fan and inspect as per
the Conditions Chart.
30 Minute Interval
Inspect bolts, setscrews, and motor mounting bolts.
Adjust and tighten as necessary.
8 Hour Interval
Inspect belt alignment and tension. Adjust and tighten as
necessary.
24 Hour Interval
Inspect belt tension. Adjust and tighten as necessary.
Maintenance
Establish a schedule for inspecting all parts of the fan.
The frequency of inspection depends on the operating con-
ditions and location of the fan.
Inspect fans exhausting corrosive or contaminated air
within the first month of operation. Fans exhausting con-
taminated air (airborne abrasives) should be inspected
every three months.
Regular inspections are recommended for fans exhaust-
ing non-contaminated air.
It is recommended the following inspection be conducted
twice per year.
• Inspect bolts and setscrews for tightness. Tighten as
necessary.
• Inspect belt wear and alignment. Replace worn belts
with new belts and adjust alignment as needed. Refer
to Belt and Pulley Installation, page 3.
Recommended Torque for Setscrews/Bolts
Setscrews
Hold Down Bolts
Size
Key Hex
Across
Flats
Recommended
Torque
Min.
Max.
Size
Wrench
Torque
No.10
3/32”
28
33
3/8”-16
240
1/4”
1/8”
66
80
1/2”-13
600
5/16”
5/32”
126
156
5/8”-11
1200
3/8”
3/16”
228
275
3/4”-10
2100
7/16”
7/32”
348
384
7/8”-9
2040
1/2”
1/4”
504
600
1”-8
3000
5/8”
5/16”
1104
1200
1-1/8”-7
4200
3/4”
3/8”
1440
1800
1-1/4”-7
6000
(IN/LB)
Wiring Installation continued
NOTICE! Follow the wiring diagram in the dis-
connect switch and the wiring diagram provided
with the motor. Correctly label the circuit on the
main power box and always identify a closed
switch to promote safety
(i.e., red tape over a
closed switch).
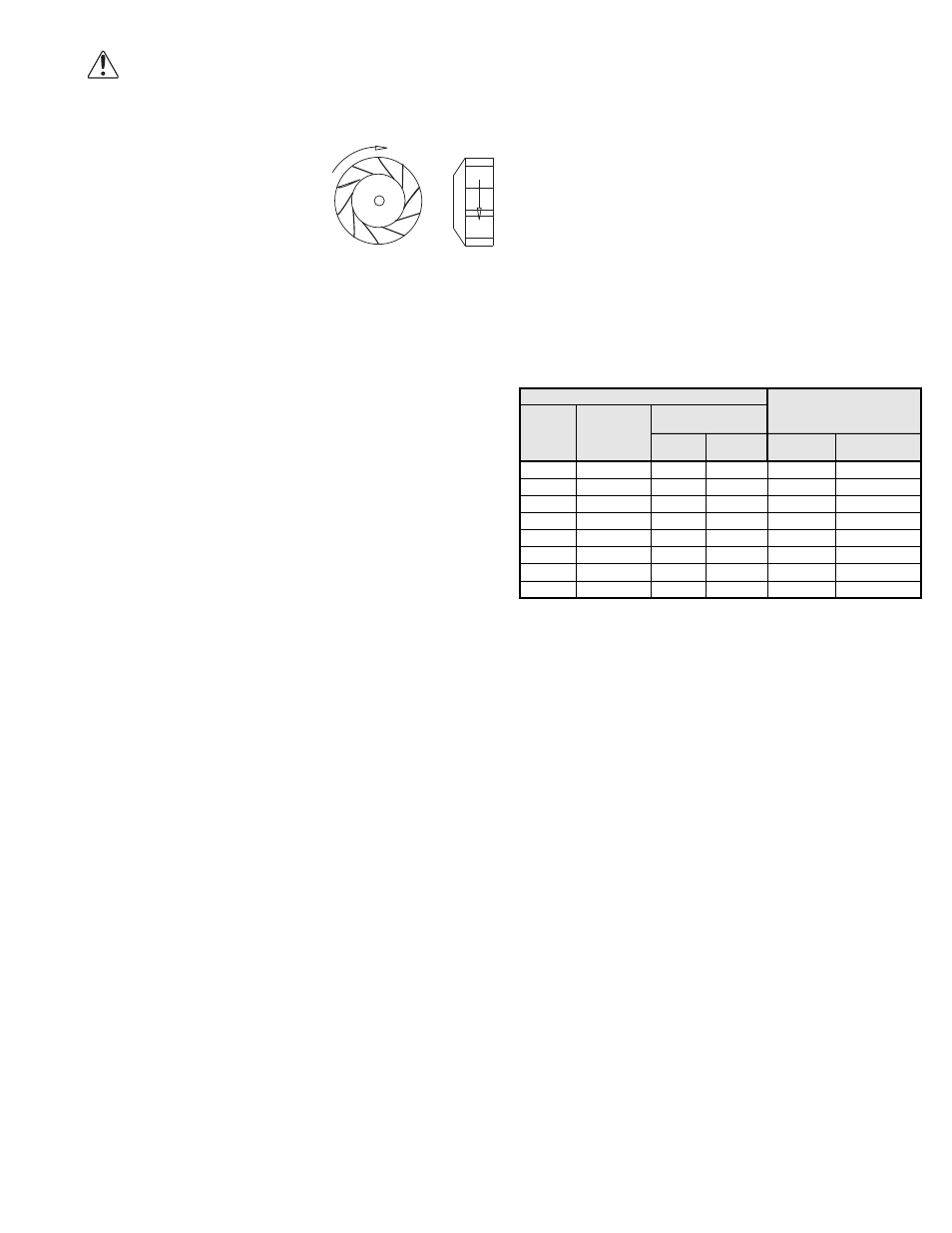
Wheel Rotation
Test the fan to ensure the rota-
tion of the wheel is the same as
indicated by the arrow marked
Rotation.
115 and 230 Single Phase Motors
Fan wheel rotation is set correctly at the factory. Chang-
ing the rotation of this type of motor should only be
attempted by a qualified electrician.
208, 230, and 460, 3 Phase Motors
These motors are electrically reversible by switching two
of the supply leads. For this reason, the rotation of the fan
cannot be restricted to one direction at the factory. See
Wiring Diagrams for specific information on reversing
wheel direction.
NOTICE! Do not allow the fan to run in the wrong
direction. This will overheat the motor and cause seri-
ous damage. For 3-phase motors, if the fan is running
in the wrong direction, check the control switch. It is
possible to interchange two leads at this location so
that the fan is operating in the correct direction.
Final Installation Steps
a. Inspect fasteners and setscrews, particularly fan
mounting and bearing fasteners, and tighten according
to the recommended torque shown in the table Rec-
ommended Torque for Setscrews/Bolts.
b. Inspect for correct voltage with voltmeter.
c. Ensure all accessories are installed.
Operation
Pre-Start Checks
a. Lock out all the primary and secondary power
sources.
b. Ensure fasteners and setscrews, particularly those
used for mounting the fan, are tightened.
c. Inspect belt tension and pulley alignment.
d. Inspect motor wiring.
e. Ensure belt touches only the pulley.
f. Ensure fan and ductwork are clean and free of debris.
g. Inspect wheel-to-inlet clearance. The correct wheel-to-
inlet clearance is critical to proper fan performance.
h. Close and secure all access doors.
g. Restore power to the fan.
Start Up
Turn the fan on. In variable speed units, set the fan to its
lowest speed and inspect for the following:
• Direction of rotation.
• Excessive vibration.
• Unusual noise.
• Bearing noise.
• Improper belt alignment or tension (listen for squeal-
ing).
Tubular Centrifugal Inline
