Salinity – the problem – Campbell Scientific Sentek TriSCAN® Manual v 1.2a User Manual
Page 9
TriSCAN Manual Version 1.2a
Copyright © 1991 – 2004 Sentek Pty Ltd All rights reserved
Page 2
When ionically bonded compounds like NaCl are added to water, they dissociate (break up) into their
constituent positively and negatively charged ions (Na
+
and Cl
-
). This phenomenon causes water, which in
its pure state is a poor conductor of electricity, to become a good electrical conductor. The EC of a solution
is dependent on the type of ions present, their concentration and the temperature of the solution. Therefore,
if the EC of the solution is measured, and if the temperature is known, then the EC can be used to determine
the concentration of ions in the solution.
Salinity is quantified in terms of the total concentration of such soluble salts, or more practically, in terms of
the EC of the solution.
It is not a simple process to measure the concentration of ions in an aqueous soil solution. Soil consists of
an intricate combination of organic and inorganic compounds, each with their own ionic properties. In an
attempt to standardize measurements and to establish a reasonable reference for comparison purposes, soil
salinity is commonly expressed in terms of the EC of an extract of a saturated paste (EC
e
) from a sample of
the soil.
The value of EC for a particular soil sample will vary according to the preparation of the sample. Due to
these differences, it is important to state the technique for sample preparation when defining soil salinity.
The following terms are used is this manual to describe various preparation techniques:
EC
1:5
Electrical conductivity of an extract of a 1:5 mixture of soil:water
EC
e
Electrical conductivity of a saturation paste extract
EC
p
Electrical conductivity of an aqueous extract of a soil sample, or pore water salinity
The effect of dissolved or ionized salts on plant growth depends on their concentration in the soil solution at
any particular time. Therefore there is a strong need to be able to measure the concentration of salts
through the soil profile on a continuous basis. Current methods of measuring soil salinity based on
destructive sampling make this extremely difficult. The TriSCAN technology overcomes this problem.
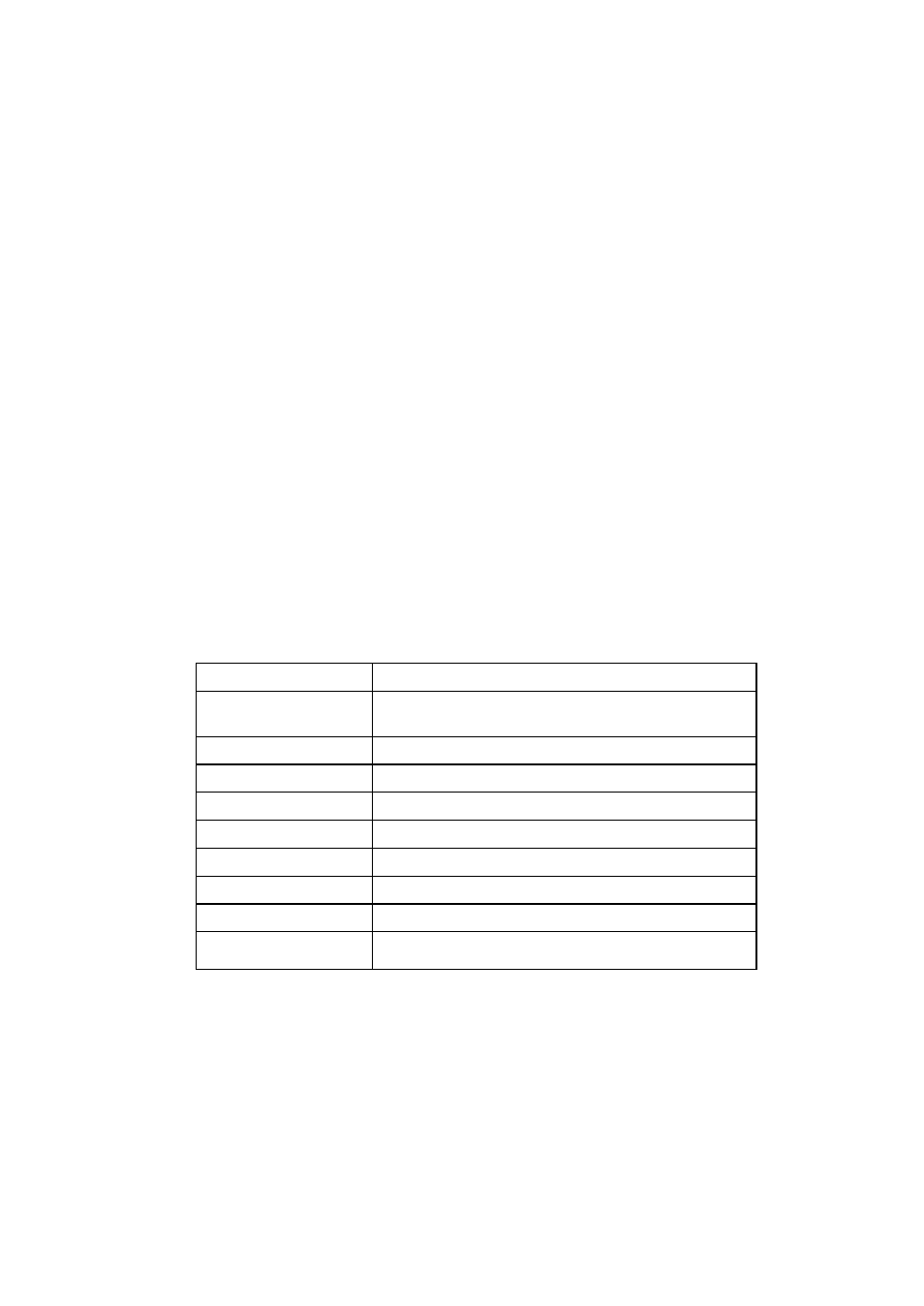
Table 1. Salinity Measurement Units and their Abbreviations
EC
Electrical conductivity
EC
1:5
Electrical conductivity of an extract of a 1:5 mixture of
soil:water
EC
w
Electrical conductivity of water
EC
e
Electrical conductivity of the saturated soil extract
dSm
-1
deciSiemens per meter (dS/m)
mmolL
-1
Millimoles per litre (mmol/L or mM)
TDS
Total dissolved solids
ppm
Parts per million
mgL
-1
Milligrams per litre (mg/L)
gm
-3
Grams per cubic meter (g/m
3
)
Salinity – the problem
Saline soils can be defined as soils containing sufficient soluble salts to adversely affect the growth of
plants. The soluble salts are chiefly sodium chloride and sodium sulfate, but saline soils also contain
appreciable quantities of chlorides and sulfates of calcium and magnesium. For purposes of definition, saline
soils are those which have an electrical conductivity of the saturation soil extract of more than 4 dSm
-1
at
25°C.
In field conditions, saline soils can be recognized by the poor growth of crops and often by the presence of
white salt crusts on the surface. When the salt problem is only mild, growing plants often have a blue-green
tinge. Barren areas and stunted plants may appear in cereal or forage crops growing on saline soils. The
